


Written by KP, Jehn, CH, Ponyo, TraceØ, Crypto_Gang, JiSung Jung, Hyewon Jeong, Jinuk Hwang, nerdsuh, YoungWook Cho, Jaewook Lee
Table of Contents
Intro
1. Tightening Continues, Don’t Fight the Fed
1-1. Bitcoin as a Financial Asset
1-2. Institutional Adoption Drives Bitcoin to Become More Mainstream
1-3. Recession Predictions Mount – Here’s How to Prepare
2. In the End, Blockchain Will Become Faster and Cheaper
2-1. 2022 L1 War Claims the Battlefield Full of Scars with Ethereum as the Sole Survivors
2-2. A Full-Blown L2 War to Scale Up Ethereum
2-3. Modular Is the Mainstream! Projects Take After Ethereum
2-4. Monolithic Blockchains Gearing Up for Counterattacks
2-5. In the End, Resolving the “Blockchain Trilemma” Is the Key
3. The Evolving Blockchain Ecosystem Infrastructure
3-1. Native Verification: Solution to Lock-and-Mint Bridge Exploits
3-2. Chainlink Maintains the Largest Blockchain Oracle
3-3. Chainlink to Serve as Secure Blockchain Middleware Beyond Oracle
3-4. Decentralized Data Storage: Challenges and Prospects
3-5. Crypto Custody Wallet: Improving the Drawbacks for Mass Crypto Adoption
3-6. MEV: Network Activity is Key to Boost Validator Rewards
3-7. DAO, A New Structure to Keep Governance Decentralized
4. Blockchain Content Never Ceases to Evolve
4-1. Despite the Brimming Potential, Anticipation Should Be Kept Low Key at Least Until the End of Next Year
4-2. DeFi: Locking the Barn and Finding the Next Meta
4-3. Web 2.0 Companies Spearheading NFT Adoption
5. Inevitably Introduced, Regulations Will Support Mass Adoption in Long-Term
5-1. Introduction of Crypto Regulations Can No Longer Be Opposed
5-2. Difficult Time for Exchanges as Well: Every Exchange for Itself
Closing Thoughts
Intro
The year 2022 will be marked as one of the most turbulent in the history of the crypto industry. The global macroeconomic conditions worsened when the U.S. Federal Reserve began shrinking its balance sheet starting in Mar 2022, and the Luna-Terra crisis is believed to have fueled the start of a long crypto winter. Then a string of failures followed as Celsius, Three Arrows Capital (3AC), and BlockFi went bankrupt, and FTX joined the list as another crypto giant going under after devising a scheme to defraud investors, completely shattering investor confidence. After the FTX collapse, fears have centered around the Digital Currency Group (DCG) and its subsidiaries, Genesis and Grayscale. The downfall of many top crypto companies heralded a mass exodus from crypto, and as a result, the total market cap of crypto assets has fallen to one-third compared to the beginning of 2022. While it is unclear what the Luna-Terra collapse and FTX fallout would mean for the wider market, a new year is upon us.
Looking ahead to 2023, the Xangle research team expects the crypto market to bottom out, while it remains uncertain when we might see a “dovish pivot.” The Fed is still on a hawkish path to maintain a restrictive policy stance, and the adverse macroeconomic conditions are likely to continue, but we believe the following trends are heading into 2023: i) The impact of tightening on the real economy is likely to be relatively modest as the unemployment rate is expected to remain low, ii) the blockchain ecosystem infrastructure continues to steadily develop regardless of market conditions, and iii) Web2 companies like Meta, Nike, and Reddit are lining up for the Metaverse race, which, in turn, would accelerate the mass adoption of the blockchain technology. In this 2023 outlook, the Xangle research team shares diverse views on where the crypto market is headed. We hope you find this outlook informative in understanding the latest crypto market movements.
1. Tightening Continues, Don’t Fight the Fed
1-1. Bitcoin as a Financial Asset
Despite a crash in the value of cryptocurrencies in 2022, Bitcoin has been noticeably linked to risk assets such as real estate, high-yield bonds, and stock price index, indicating that Bitcoin has begun to establish itself as a "financial asset class."

For the past year, crypto and equity markets have traded tightly together, experiencing record-high correlations with benchmark stock indices for the U.S., S&P 500, and Nasdaq. Correlation between crypto and equity markets increased notably as central banks around the world lowered interest rates, expanding liquidity and driving demand for high-risk assets. Compared to pre-pandemic years, Bitcoin prices have become increasingly linked with equities as retail and institutional investors holding both traditional assets and Bitcoin piled into the crypto space.

However, high liquidity alone cannot explain the tight correlation between Bitcoin and other risk assets for the following reasons: i) Decoupling periods were observed in 2021 when both assets encountered strong rallies, and ii) correlations strengthened even after the Federal Reserve raised rates in 2022. With retail investors anchoring to the sidelines and institutional investors sinking money into the crypto space, Bitcoin has become increasingly correlated with the stock market. We believe this is largely due to institutional investors who often execute funds simultaneously across all asset classes according to macroeconomic variables, resulting in a greater correlation between Bitcoin and risky assets.

We notice that Coinbase deposits by retail and institutional investors plunged by more than 50% in 2Q 2022 as Terra Luna crashed and the Federal Reserve began tapering. On the other hand, the trading volume of institutional investors increased steadily, reaching 85% in 3Q 2022. Although the steady increase in the number of institutional investors is because a large number of retail investors moved to Binance and FTX, it is undeniable that more and more institutions are ramping up their exposure to the cryptocurrency sector.

According to the Institutional Demand for Cryptocurrencies Global Survey 2022 by Cointelegraph Research, which had 84 responses from institutional investors across the world, 45% of the professional investors have exposure to cryptocurrencies and are primarily holding Bitcoin (94%). Interestingly, 44% of respondents said that the most important consideration for investing in digital assets is their risk-return ratio, while responses to “diversification” and “my company is convinced that the technology will be important in the future” are clustered in the middle, meaning that these factors are moderately important. The responses indicate that many institutional investors are leveraging Bitcoin as a risk asset and a portfolio booster, not as an independent asset without any links to traditional finance. There are three main reasons why Bitcoin is being recognized as a risk asset by institutional investors and driving institutional demand.
1-2. Institutional Adoption Drives Bitcoin to Become More Mainstream
A. Infrastructure Improvements Lead to Greater Accessibility of Bitcoin

Bitcoin became more accessible as large traditional financial institutions began actively engaging in financial infrastructure projects to support crypto assets starting in 2H 2021. In Aug 2022, BlackRock partnered with Coinbase Prime to allow its clients to access Bitcoin via its Aladdin platform, and in Oct 2022, BNY Mellon launched a new digital asset custody platform to support Bitcoin and Ethereum. As such, the world’s largest asset managers and banks are offering solutions for digital asset technology by tapping TradFi infrastructure that includes risk management, accounting, and research (Table 2). The launch of these “all-in-one solutions” could perhaps attract more institutional investors who are not familiar with digital assets to trade.
B. Emergence of Use Cases
The crypto bull market in 2017 was highly speculative. Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) took 2017’s crypto market by surprise, and countless crypto projects jumped on the bandwagon of this new form of crowdfunding to list tokens. According to ICO Rating, an ICO research and rating provider, 314 projects raised $5.9712B through ICOs in 2017, but about 30% of the tokens were delisted within a year. To institutional investors, the 2017 crypto market was a retail-driven speculative frenzy, and they would have thought themselves fortunate for not having been lured by market momentums in 2017.

However, the crypto bull market from 2020 to 2021 was different. As the previous crypto winter eliminated scam coins and weaker players, Bitcoin stood strong as the largest cryptocurrency by market cap. Ethereum's fee steadily increased as numerous smart contracts were onboarded on its network, and with its transition into a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) network following the Merge upgrade, it succeeded in generating organic revenue. Following the "DeFi Summer" in 2020 and the "NFT Boom" in 2021, numerous projects with actual use cases have emerged, achieving exponential growth. The increasing use cases and public interest naturally attracted institutional investors to invest in Bitcoin, the undisputed leader of cryptocurrencies. Digital assets and blockchain are gradually becoming mainstream technologies – DeFi market's TVL has grown to $291B at the end of 2021, comparable to the market cap of the top 30 U.S. companies, and large Web 2 companies like Starbucks and Disney have begun entering the NFT space. The increasing number of use cases and public interest naturally attracted institutional investors and, in turn, led to Bitcoin investment.
Consensus 2022, the world's largest blockchain gathering, was held in Jun 2022, bringing together many institutional investors in the traditional financial sector from Wall Street. Even after the Luna-Terra crash, many predicted the continued growth of the blockchain industry. As if to represent this, Fidelity's CEO Abigail Johnson said, "There were voices of concern that the crypto industry might disappear during the 2018 bear market. But the situation is different this time in 2022, as investors are asking when and how much to invest." It means that many institutional investors want to continue investing in the market despite entering the bear market.
C. Navigating Market Volatility
Institutional investors are sensitive to volatility. Assets with high volatility hinder the predictability of future profits and losses, making it difficult for investors to invest a large percentage of their portfolio in volatile assets. The S&P 500’s annual realized volatility from 2014 to 2019 is 12.7%, which means that the actual return for a year deviates ±6.4% from the expected return. On the other hand, Bitcoin’s volatility over the same period is 77.1%, roughly six times that of the S&P 500; from the institutional investor’s point of view, Bitcoin’s high volatility is a huge obstacle to investing, even considering its high risk-return rate.

However, a lot has changed over the past 20 years. Since 2020, the S&P’s annual realized volatility has increased significantly to 23.5%, while Bitcoin’s volatility has decreased to 71.6%. As a result, the volatility ratio between the two assets has also been halved. Over the past three years, institutional investors were able to build a tolerance to volatility after witnessing usually stable TradFi assets riding a painful roller-coaster – with the NASDAQ Composite falling more than 12.3% in a day and WTI oil prices going negative. Furthermore, Bitcoin’s high volatility has relatively settled, which could be an incentive for investors to allot percentage of their portfolio to cryptocurrency.

As Bitcoin has begun to establish itself as a financial asset, its price is increasingly affected by macro-financial factors. As Fed’s tightening monetary policy hit risky assets in 2022, Bitcoin was no exception. The US 10-year interest rate and price of Bitcoin, which did not display much correlation until last year, began to move opposite from each other since 2022.
Bitcoin will continue to mature and evolve as a financial asset in 2023. In light of the Terra Luna catastrophe and the collapse of Three Arrows Capital (3AC) and FTX, regulators will likely use these as grounds to push for more stringent rules around cryptocurrency. Regulatory policies that would drive away investors – setting a leveraging limit, requiring crypto businesses to implement KYC procedures, and securitizing digital assets – are highly likely to be introduced to ensure investor protection. However, more regulations could mean more stability in a volatile crypto market, which could draw more investment from TradFi institutions that abide by stringent regulations.

There also appears to be plenty of room for institutional investors to increase their Bitcoin holdings, which account for only 7.8% of the maximum supply; a relatively low percentage compared to common traditional financial assets such as gold and the S&P 500. What is noteworthy is that even though Bitcoin spot-based ETFs are yet to be listed in the U.S., the fund's share is 3.9%. Of the 3.9%, Grayscale Bitcoin Trust accounts for 3%; however, there will be a significant number of institutional investors who are reluctant to invest as Grayscale products are subject to significant limitations on resales and transfers with a statutory holding period of six months, and liquidity in the market is also insufficient. If the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) approves the spot Bitcoin ETF, a major influx of new institutional investments is expected to be injected. Meanwhile, ARK 21Shares submitted an application to the SEC for a spot Bitcoin ETF to be listed on an exchange. The continued attempts to list spot Bitcoin ETFs showcase investment commitments from institutional investors who will continue investing in Bitcoin in 2023.

1-3. Recession Predictions Mount – Here’s How to Prepare
The bottom line is that Bitcoin prices are unlikely to make a dramatic comeback in 2023. As the influx of institutional investors strengthens Bitcoin’s characteristic as a macro-influenced risk asset, the much-foretold recession of 2023 will dent investor confidence while the Fed is likely to continue raising interest rates, draining liquidity from the market.
As U.S. inflation slowed recently, Bitcoin prices rebounded, reflecting the expectations that the Fed will slow down its tightening measures. Bitcoin prices soared even when the Consumer Price Index (CPI) print for October and November came in below expectations and when the Chair of the Federal Reserve Jerome Powell suggested that the Fed may ease off interest rate hikes in a speech at the Brookings Institute. Now all that remains is the Fed’s interest rate hike, as forewarned by many experts. The Fed projected a terminal rate of a 5.0-5.25% range in Q2 2023 and will continue to remove liquidity throughout 1H 2023 to tame inflation. While interest rate rises, Bitcoin prices will remain flat in general as it is unlikely for the prices to fall sharply and cause a surprise rally.
Even after the Fed halts interest rate hikes, a similar trend is expected to continue in the second half. For Bitcoin prices to hike even during an economic recession, investors should hope for a “Dovish Pivot,” in which the Fed lowers the interest rate to stimulate the economy. However, given that the severity of the 2023 recession is expected to be significantly lower than that of the 2008 financial crisis and the 2020 pandemic recession, we deem that it is unlikely that the Fed will cut interest rates prematurely in 2023. Rather, the Fed is expected to maintain interest rates on hold until inflation is fully tamed. As the end of the year approaches, expectations for interest rate cuts in 2024 may rise, and the price of bitcoin may rise again, but considering that the interest rates will be adjusted slowly and cautiously, we will not experience a crypto surge similar to 2020-2021’s bull markets.
A. Battle Against Inflation to Continue in 2023
Inflation is reflected in the prices of goods and services in an economy. Commodity prices are stabilizing – food and energy price shocks from the Ukraine war began to ease. WTI oil prices, which once exceeded $120 per barrel, settled at $80 per barrel, and wheat prices slumped 20% from their peak to pre-Ukraine crisis levels. Global supply chains suffered severe challenges during the pandemic, and we are starting to see easing pressures, especially in shipping and transportation. Shipments from North America to China remained at around $21,000/FEU (forty-foot equivalent unit) in Sep 2022, but as of writing, rates are pushed back to 2,500/FEU with much faster transit time. The Fed’s Global Supply Chain Pressure Index (GSCPI) also indicates that global supply chain pressures have begun to moderate, improving to within one standard deviation by historical standards.

On the other hand, service prices show no sign of slowing down. Although new sales of homes are on the decline, rental vacancy rates did not increase significantly until 3Q 2022. In particular, shelter inflation is likely to stay elevated for a while. As mortgage rates rise, a growing number of people who can’t afford to buy homes are instead turning to rent, which drives up rent fees.

The U.S. labor market remains tight, indicating that wage growth will remain high. Data shows the job market is holding up despite widespread predictions about a recession, with the unemployment rate at a historic low of 3.7%. Wages are up sharply in the U.S. – The annual wage growth in the Atlanta Fed wage growth data was more than 6%. According to the U.S. NFIB Small Business Survey, the percentage of businesses planning to increase wages in the next three months remained elevated at 32%, and as demand is outpacing supply in the labor market, upward pressure on wages remains. The labor market is keeping the Fed on its toes as the latest nonfarm payrolls report (published on Dec 2, 2022) and the wage growth rate blew out expectations.

Although inflation dipped in August, price levels will not go down dramatically as they remain well above the Fed’s goal of 2%. Inflation is expected to decline in 2023, with most investment banks predicting it to reach around 3-4% towards the end of December and ease to around 2% by the end of 2023.

Despite being widely panned for using the term, “Inflation is Transitory,” the Fed has insisted on the narrative for over six months. In an effort to tame inflation, the Fed is likely to tighten the monetary policy further through more interest rate hikes and is willing to sacrifice the U.S. economy to ensure stability. The Fed is under pressure to back up its hawkish stance. Every Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meeting is making headlines around the world, even pointing out how many times the word “inflation” has been mentioned during the meeting, and the world is watching whether the Fed’s credibility as an inflation fighter can be kept.
The Fed’s effort to bring inflation under control is to ward off the threat of stagflation similar to that of the 1970s, during which the Federal Reserve policymakers decided to ease the monetary policy early and pulled back on rate hikes too soon to blunt the risks of a recession. Against this backdrop, even if the Fed decides to pause interest rates around 2Q 2023 under less recession fear, the Fed will lower rates only after the data provides confidence that inflation is moving down to its target goal in a sustained way. Since it took five months for the CPI to peak and enter a downward trend after the first rate hike since the pandemic in Mar 2022, the Fed will monitor the inflation indicators for at least five months or longer before deciding whether to cut interest rates. For this reason, it is unlikely for the Fed to become dovish again until at least the year's end, and so will the rise of Bitcoin prices.
B. Economists Predict “Mild Recession” in 2023
Key economic indicators have already implied that a U.S. recession is on the way in 2023. The long-term and short-term government borrowing rates have been inverted (10 year-3 month treasury yield spread), and the ISM manufacturing index also fell to 48.4% in December, falling below 50% for the first time since the pandemic broke out. The 2023 earnings guidance of companies is also being revised. Though a recession will likely hit in 2023, predictions say it could be “mild.”

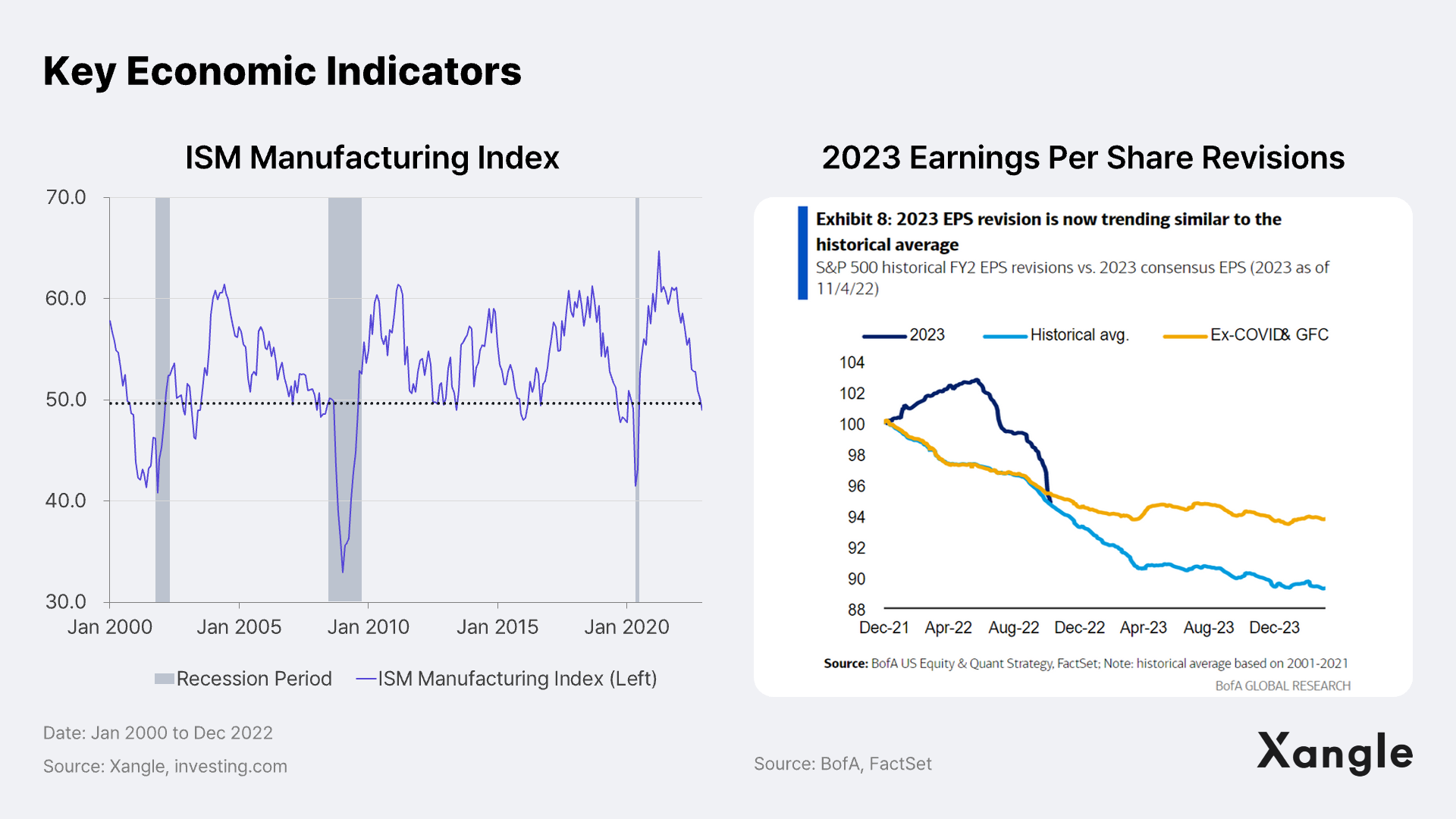
In 2023, as prices become more stable and interest income rises, especially among high-income households, we expect consumer spending to remain relatively strong. Although real disposable income for each household has decreased sharply after the suspension of the Covid-19 relief funds and as inflation exceeded wage growth, the pace of decline is gradually slowing starting in 2H 2022. Goldman Sachs expects a consumption growth of roughly 1.5% in 2023. Black Friday online sales hit $9B despite fears over an economic recession from high inflation. Considering most sales came from electronics and apparel, durables that have stayed stable in price or declined compared to other durables, we see that the rise in sales figures was driven by real demand, and not inflation, a promising indicator of the spending power of U.S. households.

The unemployment rate remained essentially unchanged at a historic low of 3.7%, well below the natural rate of unemployment. According to the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER), the natural rate of unemployment spiked in the U.S. at the onset of the Covid-19 pandemic, from 4.5% at the end of 2019 to 5.9% at the end of 2021 - the rate rose as the pandemic contributed to a boost in remote working and as the number of freelancers with multi jobs increased. The natural rate of unemployment is a useful construct for the Fed to gauge the unemployment-inflation trade-off as it is consistent with full employment and stable inflation, meaning that it can be an indicator to keep the interest rate unchanged. It also means that if the unemployment rate rises, downward pressure is placed on prices.
Given that the Fed underwent insurance cuts twice by 75 basis points in late 2019 in response to growing concerns over an economic downturn, there is a possibility that the Fed could cut rates in 2023. But circumstances are different in 2023. Inflation will remain above the Fed’s target, and recession will likely be shallow and mild. As the end of the year approaches, attention will turn to 2024, and expectations for rate cuts could potentially boost Bitcoin prices; however, the Fed will not be comfortable cutting rates until inflation declines close to its 2% target. Unlike in 2020, it will require some time to lower interest rates as the Fed does not want to overtight the economy. For this reason, it is unlikely for market liquidity to undergo dramatic expansion and Bitcoin prices to rebound drastically.
2. In the End, Blockchain Will Become Faster and Cheaper
2-1. 2022 L1 War Claims the Battlefield Full of Scars with Ethereum as the Sole Survivors
A. The Brutal L1 War of 2022
No one would question the Layer 1 (L1) War as the keyword that generated the most buzz in the bull market of 2021. The cut-throat competition to determine the survival of L1s was just that fierce. That heat was carried well over to the first half of 2022, pushing up the market cap of Solana, one of the major L1s, with over a remarkable 130-fold growth during that period.
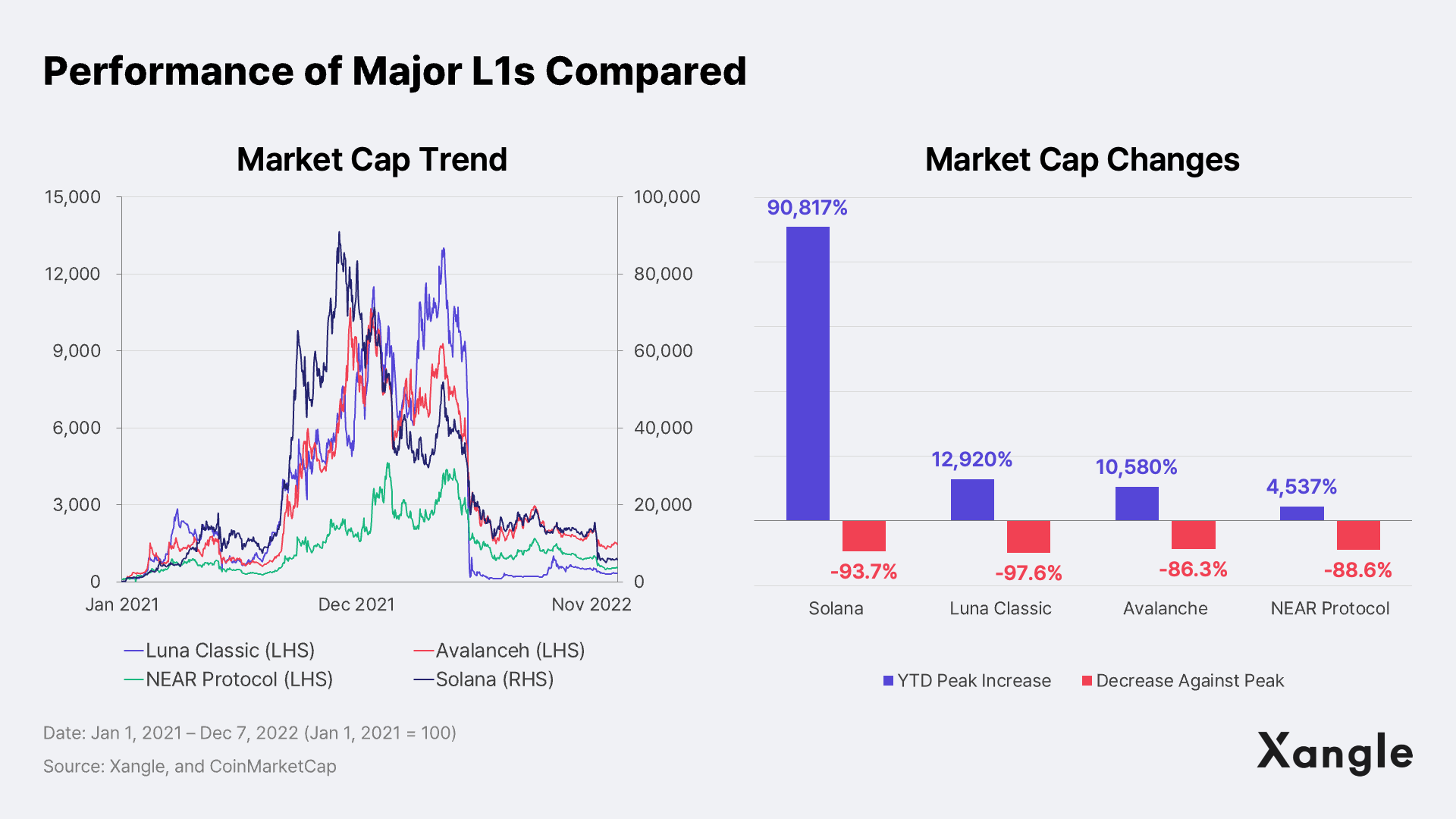
However, the L1 war was brought to its gruesome end after only one year due to the unfavorable macro environment coupled with the fall of two major L1s, Terra in early 2022 (refer to the Xangle report, “Terra Becomes the Battlefield for the Layer 1 War” available in Korean) and Solana at 2022 end (refer to the Xangle report, “A Vitals Check on Solana and Layer 1 Ecosystem since the FTX Debacle”) brought on by their lax risk management.
The L1 tokens that dominated the top market cap, raking in the first half of 2022, handed their seats over to stablecoins and dApp tokens in the latter half of the year as the L1 war came to a close. Ironically, the only L1 left standing after the war – dubbed the “Ethereum Killer” – was none other than Ethereum itself. Interestingly, while Ethereum formidably held its position with the second largest market cap, other assets related to Ethereum 2.0, such as USDC, DAI, and stETH, also rose to the top of the cream in terms of market cap ranking.

B. Ethereum Finally Merges after Achieving Their Milestones in Wartime
A Successful Merge and Its Significance
While most projects were left tattered with only scars from the L1 War, Ethereum victoriously accomplished its long-awaited goal and ambition. In mid-September 2022, Ethereum completed its transition from the PoW (Proof-of-Work) to the PoS (Proof-of-Stake) consensus algorithm. The key to the Ethereum Merge is changing the consensus algorithm to PoS and enabling stable network operation by securing enough validators through staking.
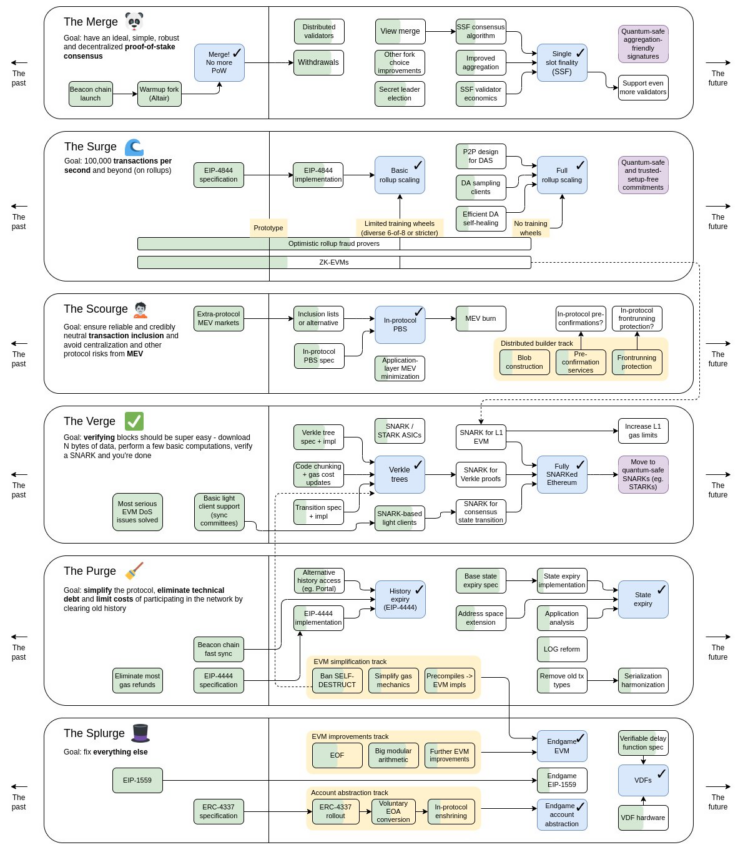
The impact of the Merge may seem minimal from the mainnet infrastructure perspective. However, it boosts up the attractiveness of Ethereum from an investment point of view. A cryptocurrency data platform, Messari, claimed that the Merge ultimately changed the tokenomics of Ethereum to “Staking Economics” in its Ethereum 2.0 report published in 2020. It determined that the nature of the assets will be upgraded once more as Ethereum officially changes its structure to enable its users to earn interest through staking.

On the PoW chain of the past, Ethereum was an asset with some value storage functionality and characteristics of commodities. It was used as the key currency in its ecosystem and the gas fee to execute smart contracts. However, after the switch to PoS, Ethereum will have added characteristics as follows:
- Deflation can be expected as issuance volume is reduced and burn volume increases as per the network activity level.
- Interests can be earned through staking, and the staked Ethereum can be liquidated.
This means that Ethereum can further pad its attractiveness as a store of value as well as have an additional characteristic as a capital asset, similar to a hybrid perpetual bond, as staking interests can be earned. Ethereum has secured various ingredients for price increase as below. Let us explore how each of them is doing now, three months into the Merge.
Deflation Due to Issuance Reduction and Burns → Role as Store of Value Asset
As of December 11, 2022, about three months after the Merge, Ethereum is showing a +0.004% p. a. inflation rate according to ultrasound.money, which was expected to be about +3.579% p. a. if the network maintained its PoW-based operation as before. In summary, the inflation rate decreased by almost 99.9% after the Merge.

On top of issuance volume reduction after the switch to PoS, the network’s burn mechanism from EIP-1559adopted with the “London Hard Fork” in August 2020, preceding the Merge, is also considered to have acted as the cause for the decrease of Ethereum inflation. In other words, Ethereum is more likely to become a deflationary asset as network activity increases.
In fact, Ethereum recorded deflation for about 25% of the period since the Merge. The momentary hype for Xen Coin made by Jack Levin, one of the early Google founders, in October and the surge in demand for decentralized exchanges and stablecoins since the FTX incident in November are identified to be the causes driving up the network activities and burn volume.

If the volume of staked Ethereum on the network is maintained at 30 million ETH and gas fees at 60 gwei, Ethereum supply is expected to continue downward for the next two years. A decrease in Ethereum supply increases its attractiveness from the relative scarcity and provides a footing to view Ethereum as a means to store value. It would be like Bitcoin rising up as a store value asset through its contract enforcing the 21-million-coin supply cap.

Staking Yield and Asset Liquidation → Rising as a Capital Asset
As of December 12, 2022, the total deposit in Ethereum is recorded at around 16 million ETH, about 13.5% of the total supply issued and equaling 21 billion in U.S. dollars.

When users stake Ethereum, they will also get about 20% interest in ETH in five years as of now. Such yield calculation is before considering the increase in Ethereum price.
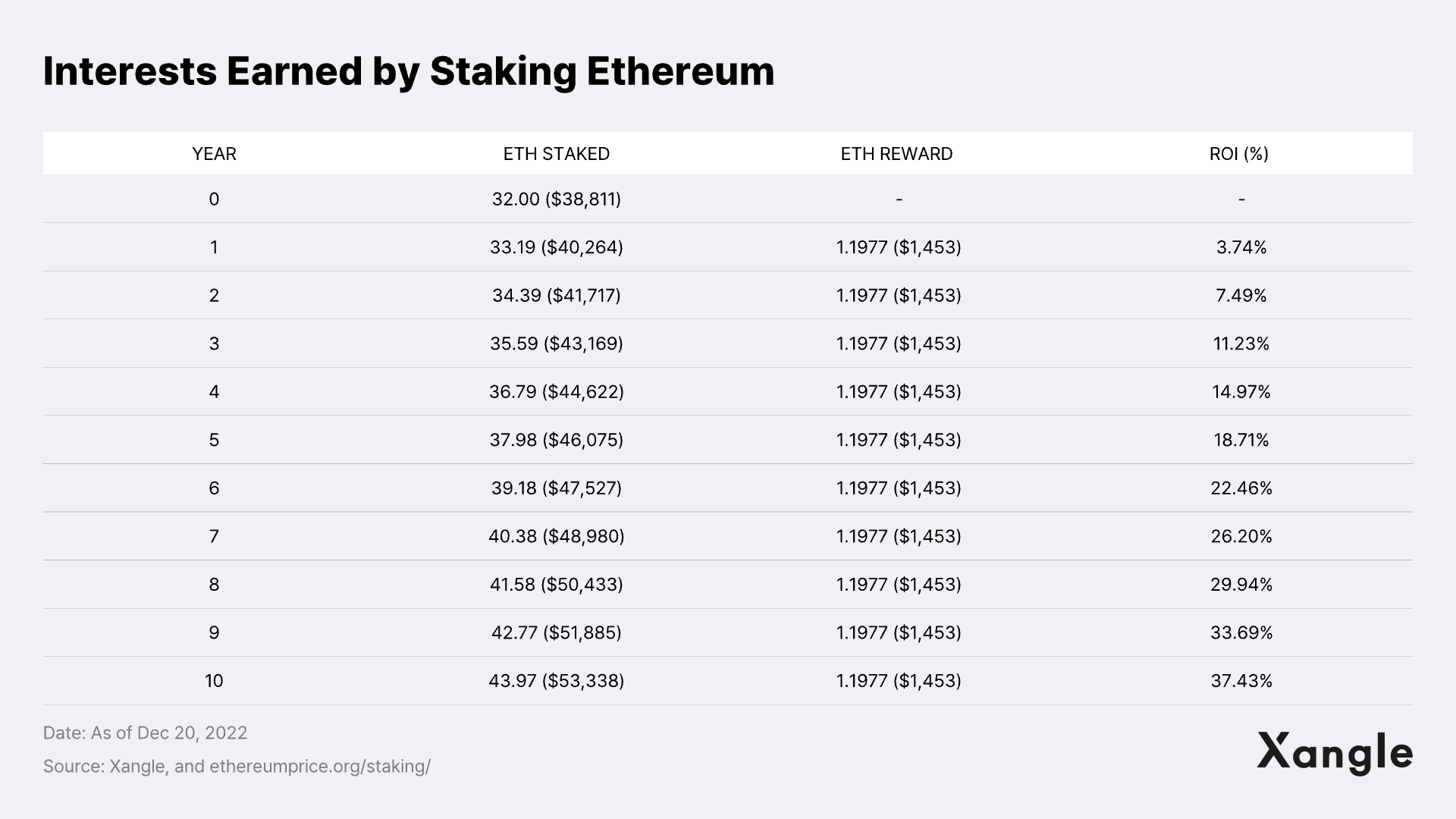
Moreover, the staked ETH can be liquidated through a wide range of protocols, such as Lido, Binance, and Rocket Pool, which currently offers Ethereum staking derivatives.
- Lido: Lido is a DeFi platform offering liquidation staking services based on stETH tokens based on the Ethereum blockchain. Currently, the total ETH deposited via Lido takes up about 29% of total ETH deposits to Beacon Chain.
- Binance: Binance offers an Ethereum staking derivative products from centralized exchanged. Like Lido, Binance uses BETH (Binance wrapped token - ETH). Currently, the total ETH deposited via Binance takes up about 6% of total ETH deposits to Beacon Chain.
- Rocket Pool: Rocket Pool is a platform that provides Ethereum staking liquidation services and node operation services. It offers rETH and only requires a deposit of 16 ETH to create a new Ethereum validator via an Ethereum staking pool called a “minipool.” Currently, the total ETH deposited via Rocket Pool takes up about 2% of total ETH deposits to Beacon Chain.
As of December 15, 2022, stETH, a liquid asset offered by Lido, which has the highest market share among the examples above, has USD 61 billion in market cap and is ranked 11th in the market.

Some claim that it is only natural that the scale of staked Ethereum is growing since there is no technical support for redeeming the ETH deposits yet. However, the derivatives that can liquidate ETH deposits are showing high activity.
Suppose asset liquidation were to remain as easy as such. In that case, Ethereum’s attractiveness as a capital asset will only increase since users can earn interest from staking Ethereum and leverage the liquid asset for other opportunities. This not only makes Ethereum a more attractive investment asset but, at the same time, also reminds us that there are various types of services and infrastructures already established in the Ethereum ecosystem.
2-2. A Full-Blown L2 War to Scale Up Ethereum
Ethereum’s true competitive edge may shine as it secures scalability through L2 solutions and sharding. While it is expected to take some time to adopt sharding which changes the structure of the Ethereum chain to enable parallel transaction processing, the market’s focus naturally shifts to Layer 2 (L2) solutions.
With Ethereum’s utility improved after the DeFi Summer of 2020 and NFT Summer of 2021, the interest in L2 that can enhance Ethereum’s scalability has continued since early 2022. The chart below displays the outstanding performances of major L2 projects in terms of token price, TVL trend, and investment. In particular, rollups – specifically Optimistic Rollups (ORs) based on fraud proof, such as Arbitrum and Optimism – have achieved significant growth.

ZK-rollups based on validity proof have also been very much talked about. However, with a few exceptions of app-specific ZKR solutions like StarkEx, most of the general-purpose ZK rollups remain at a testnet phase or require significant improvements. In this regard, StarkNet launched an alpha version in November 2021, and zkSync launched a baby alpha mainnet in late October 2022. Other promising ZKR solutions, such as Scroll and zkEVM, are also scheduled to launch their own mainnets in 1Q 2023. Considering the development progress of ZKR, it will be some time before ZKR reaches mass adoption. However, since it is emerging as the endgame of rollups, ZRK solutions’ mainnet launch and other movements are some of the key points to watch out for in 2023.
With the full-fledged growth of the L2 ecosystem anticipated in 2023 and many different L2s planned to launch their mainnets, the competition among L2s to claim their portion of the Ethereum pie will only get fiercer. Since they all have their own strategy and tokenomics, the game will get even more interesting.
A. OR to Have an Upper Hand over ZKR for the Time Being In 2023
In 2023, it may be advisable to look to Optimistic Rollups (ORs) such as Arbitrum and Optimism rather than ZKRs. Although it is true that ZKRs will have a stronger competitive advantage as the technology develops, ORs look more promising in the mid-to-long-term for the following three reasons (Please refer to the Xangle research article, “Would Optimistic Rollup Remain as a Viable Candidate Even After ZK Rollup Is Fully Developed?”):
- Closing the Technology Gap: While ZKR takes a definite upper hand in scalability, OR is determined to have a good chance to claim the win considering the actual processing speed of Optimism and Arbitrum is currently at around 3-4 TPS. The gap in cost between the two rollups is likely to narrow down as time passes, with Optimism introducing Bedrock technology and using blobs instead of calldata for data availability after the Surge. In terms of trust, OR assuming at least one out of N number of nodes to act honestly cannot take an advantageous position over ZKR, guaranteeing the trustworthiness of each batch via mathematical computation. However, the structure of OR that utilizes the game theory does not pose many issues either, which is evident in the fact that there has not been a single hacking incident in the one-year period that Arbitrum and Optimism have been operating their mainnets. Moreover, what had often been dubbed OR’s critical pain point and a disincentive for users – the seven-day DTD (Dispute Time Delay) – can be circumvented by using quick withdrawal services offered by market makers (MMs), making it unlikely for the end-users to feel much inconvenience.

- OR’s First-Mover Advantage: While Optimistic Rollups have been maintaining a stable operation of their mainnets and growing their ecosystem for over a year, most of the Zero-Knowledge Rollups have not yet launched their mainnets. Of course, the OR ecosystem is much larger. According to L2Beat, the total TVL of L2s is about USD 4.5 billion as of December 5, 2022, of which Arbitrum takes up 53% of the L2 market share with USD 2.35 billion and Optimism takes up 27% with USD 1.2 billion. Even if the TVL of all the app-specific ZKRs were to be combined, it would not amount to USD 1 billion. In terms of UAW (Unique Active Wallets) number, Arbitrum and Optimism reached 1.1 million and 1.4 million respectively, with their daily transactions also rising to exceed 400,000 recently. The market cap for stablecoins of Arbitrum and Optimism also reached USD 1 billion and USD 500 million each, with many competitive dApps onboarded, such as GMX, Uniswap, Aave, and Stargate Finance. On the other hand, most of the ZKRs have not even launched their mainnets and the ones launched are not ready for public use. In the meanwhile, ORs will get a first pic of the users and major dApps, getting on track to fully advance in their growth. The first-mover advantage will make it difficult for ZKR to narrow the gap in a short period of time. ZKRs will require more time to win over the trust of users and make meaningful growth in terms of network activity. For ZKRs, the year 2023 would be the time to lay a firm foundation, as 2022 was for ORs.


- EVM-Compatibility: Optimism and Arbitrum are already offering general-purpose rollup solutions with very high EVM-compatibility and well-established development libraries. Equipped with a development environment that makes it easy to onboard rollups, it is also relatively easy for projects to develop dApps on or migrate to OR, which is a formidable advantage, especially when considering Ethereum’s vast pool of developers. On the other hand, Polygon, ZKSync, and Scroll, which have declared the launch of their ZKEVM, fall under the category of Type 4 systems from the various types of ZKEVM that Vitalic Buterinproposed. The Type 4 ZKEVMs work by compiling smart contract source codes written in high-level languages into languages that can be used in the ZK-SNARK environment, having the upside of quickly generating validity proof at a relatively low cost but also with the downside of lowest EVM-compatibility. The fact that EVM was never designed with ZK technology in consideration makes it that much harder for development.

B. Polygon with an Ambition to Put an End to the L2 War
Although Arbitrum and Optimism do have high potential and are showing great performances lately, the L2 project emerging as the favorite to win is actually Polygon. The expectations are riding high for Polygon because it has i) the most global Web2 companies, such as Meta (former Facebook), Starbucks, and Nike, and ii) established a rollup pipeline that can fulfill various enterprise needs from PoS chain to ZK solutions. Some point out the fact that the Polygon PoS chain has its own validator and consensus algorithm and claim that Polygon is not L2. However, considering how Polygon is using Ethereum as the DA (Data Availability) Layer via checkpoints and is planning to evolve as an all-in-one comprehensive L2 solution in the future, we at the Xangle team expect such claims will die down soon enough.

C. StarkNet Aiming for the Win with Cairo: Ecosystem Growth Is the Key
StarkNet and its moves stand out from the many ZKRs. The most remarkable feature of StarkWare would be that it broke away from EVM by establishing its own development environment, Cairo, despite being an L2 project. In fact, major ZKRs other than StarkWare, such as Polygon, Scroll, and zkSync are developing ZKEVMs that mimic the EVM environment. This is an extremely valid strategy considering that it can easily attract Ethereum developers, of which there is a whopping number in the Web3 ecosystem. However, StarkWare stands out like a sore thumb and does not consider ZKEVM to be its ultimate goal because it believes that i) we need to build languages and VMs optimized to ZKRs rather than advocating EVM compatibility in order to reach high scalability, and ii) the importance and influence of EVM would fade as time passes since all the dApps will be run on L2 in five years’ time anyways.
Of course, StarkWare cannot completely look over the EVM developer ecosystem in mind, and is getting ready to offer Warp, a service to transpile Solidity codes to Cairo codes on StarkNet, as a part of its consideration for such consideration. However, it is much more focused on advancing Cairo, and even having released Cairo 1.0, optimized for STARK technology, as an open-source recently. Only time will tell if the winning move by StarkWare will indeed get them the win they seek. However, there is a good chance that Cairo might claim the position as the standard language for Ethereum developers in the future. (Refer to the Xangle report, "StarkNet Sheds a Light on a New Direction for ZK Rollups.") In this aspect, it is a positive sign that over 100 projects have already been onboarded on StarkNet.

D. zkSync and Scroll Forewarned Their Part in the Competition

On top of Polygon, Arbitrum, Optimism, and StarkNet – the projects aforementioned to watch out for the new year- zkSync and Scroll deserve our attention in 2023. zkSync is a ZK rollup being developed by Matter Labs, a Series C investment round startup, having attracted a hefty sum of USD 258 million from major investors, including a16z, Lightspeed Ventures, and Consensys. zkSync boasts of having the largest ecosystem among ZK rollups, along with StarkNet, which undoubtedly makes it one of the more promising ZKRs. However, considering it has been little over two months since zkSync launched the zkSync 2.0 baby alpha mainnet, and only to be used within the team, it will take some time until the project gains the trust of its users, launch its service, and increase the network activity to a significant level.

Scroll is developing EVM-equivalent ZK rollups based on its superb technological capabilities. However, unlike other projects that have already launched their mainnets or whose launch is imminent, such as StarkNet, zkSync, or Polygon, Scroll is still in the pre-alpha testnet phase. We could put a pin on this project and keep a close eye.

E. Level of Decentralization to Emerge as Critical Metrics in L2 Assessment
Today, all the L2 solutions are run in a centralized structure. The biggest issue with the centralized sequencer is that it has a single point of failure (SPOF) that can cause the whole network to shut down. This was proven true in January 2022 when Arbitrum went offline due to sequencer problems. The industry had looked the other way when it came to L2’s centralized operation, citing various practical issues. However, as the L2 market grows, they are likely to start considering decentralization of the rollups as one of the key factors in 2023. The foundation of L2 network decentralization is the L2 tokens, which can contribute to network decentralization in two aspects as below:

First is governance. Token holders will be able to participate in the decision-making process for key agendas regarding the protocol. Take a look at the structure of $OP that came into the market in May 2022, for example. Optimism took a two-house governance system comprised of the Token House and the Citizens’ House. $OP holders can participate in the Token House, where major financial decisions are made, including the ones on protocol upgrades, grant programs, $OP inflation, key personnel changes, and usage of the treasury. The members of the Citizens’ House are selected with $SBT and will be handling matters regarding the Retroactive Public Goods Funding (RPGF).

Second is the decentralization of the sequencer. OR uses the concept called slashing, much like the PoS blockchains. For anyone to participate as the sequencer to the rollup, they must deposit the fidelity bond as a sort of collateral, which is slashed as a penalty if they ever commit any malicious behavior such as double payment. Today, the OR solutions, including Arbitrum and Optimism, are operating their own sequencers. When tokens are issued, other players would also be able to participate as the rollups’ sequencers by depositing the L2 native tokens as the fidelity bond.

However, in 2023, many L2 projects are scheduled to release their tokens, including Arbitrum (4Q 2022 or 1Q 2023 expected), zkSync (2023 expected), and StarkNet (already deployed on November 17, but distribution and transaction support expected to take place in early 2023). Since most protocols use the newly issued tokens as a strong marketing tool to boost ecosystem activities, we may also want to keep a close eye on the trend of performance indices such as the network TVL post token issuance and how the token economics unfold after the initial distribution.
2-3. Modular Is the Mainstream! Projects Take After Ethereum
A. BNB Chain Is Following the Ethereum L2 Strategy

After the successful Merge, Ethereum is charging on to become a full-fledged modular blockchain with various L2 solutions also joining. Not only that, but other Layer 1 protocols are also actively adopting the modular blockchain format by benchmarking Ethereum or in their own way.
Binance Smart Chain (BNB Chain)
Binance Smart Chain, launched by Binance, the world’s number one cryptocurrency exchange, made fast growth by leveraging Binance’s wealth of human resources and capital. Binance Smart Chain is one of the few chains producing significant results after the Ethereum chain today. As of December 19, its TVL remains around USD 7.08 billion, about 10% of the total market share. Its cumulative revenue is recorded at USD 54 million, the third largest after Ethereum and Avalanche.

The chain also announced last September that it would launch a zk-SNARK-based ZK rollup. It completed the testnet launch in November and is targeting its mainnet launch within 1Q 2023. zkBNB was also designed to resolve BSC’s scalability issue and is expected to provide the following functions:
- Same Security as That of L1: The zkBNB shares the same security as BSC does. The security is also guaranteed cryptographically via the use of zkSNARK.
- Seamless L1-L2 Communication: BNB and BEP tokens created on BSC or zkBNB can be moved freely between the two chains.
- Fast Transaction Speed, Fast Finality, and Low Fees: zkBNB, putting BSC performance improvement as its first priority, showed off its ability to support 100 million addresses and up to 10,000 TPS. Also, zkBNB fees are paid in BEP20 or BNB at as low as 10-fold lower price.

With detailed plans about technical specifications undisclosed so far, the visibility into the specifics of the increase in TPS and reduction in gas fees after the launch is limited. However, it is evident that they expect the same impact as Ethereum’s L2 rollups. The key is whether Binance Smart Chain could keep up its competitive advantage going forward by adopting Layer 2 and securing scalability via zkBNB.
Binance is not alone on this journey. There are many other Layer 1s also striving to transform themselves into modular blockchains. For example, TRON acquired the Peer-to-Peer (P2P) file-sharing service, BitTorrent, last year and made an attempt to charge into the battleground of the L2 War. BitTorrent paved its way to evolve as a comprehensive Layer 2 solution with the launch of its BitTorrent Chain (BTTC) in December 2021.
Klaytn and Wemix have also announced their plans to improve scalability via L2 solutions. Although there are no updates on specific progress made so far, the fact that many projects are declaring their intentions to adopt Layer 2 chains left and right as a means to secure scalability reminds us that the modular blockchain is the way to go right now.

B. Cosmos Seeks to Set Itself Apart with Appchains
The Cosmos network is structured into a Hub and Zones. App-specific chains or Appchains, which are “zones” in Cosmos, are interconnected thanks to the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol officially live since April 2021. A total of 53 zones are connected via IBC today, with 49 of these zones activated and IBC’s cumulative transaction amount for the last month reaching USD 834 million.

Major players within the Cosmos ecosystem today can be briefly summarized below:
- Osmosis: The first Cosmos DEX launched in 2021. Osmosis acts as a liquidity hub that is connected to the assets across the entire ecosystem. Osmosis sets itself apart from other DEXs as it offers i) customized Automated Market Maker (AMM) algorithms and ii) superfluid staking. Users can make decisions and design their own AMM algorithms customized to their needs, selecting the type and ratio of tokens they want when creating a pool.
- Axelar Network: A cross-chain messaging protocol based on the Cosmos SDK. Axelar’s strong point is its superb scalability. Axelar Network supports around 30 major chains, including Ethereum, BNB Chain, Polygon, and Avalanche, and recorded a cumulative transaction amount of USD 1.6 billion.
- Juno: A Layer 1 based on the Cosmos SDK. Juno is an application-building platform equipped with interoperability between different chains. The mainnet was launched on October 1, 2021, providing a multi-chain smart contract environment by adopting CosmWasm. Over 30 projects are onboarded currently.
- Sei: A decentralized orderbook protocol based on the Cosmos SDK. Sei aims to become a DeFi hub within the Cosmos ecosystem as a DeFi-specialized Layer 1 that not only provides various features for dApps (such as its own order matching engine and its own price oracle) but also enables the use of both a virtual machine, CosmWasm, and a communication protocol, IBC.
It is also worth noting that there were barely any security breaches within the IBC ecosystem, considering the numerous bridge-related incidences that continued throughout 2021 (to be discussed further in the section below on bridges). In addition, Cosmos is preparing Interchain Security (ICS) to improve appchain security and token economics. This system involves a certain chain (mainly the Cosmos Hub at the moment) acting as a provider chain and providing security to consumer chains, who would then pay back with native tokens as rewards.
Although the attempt to introduce interchain security and staking liquidity system at the same time with ATOM 2.0 was dismissed by the community, unfortunately, various attempts to improve the ecosystem are continuing. After Ethermint and EVMOS, the idea that is gaining the most interest as of late is inspired by ZK rollups and proposes connecting IBC to Ethereum.
The Cosmos camp is deemed not only to have a competitive edge over the connectivity between blockchains but also with Web2. The market witnessed many existing Web2 players with the ability to secure their own users and security choosing Cosmos for their fast speed and scalability, such as Com2us, a major Korean gaming company (with KRW 800 billion market cap as of December 19); and Line, a messenger service by NAVER (with KRW 29.8 trillion market cap as of December 19) announcing their plans to launch their mainnets on Cosmos last August and December, respectively, following the footsteps of dYdX, a futures exchange previously based on Ethereum Layer 2.
2-4. Monolithic Blockchains Gearing Up for Counterattacks
Though the landscape looks like the modular blockchain camp, led by Ethereum, has won the L1 War of 2022, the monolithic blockchain camp still bears the torch to retaliate. The rivalry between Aptos and Sui emerged as the hot potato of the second half of 2022, and the eyes are on Solana to see if it would be able to reclaim its reputation after the struggle it endured in regard to the FTX debacle.
A. Monolithic 2.0: Aptos and Sui
Aptos and Sui projects are both new L1 blockchains derived from Meta’s blockchain endeavors that drew keen attention from all over the globe. The two blockchains are similar in that they both are ultra-high TPS L1 blockchains that seek to find scalability solutions on their base layer chains. However, their vision and approach to scalability enhancement, such as consensus algorithms and architectural design differ greatly. While Aptos is closer to an orthodox L1 per se, Sui brands itself as an object-centric blockchain with a development environment with much more freedom. For further exploration into the analyses and comparison of the two, please refer to the Xangle report, “Aptos vs. Sui Comparison: Similarities and Differences.”

In the year 2022, Aptos and Sui each achieved various milestones, as below. Both projects are highly competitive as the new monolithic L1 blockchains equipped with a high level of security, scalability, and convenience, based on outstanding developers, ample resources, and technological prowess. What is crucial is how the dynamic will unfold in the full-fledged competition for ecosystem expansion after their mainnets are launched. In this regard, both projects are showing great interest in the Korean market, as Aptos successfully secured a partnership with NPIXEL to build on its network, and Sui with Netmarble. All in all, it looks like Aptos is slightly ahead of Sui in the race. However, the game has only just begun.

B. Will Solana Be Able to Bounce Back?Will Solana Be Able to Bounce Back?
In the meanwhile, there is no argument the recent fall of FTX has cost Solana, the most representative monolithic chain of them all, its strongest supporters and left it in a lurch. FTX and Alameda Research under its wings have strongly driven the growth of Solana’s ecosystem, having participated in multiple funding rounds for Solana and actively investing in other Solana-based projects. FTX also gave much direct and indirect help in support of the Solana ecosystem’s growth as an exchange that most actively and enthusiastically listed Solana-based tokens, and operating Serum, a Central Limit Orderbook (CLOB) exchange as well as an NFT marketplace and Solana’s representative DeFi project. With FTX gone, Solana projects will face more difficulty attracting new investments and getting listed on major CEXs, and there is much less of an appeal for dApps to get onboarded on Solana.
Against this backdrop, Solana is embarking on its journey to stand on its own. In the past, Solana had been jeered at as a “VC Chain” in the crypto world for their close to 50% token distribution carved out for its team and investors for the initial funding round. So, the recent crisis could be a blessing in disguise as it serves as an opportunity to build decentralized governance and put more focus on the fundamentals. What the market can expect from Solana sans the VC support are as follows:
Strong Developer Community
Solana has a strong and firm developer community. What used to be a group of only 2,400 developers in August 2021 has rapidly grown 761% in a matter of one year to become an army of 20,717 by November 2022. Solana has the largest group of developers among Layer 1 blockchains, next to Ethereum right now. Such popularity is evident in the fact that the Solana Hacker House has risen to become one of the most sought-after blockchain events (with a total of about 64,000 participating in Solana conferences in 2022).

Remarkable Achievements in NFT Market
Solana achieved a remarkable performance in the NFT sector. Solana’s NFT market share is currently at the number two position among Layer 1 blockchains by transaction amount, having produced many of the highly recognized NFT projects, such as DeGods, y00ts, Okay Bears, Solana Monkey Business, and Degenerate Ape Academy (DAA). With Instagram recently announcing that it would support Solana NFTs, anticipation is rising for Solana to continue its growth in the NFT market in the future.

Continuous Improvements in Technology and Usability
It is also encouraging that Solana continues to make improvements in its technology and usability. For example, Solana recently successfully adopted QUIC (Quick UDP Internet Connection) and QoS (Stake Weighted Quality of Service) from the three ways to stabilize its network (QUIC, QoS, and local fee market) as announced in 1Q this year, and Solana’s smartphone, Saga, is well on its track for the launch in 1Q 2023. After Saga is launched, Solana is likely to overcome the limitations of having to offer Web3 services under the existing hardware and operating system and be able to offer a mobile-friendly Web3 environment.
It is also worth noting that there may be significant progress made in terms of network stability and decentralization once Firedancer is launched. Firedancer is a Solana validator client developed by Jump Crypto, with fewer bugs and faster transactions than existing clients. Lastly, the partnership Solana recently forged with Google Cloud on the blockchain node engine development will enable anyone to participate as a Solana node without having to go through all the complicated hoops and hurdles.

Creating a Modular Ecosystem with SVM (Sealevel Virtual Machine)
It is also an interesting development that L2 solutions, once thought of as mere relics of Ethereum, are being built on top of Solana. Solana’s Sealevel Virtual Machine (SVM) is quickly rising as the favorite choice for dApps demanding fast speed, with the ability to process transactions in parallel. Catering to such needs, SVM-based L2 solutions such as Nitro (a Sei Network-based Optimistic Rollup with SVM-compatibility) and Eclipse(an L2 solution enabling users to build SVM-based customized rollups) are also gaining attention.

2-5. In the End, Resolving the “Blockchain Trilemma” Is the Key
The modular method – increasing transaction speed and lowering gas fees by dividing blockchain functions to be handled by different chains – and the monolithic method – maximizing the blockchain’s performance to solve the scalability issue are not mutually exclusive concepts. Ultimately, they are simply different approaches to solving the same problem: the blockchain trilemma.

The blockchain trilemma refers to the impossible position we are in where the three main issues of blockchain – scalability, decentralization, and security – cannot be solved at the same time. While sacrifices would need to be made within the trilemma, and such sacrificial relationships among these three characteristics would not be changed by scaling up the triangle that makes up the trilemma, it would indeed increase the maximum size itself. In fact, this is the direction many of the chains are taking on.
In this regard, what makes or breaks the next L1 War would, of course, be which project can secure lower cost and high speed as well as security and decentralization. It seems that the modular blockchain camp, spearheaded by Ethereum to come out on top of the first L1 War and to forge alliances with the L2 camp, would dominate the market for the time being. For the year 2023, we would have to wait and see how other projects, each with their unique advantages and characteristics, such as Binance, Cosmos, and other monolithic blockchains, would secure scalability.
3. The Evolving Blockchain Ecosystem Infrastructure
The blockchain infrastructure sector struggled in 2022 due to the overall market downturn. Some sectors contributed to the market's downturn, while others have shown signs of aligning with the slump. 2022 was a record year for crypto hacks, bridges – in particular, Lock-and-Mint bridges* – being the prime target, accelerating the market downturn. The lock-and-mint bridges suffered the most from malicious attacks, exposing security risks as four of the five largest exploits during the year were bridge exploits. On the other hand, Oracle and storage networks are amongst the sectors affected by the market's decline. Oracle's TVS plunged amidst the overall industry deleveraging across DeFi, one of the major Oracle customers. Data storage networks are also on a steady decline, putting the narrative of decentralized NFT storage to shame. While MetaMask continues to attract more users, being one of the most popular wallets, Reddit surprised the crypto scene in 2022 as it launched an NFT-based marketplace that attracted millions of users to open the company's wallet. Though emerged as the meta to lead in 2022, DAOs failed to attract meaningful use participation and did not produce practical results.
*Lock-and-Mint bridges lock the original assets inside a smart contract on the sending side (A) while the receiving network (B) mints a replica of the original token on the other side.
3-1. Native Verification: Solution to Lock-and-Mint Bridge Exploits

Demand for cross-chain bridges is expected to slow down in 2023 – not only are Ethereum and Ethereum Layer 2 adoption booming but also the increasing number of Lock-and-Mint bridge exploits are exposing the bridges’ vulnerabilities. Blockchain bridges deployed today lack the strenuous testing necessary to ensure the technology’s stability and security. The demand for cross-chain asset transfers has risen sharply with the growth of alternative Layer 1 solutions called SoLunAvax. As a result, Lock-and-Mint bridges became immensely popular since they were simple, cheap, and did not require additional liquidity. However, since Lock-and-Mint bridges utilize a set of external verifiers, they are vulnerable to attacks. In the Ronin Network hack, five of the bridge’s nine validators had been compromised, and in the Wormhole hack, a flaw in the digital signature validation was exploited. The two incidents caused damage that amounted to over $2B.

In 2023, we expect that the native verification of cross-chain transactions will provide solutions to eliminate the structural risks of Lock-and-Mint bridges. Native verification requires each blockchain to create custom validators working within the other chain’s consensus mechanism. This approach could prevent exploits that the Lock-and-Mint bridges experienced as no external verifier set was introduced. As such, the crypto community has turned their attention to the natively verified blockchain bridge solution, and developers are putting hard efforts into developing the solution.
Near’s Rainbow Bridge and Cosmos IBC use native verification. As for Cosmos IBC, 53 independent blockchains are connected to Cosmos’s ecosystem, allowing increased customization and interoperability, and approaches have been introduced to bring Cosmos IBC to Ethereum. However, it will take some time for native verification of cross-chain transactions to be widely adopted for the following reasons: i) the number of users of Near and Cosmos, of which ecosystems use native verification, is less than that of Ethereum, and ii) the cost is high, and the transaction speed is low to run the solution.
3-2. Chainlink Maintains the Largest Blockchain Oracle

Total Value Secured (TVS) is a measuring stick of the adoption of price oracles. Chainlink has secured more than $70B TVS in early 2022, but the value has fallen 85% to $10B as of writing as the DeFi market suffered heavily from market volatility. However, the most popular oracle network Chainlink saw its market share increase even during the bear market. Oracle business tends to determine the growth of the oracle project depending on the growth potential of the ecosystem of the underlying mainnet. In 2022, Cosmos Oracle Band Protocol and Solana Oracle Pyth Network took a big hit, and as a result, the TVS of Chainlink, which is based on Ethereum-compatible EVM mainnets, has risen from a 79% at the beginning of 2022 to 90% as of writing.
In 2023, global companies chose the Ethereum ecosystem, particularly Polygon, for its security and stability. For this reason, we are looking forward to Chainlink’s further growth. It remains to be seen whether the publicly accepted equation of "Oracle = Chainlink" will stay unchanged in 2023.
3-3. Chainlink to Serve as Secure Blockchain Middleware Beyond Oracle

Despite a severe market contraction of the oracle market in 2022, Chainlink managed to diversify its services, which drove the network’s growth amidst the bear market. Chainlink’s Verifiable Random Function (VRF), which can be utilized in dApps including NFTs and gaming, and the smart contract automation solution Chainlink Automation(previously “Keepers”), which relies on Chainlink’s Decentralized Oracle Networks (DON), are popular among dApps. Chainlink is pushing a new system called Proof-of-Reserve (PoR) to dApps, CeFi, and exchanges as a solution to crises like the FTX collapse. Aave DAO recently approved Chainlink’s PoR, specifically covering Aave v2 and v3 on Avalanche. The recent activity on Chainlink’s VRF requests rose sharply when the NFT-based strategy game Planet IX got released on the Polygon network, indicating that Chainlink is likely to expand further if the game’s usage continues to increase.
Chainlink is also preparing to release solutions such as Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP), a cross-chain bridge solution based on a decentralized oracle network, and Fair Sequencing Service (FSS), a Layer 2 sequencer decentralized service, in 2023. Chainlink is also continuing its research into DECO, a novel privacy-preserving oracle protocol. The roadmap and milestones indicate that Chainlink is broadening its services beyond oracle, and its expansion into comprehensive middleware infrastructure services is also expected to accelerate in 2023.
3-4. Decentralized Data Storage: Challenges and Prospects
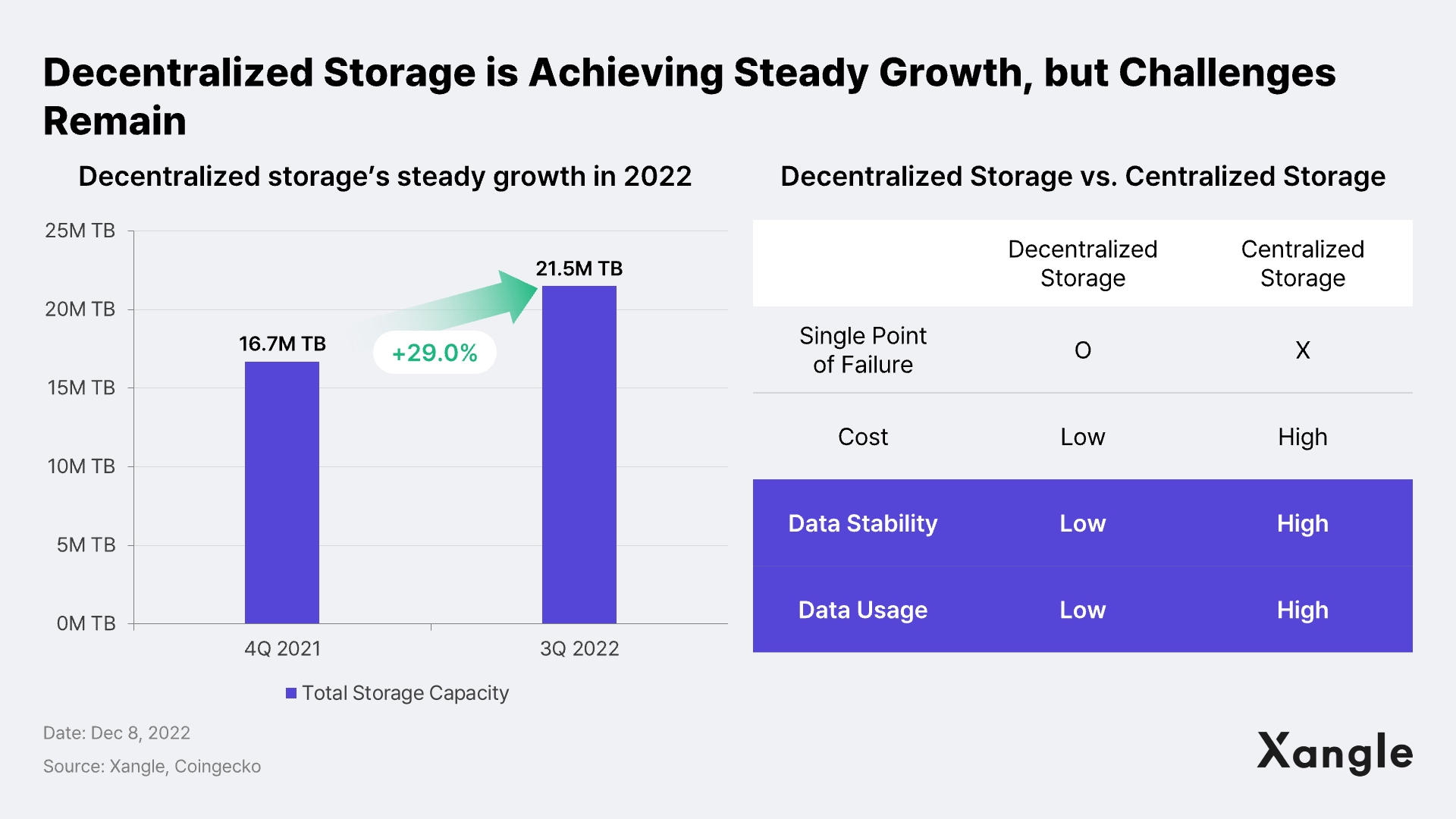
Though it fell short of delivering the narrative of decentralized NFT storage in 2022, the storage section made some progress this year. Decentralized storage does not have a single point of failure and does have low cost compared to centralized storage. Storage usage increased from 16.7M TB in 4Q 2021 to 21.5M TB in 3Q 2022, showing a growth rate of about 29%.
However, decentralized storage still presents two major challenges compared to centralized storage: the need for more stability and data utilization. For example, IPFS, on which the majority of NFTs are stored, is similar to BitTorrent – if the person who stores the file finds it not valuable enough to store a copy, the file will no longer be retained. Also, in terms of data utilization, centralized hosting services such as AWS and Azure store data and provide their own APIs to provide data analysis and machine learning. However, decentralized storage can only store data presently.
To tackle the technical obstacles, decentralized storages are working to apply data computing and programming, but it still needs to mature. Thus, the decentralized storage industry is unlikely to deliver what’s been promised in 2023. Filecoin, a leader in the sector, previously announced in 2022 that it would launch the Filecoin Virtual Machine (FVM) to bring smart contract programmability to the Filecoin storage network. FVM is expected to be officially launched in 2024 as the technology is in its nascent stages of development and has not yet been fully established. In this respect, the storage sector is unlikely to outperform the entire crypto market in 2023.
3-5. Crypto Custody Wallet: Improving the Drawbacks for Mass Crypto Adoption
Self-custody wallet, which allows users to take sole possession of their wallet’s private keys, has certain advantages. While a self-custody wallet presents clear benefits, the top non-custodial wallet Metamask did not enter the mainstream for the following reasons: i) UX issues, ii) web-based, and iii) management of independent seed phrases. For mass crypto adoption to take place in 2023, crypto wallets should work on improving their drawbacks, as new commers often find it difficult to navigate through them.

Multi-Party Computation (MPC) technology, most of which are semi-custodial, presents a solution to vulnerabilities of non-custodial wallets. MPC is a cryptography tool that allows multiple parties to make calculations using their combined data without revealing their individual input. MPC wallet divides a single private key among multiple parties, and more than n number of parties must agree for a transaction to complete. MPC wallets offer higher security as a hacker would need to attack multiple parties across systems. For this reason, BitGo, Coinbase Study, and other digital asset trust companies adopted MPC to reduce security risks. While MPC is mainly used by custodians that manage crypto wallets of institutional investors, the technology is likely to be used by various applications as it does not require seed phrases. The primary feature of MPC wallets like ZenGo is that they do not require long seed phrases but rather use facial recognition or email verification to further secure the user’s account. The aforementioned benefits of using MPC wallets indicate that it has the necessary elements for mass adoption, such as frictionless UX and password recovery functions.
Another wallet type that does not require a seed phrase is a smart contract wallet. This method has the advantage of excellent security in that the smart contract serves as a wallet, manages assets based on the smart contract, and supports compatibility with dApps. However, it is expensive to create and execute smart contracts, and an external wallet account (EOA, e.g., MetaMask) is required on the current Ethereum blockchain structure. The industry sees the smart contract wallet as the ultimate solution going forward but predicts it will take at least a year as the Ethereum design must be changed.

As mentioned earlier, many global companies are preparing to launch crypto asset services to deliver seamless UX backed by top-quality services in 2023. The integration strategy of crypto wallet services provides a glimpse into the future direction of the services – Nike and Meta will likely use the existing crypto wallet, whereas Reddit and Starbucks unveiled Reddit Vault and Starbucks Odyssey custodial wallets, respectively. While Nike and Meta non-custodial wallets place value in the ownership of users, Starbucks seems to have taken into account user convenience.
3-6. MEV: Network Activity is Key to Boost Validator Rewards
Ethereum’s transition to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) replaced crypto miners with Ethereum validators, reducing rewards for miners. This change has resulted in a 90% reduction in ETH incentives for miners, and as EIP-1559 always burns the base fee, block producers’ share further decreased. With less incentive, block producers naturally turned their attention to Maximal Extractable Value (MEV), and more and more validators adopted MEV-boosted blocks to receiving higher rewards. The graph below indicates that there has been a significant increase in cumulative MEV rewards on Ethereum in 2021.

Flashbots, a company that provides solutions to potential harms of MEV, claims that MEV will significantly boost validator rewards up to 60%. Block producers are expected to continue to execute MEV opportunities in the future as they can earn additional income through it. However, since 80% of all blocks are already using MEV solutions, it is unlikely that the size of the MEV market will increase rapidly, and it is expected that MEV profits will increase or decrease depending on the activity of the Ethereum network.

Flashbots make up the majority of the MEV-boost activity, followed by Flashbots, BloXroute, and Blocknative. As of writing, Flashbots accounts for 54.4% of the overall block production and 61.8% of MEV-boost block production. The numbers indicate that many of the Ethereum block proposed as of present used Flashbots’ MEV-boost. By censoring transactions, Flashbots complies with the Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) sanctions, and many have raised concerns over such censorship and the potential risk of undermining censorship resistance. According to MEVwatch.info (as of Dec 20, 2022), 66% of all Ethereum blocks comply with OFAC sanctions. Flashbots appears to be complying with OFAC sanctions by censoring transactions associated with Tornato Cash. To mitigate MEV-driven validation centralization risk, the Ethereum Foundation has designed Proposer/Builder Separation (PBS), where block construction and block proposing are assigned to different roles, allowing everyone to validate regardless of their ability (less computing power or resources) to capture MEV.

Today, nearly all of the current MEV activity is Priority Gas Auction (PGA)-style and less than 10% of block producers extract MEV themselves. However, a small portion of the hash rate has been observed exploiting MEV themselves, revenue-sharing with traders, and selling access to private memory pools. As network activity increases, more block producers will participate in the MEV competition.
3-7. DAO, A New Structure to Keep Governance Decentralized
Decentralized Autonomous Organization, or DAO, seemed to garner the industry’s attention towards the end of 2021 amid the growing P2E market, but the price of almost all P2E games fell in 2022 as the bear market crisis hit the blockchain gaming industry hard. 2023 is expected to be the year of DAO centered on P2E with the introduction of more sophisticated forms of DAO backed by significant advancement in software and tools in various sectors.
P2E DAO: Fostering Sustainability and Community-Building
Approximately 30,000 YGG quarterly scholarship players were registered in the first quarter, growing nearly three times compared to the previous quarter. YGG still had 20,000 scholarship players in 3Q and recorded only -30% from its peak, which is considered a sound performance during the crypto bear market.

In addition, Merit Circle and GuildFi are also maintaining their value as game DAOs through continuous business expansion and partnerships. In particular, Merit Circle is taking the lead in the business model research on gaming guilds through active governance and working hard to build a durable game DAO in the crypto market. Given that both projects remain at a similar level in terms of AUM, DAOs will serve as an important infrastructure to secure the sustainability of the project from a P2E perspective.

DAOs are Becoming the Structure of Choice for DeFi and Web2 Organizations
1) SubDAO
number of SubDAOs skyrocketed at the end of 2022, and projects are expected to continue to take advantage of the new system in 2023. In Jan 2022, Bankless defined subDAOs as a way for a superDAO to localize an experiment with sufficient autonomy while keeping them aligned with the super DAO. P2E gamers have been actively forming subDAOs since the introduction of its concept, and some of the most popular DeFi solutions have been introducing more sophisticatedly designed subDAOs to operate more efficiently.
- MakerDAO’s Endgame v3: MakerDAO’s Endgame proposal focuses on creating MetaDAOs to ensure decentralization and stability. In Oct 2022, the community voted in support of the proposal, and this move will diversify MakerDAO’s stablecoin DAI reserves.
- dYdX DAO roadmap: In Nov 2022, prior to releasing the mainnet V4, the dYdX Foundation shared with the community the short-term roadmap for the dYdX DAO. The roadmap was proposed for the dYdX community to discuss and support the introduction of subDAOs. The proposal will be voted for on-chain to provide $DYDX as financial resources for each subDAO. dYdX intends to empower the community to launch additional subDAOs in the future for treasury and other areas.
Although the views of the two projects on subDAOs are different, it is worth noting that they have proposed their respective answers to ways to increase efficiency while maintaining a decentralized form of operation amid the growing size of each project. In MakerDAO's Endgame plan, the protocol proposed to split the DAO into subDAOs, each with its own governance token, which would enable MakerDAO to achieve maximal growth at the risk of price instability. Against this backdrop, the DeFi protocols' search for the ideal subDAO will continue in 2023.
2) Tools
Meanwhile, DAOs are becoming the structure of consideration for many traditional Web2 companies – in this context, lowering the entry barrier for mass DAO adoption has become critical. There are several DAO tools built to address needs within the DAO ecosystem.

Let's take a look at some of the representative DAO tools.
- Aragon: Aragon provides a full end-to-end framework to build DAOs. Its governance model supports tools for on-chain/off-chain decision-making, tokenomics, dispute resolution, voting, and governance on a chosen blockchain. Aragon is an easy-to-use open-source software used to maintain and create DAOs.
- Gnosis Safe: Gnosis Safe is a smart contract wallet that allows users to store, manage, and transfer digital assets and tokens on Ethereum. It is a multisig wallet that guarantees asset security. DAO organizations can easily manage private keys through Gnosis Safe.
- Snapshot: Snapshot is a decentralized voting system. Snapshot supports various voting types to cater to the needs of DAOs. Creating proposals and voting on Snapshot is free as the process is performed off-chain. Voting power can be calculated with ERC20s, NFTs, and others.
- Commonwealth: Commonwealth is an all-in-one governance platform for on-chain communities to make proposals, discuss, Snapshot, on-chain voting, and network analysis.
- Tally: Tally is a platform that builds governance infrastructure for Ethereum-based DAOs. The platform offers governance tools and services, including spending and correcting budgets.
- Pol.is: Pol.is is a real-time system for gathering and analyzing data. It is an open-source software using an algorithm designed to analyze participants' opinions and interests and visualize the group dynamics. It is a helpful tool for communities to better understand each other.
4. Blockchain Content Never Ceases to Evolve
Despite the macroeconomic headwinds, content available on the blockchain has constantly pushed its boundaries along with the advancements introduced in the blockchain infrastructure. In particular, most notable use cases were found in gaming, DeFi, and NFT segments with NFT being at the forefront in the quest for mass adoption. Web3 social media platforms, e.g., Lens Protocol, Mirror, and Minds, also have potential to grow into a bigger market, but will likely take some time before they are finally able to replace existing social networking services. On a more positive note though, there has been an increased interest in Web3 social media since Elon Musk banned links promoting other platforms, including Facebook, Instagram, Mastodon, and linktre.ee, on Twitter.
4-1. Despite the Brimming Potential, Anticipation Should Be Kept Low Key at Least Until the End of Next Year
Given the hype about the blockchain games, it may not be an overstatement to say that the first half of 2022 was the year of metaverse and P2E. The craze has calmed down before long though as the public who looked for a Ready-Player-One like future were disillusioned, and P2E games like Axie Infinity and Mir4 began to suffer structural limitations. The short-lived Axie Infinity’s glory, however, inspired many mid-to-large game companies to tap their strength and IP resources to jump start blockchain game development. Web3 game companies, regardless of the market environment, keep pushing ahead with gaming initiatives with enough runways. Although lower than 4Q21, the blockchain gaming & metaverse sector raised $7B up until 3Q this year, representing more than 50% in the entire crypto market. This apparently indicates that the institutional interest in the sector is holding up strong.

So yes, the potential of this market is obvious: blockchain technology is widely applicable in games, high quality games will soon be released, and there is even a steady stream of investments. Yet, it seems prudent to keep our reaction low key and take a more conservative approach at least until the end of next year. Not to mention the blockchain gaming market is an uncharted wilderness that came into the spotlight only less than 2 years ago (development of an AAA level game takes 24-36 months), the games have not been able to strike a balance to satisfy all key stakeholders in this business—investors, gamers, and developers—since the fall of P2E games. Given a seemingly endless testing and market’s judgement that always precede a successful game, the blockchain gaming market needs time to bloom.
A. Overseas: Web3-Native Game Companies Leading the Market
Global game companies, such as Activision Blizzard, Sony, and Nintendo, are taking a conservative approach to blockchain games. Valve (Steam), Rockstar (GTA), and Mojang (Minecraft) even made it official that they would not apply blockchain. At least more favorable than the rest is Epic Games. It allowed blockchain games to be onboarded to Epic Games Store (Blankos Block Party, Grit, and Star Atlas to be supported). Unlike South Korean game companies, there are primarily two reasons overseas game companies stick to a conservative approach to blockchain adoption:
- Dominance of Single Player Console Games: Unlike the Asian market, where mobile and PC games rule, a significant portion of the North American market is occupied by console games—with it being 49% in the region in 2021. Driven by the inherent characteristics of tokenomics and NFTs, blockchain is hardwired to thrive in MMORPG type games where users interact with each other to form a social economy (Please check ArcheWorld’s Off to a Strong Start for more information). Console games, on the other hand, are predominantly played by single players, and a multiplayer mode often comes as an additional option.

- A Small Market: The share of blockchain games in the gaming market is miniscule. There are only less than 900 blockchain games available, and even the MAU of the top-performing blockchain game, Alien Worlds, amounts to a meager 0.4% of that of League of Legends. Yet, their revenues stand in an even more stark contrast. Put more simply, the current market size of blockchain games is not appealing enough to grab the attention of global gaming giants devouring billions in revenue. Indeed, Blizzard would find little or no incentive to introduce blockchain games when it is raking in $8.8B in revenue as of 2021. Despite the long road ahead, it is still positive that ownership and ownership distribution, the notions that lie at the core of blockchain games, have become more popularized.

In this sense, at least for the near to mid term, Web3 game companies will stay at the helm of the markets overseas. Not until Web3 companies proves the potential of blockchain games with world’s top selling records and becomes a force to be reckoned with in the market, would such established game companies be willing to take up the gauntlet.
Despite the lack of powerful IPs and track records, we do see potential of a breakout title in Web3 games that could even be as wildly successful as traditional mega-hit games. To start with, overseas Web3 game companies are in no way financially stretched. Given that blockchain projects, such as Forte, Sorare, Animoca, and Immutable, have raised $150M-$900M in investments, they will be able to comfortably cover the cost of developing an AA- to AAA-rated titles, which usually require $100M-$300M. For reference, the estimated costs of a few most typical examples of AAA-rated games are: Final Fantasy VII Remake ($80M), GTA V ($265M), Star Wars: Old Republic ($200M), and Destiny ($500M, marketing expenses included)

Another growth engine for Web3 game companies is their developers who previously worked for big game companies. Aurory, Solana’s blockchain game development unit, for instance, has around 60 developers who are former members of top-tier game companies, such as Ubisoft, EA, and Atari. As a result, the quality of Web3-native games has gone through a sea change, rivaling that of traditional games. Indeed, gameplay videos on YouTube, including Treeverse, Aurory, Iluvium, Ember Sword, Guild of Guardians, and Star Atlas, speak to the quality and edge of the games.
B. South Korean Game Companies Showing Strong Potential Among Traditional Web2 Companies
Unlike game companies in other countries, South Korean game companies like Nexon, Netmarble, Kakao Games, Com2uS, Wemade, and Neowiz are actively developing blockchain games. We consider there are two main reasons: i) MMORPG is prevalent in the gaming market in South Korea, where users get to build social economies and organic ecosystems and ii) WEMIX’s resounding success showcased how a blockchain game can pave the way for global presence. Although the uptrend has let up significantly, Mir4’s MAU hit 6.2M in 4Q21 and concurrent player counts surpassed 1.4M in Nov 2021, evidencing that a blockchain game can translate into a money-making business.

Traditional game companies have an edge over Web3 game companies in terms of game IP, development knowhow, and user pool. South Korea’s top-performing game company, Nexon, has announced its plan to roll out a blockchain version of one of its biggest IPs, MapleStory. With such a massively popular game played by more than 20M users for almost 20 years, the release is expected to significantly contribute to the expansion of the blockchain market. In some sense, the company is also taking a cautious approach, limiting NFTs and blockchain technology to certain items and features.

C. Asian Market Brimming with Potential
Being the largest and fastest-growing market, Asia’s gaming market holds promise. The number of users takes up 55% of all the gamers around the world, exceeding 1.7B, and 52% of the revenue comes from this region with the yearly figure hovering around as high as $72B. Looking at the pace of growth of Asia’s GDP per capita, the purchasing power of an individual will likely grow higher, taking over an even greater share of the market.

It is worth noticing that Southeast Asian countries were the earliest adopters of P2E games. The P2E boom in this region can be explained by its average income relatively lower than other regions. Although no longer so, Axie Infinity users’ monthly average earnings reached around $200 at the beginning of 2022. The amount is equivalent to 66% of the average monthly wage of the workers in the Philippines and Vietnam. This implies the possibility of an explosive growth of profit-sharing, income-generating blockchain games in lower-income countries in Asia.

D. Casual Games Deserve Attention
Casual game is a game genre where, typically, sessions are short and controls are simple. While the best known examples of casual games are Candy Crush and Anipang, and the Hero Blaze: Three Kingdoms, an unexpected driving force behind the P2E boom in 2021 in South Korea, is also a casual RPG game. As the specs required for casual games are relatively low, they are a better fit for blockchain technology, especially at this stage of facilitation. Considering the level of scalability of L1s and L2s, onboarding an AAA-rated MMORPG with tens of millions of concurrent players on a public blockchain may not be a viable option at this point and should really be preceded by advancements in blockchain technology.

The fact that in-app ads are a major source of revenue for casual games is another befitting attribute for the combo. In-app ads appear when an app is launched or during the game in the forms of a banner at the top or bottom of an app. Unlike RPGs that induce users to spend heavily on the game, casual games try to attract as many people as they could to have them exposed to ads and collect fees from advertisers. In other words, the more the game played, the greater the revenue from ads. The combination of in-app ads and blockchain games that are quick to build a significant userbase early on can have more synergy than expected, as has already been illustrated by Axie Infinity, Hero Blaze: Three Kingdoms, and Mir Global.

E. The Prerequisite for Metaverse: Hardware Development
One thing’s for sure about metaverse: the age of metaverse may not come as soon as expected. Some may think of the movie Ready Player One as what the world of metaverse would look like in the future. We think of metaverse as a world where we i) dwell longer in a digital world than reality, ii) consider our digital identities as valuable as IDs, and iii) perform social, economic, and cultural activities just like we have done in reality.
WAX co-founder William Quigley once pointed out that we were in no way near a true metaverse, for which investment in hardware to create a life-like, immersive environment, such as AR/VR, next gen semiconductors, and hologram, should come first. He argued that most investment entities, including VCs, had placed their investments in software companies in pursuit of high ROI, and as a result, hardware had been somewhat left out of technological advancements. The Sandbox COO Sebastien Borget also said that the way web apps were running games clearly had limitations and restrictions. Indeed, many lamented the quality of the Horizon Worlds since it was launched by no other than Meta, which proclaimed to invest more than $10B in metaverse.

Moving forward, the hardware sector—particularly the areas of 5G, IoT, next gen semiconductor, AR/VR lens, quantum computing, and neuroprosthetics—is expected to attract a lot of investment in the coming years, making the progress metaverse needs. Only then may we be able to shape the true metaverse we dream of into reality.

F. Overvalued First-Gen Blockchain Games Need to Prove Their Value
The Sandbox and Decentraland are the leading examples of first generation blockchain games and metaverses that saw the hype outrunning the reality. We consider that the tokens are still overpriced even with a sharp decline in their prices (-85% YTD) throughout this year. The valuation per user of The Sandbox and Decentraland is 49x and 138x higher than its peer, Roblox. The multiples grow even higher when the results are converted into FDV, shooting up to 94x and 486x. Even if the differences between Web2 and Web3 game business models are considered, it is hard to find the rationale for The Sandbox’s TTM PSR of 20.7 (based on FDV) given Roblox’s PSR of 8.6.
The key to improving their fundamentals and justifying their valuations is a larger reservoir of content and user base. For this reason, it remains to be seen if The Sandbox pulls off quality content with its partners in 2023 and afterwards, if it manages to rev up UGC (User Generated Content) once the official version is released.

4-2. DeFi: Locking the Barn and Finding the Next Meta
In 2022, DeFi was hit hardest by volatility. Aside from the obvious fact that the liquidity contraction resulted in a widespread correction in the assets market, DeFi is trailing Bitcoin primarily because of its weak fundamentals, such as i) lack of infrastructure, ii) excessive leverage, and iii) absence of risk control.

While the realization of limitations of DeFi is prompting many players to withdraw their money from the space, institutional investors’ divestment is particularly conspicuous. The OECD found that the amount of incoming institutional investment has been on the wane since Jun 2021. In the wake of a series of collapses surrounding UST, Celsius, and FTX, many institutional investors seem to have already withdrawn a significant portion of their investment. This is evidenced by institutional trading and OTC brokerage service provider Genesis’ OTC trades that are obviously drying out fast, down 53% YoY in Q3 2022. This crypto winter that has come may surely be unprecedented.

Ironically, though, a market void of excessive liquidity largely driven by institutional investors that have spearheaded the bull market since 2021 signals the need to focus on the essence of DeFi. Ethereum Founder Vitalik Buterin recently commented that DeFi “started off honorable but turned into somewhat of an overcapitalized monster that relied on unsustainable forms of yield farming, and is now in the early stages of setting down into a stable medium, improving security and refocusing on a few applications that are particularly valuable.”
In this sense, 2023 will be the year DeFi projects that focus on the traits and merits that constitute the core of decentralized finance will warrant attention. Already, projects that have highly sophisticated smart contract structure and offer both high level of decentralization and stability are increasingly gaining traction in the market. In the following section, we will take a deeper dive into i) stablecoins featuring a new structure, ii) non-custodial perpetual futures exchange, iii) liquid staking, and iv) uncollateralized lending.

A. Renewing Programmable Money: Stablecoin 3.0
Once regarded as a reliable tool to store value and provide collateral, stablecoins had been one of the key pillars of the DeFi infrastructure. Since the collapse of UST, however, the confidence in the stability of unsecured stablecoins has crumbled, and only the centralized IOU stablecoins backed by treasury bonds have survived.

In the aftermath of the unraveling, stablecoins have made new attempts, introducing more sophisticated programming to achieve decentralization. Notably, one of the most prominent examples that have come into the spotlight include 1) $GHO (Aave, $AAVE) and 2) $crvUSD (Curve, $CRV). Stablecoin models the projects are set to launch will not only introduce new mechanisms, e.g., decentralizing and diversifying issuing/burning entities and applying a phased liquidation process, but also have significant utility attributes to ensure greater utility and stability than the existing models.

$GHO: Using Multiple Facilitators Distributed Across the Network
The major differences are pegging mechanism and utility. $GHO have entities called facilitators responsible for minting and burning. Because separate facilitators are distributed across the network, $GHO is expected to prevent the UST-LUNA type of loophole caused by a centralized entity controlling both minting and burning.

$crvUSD: Introducing Automatic Partial Liquidation
$crvUSD, on the other hand, is the result of repetitive research on reducing the impact of liquidation. Its stablecoin model is called LLAMMA(Lending-Liquidating AMM). The notion that sets it apart from others is an automatic liquidation that takes place in phases during the minting and burning processes. The mechanism not only allows stablecoin users to disperse depeg or liquidation risks by diversifying positions into different bands, but can also alleviate the fallout of a rapid decline that has been crippling for DeFi platforms as it liquidates assets in phases.

The difference between the two stablecoins does not stop at structure: $GHO and $crvUSD are expected to build different use cases. While $GHO is likely to tout wider utility given the variety of utility options Aave and each facilitator can offer, $crvUSD will likely set itself apart with stable pegging mechanisms backed by Curve’s stable CFMM liquidity pool**.** $GHO and $crvUSD came at a time when few seemed willing to openly discuss “stablecoin” after UST’s depegging. Now eyes are on the two ambitious stablecoin models of prominent projects to see if they manage to win the top spots, standing side by side with $DAI and $FRAX.
B. Trustlessness and Transparency: Perp DEXs and Unsecured Lending Protocols
The liquidity crunch that sent 3AC and Celsius bankrupt was largely driven by the abuse of the stETH/ETH AAVE flywheel strategy that apparently leveraged Lido’s liquid token, stETH.

Even if completely eradicating the risk of excessive leverage stemming from DeFi’s composability may be difficult, protocols focusing on managing and preventing such risks to enable greater transparency and trustlessness deserve our attention.
One of the solutions among the most typical DeFi services would be non-custodial exchange services while perpetual futures trading on DEXs, in particular, is expected to rise.

As for DeFi lending protocols, unsecured loan providers are increasingly gaining attention. The notion has come into the spotlight as a solution to the limitations in the prevalent overcollateralization practice in the DeFi lending market. The biggest advantage is enhanced transparency as all data related to the loans will be recorded on the chain.

vAMM DEX & GMX Using Oracle
Among the various types of perpetual DEXs (e.g., oracle-based VAMMs, order-book DEXs with rollups), a rapid growth of oracle-backed perpetual trading services is particularly visible. The leading examples are projects like GMX and GNS: they apply a price discovery mechanism using Virtual AMM (vAMM) and Chainlink ($LINK) oracle. Trades are executed based on oracle prices instead of liquidity-based atomic swaps. This allows them to lower the fees and prevent slippage

As opposed to the merits such as smoother onboarding and bootstrapping, there are shortcomings in oracle pricing. Though one of the most alarming examples was the GMX exploit where the attacker, allegedly a whale, manipulated the price oracle of $AVAX, the exchange swiftly took appropriate action to fix the problem. If GMX pulls off the task of maintaining both the advantage of being a non-custodial exchange and the risk management competency of its members, the project can leverage trustlessness and transparency to turn itself into one of the key drivers of DeFi’s growth in 2023.

DYDX, the Orderbook-Based Perpetual Futures DEX
If we are to discuss the most successful futures DEXs, dYdX can never be left out of the list. At its peak, dYdX’s user-friendly UX/UI, orderbook-based price discovery mechanism, and StarkEX-powered excellent scalability as high as 9,000 TPS earned it $1.1B worth of daily trading volume (Sep 28, 2021) and $6.8M of daily transaction fees, turning this non-custodial exchange into a poster child of the top-performing futures DEX. Although the trading volume has consistently been on the wane since liquidity began to dry up, an increase in demand for perpetual contracts and decentralized exchanges after the FTX/Alameda scandal pushed up the daily trading volume to $528M as of Nov 14, 2022 and the monthly trading volume to $27B for the month, demonstrating its prowess.

dYdX will migrate to standalone appchains using Cosmos SDK (Check this Xangle report for more details: The Past, Present, and Future of dYdX: Will Tokenomics Sway the Rise and Fall of dYdX?). Slated for 2Q 2023, the migration is expected to contribute to tokenomics improvement, service decentralization, and reduced regulatory risk.

As we watch the developments unfolding in this space, e.g., 1) oracle pricing models of GMX and GNS and 2) strong performance numbers, roadmap, and appchain migration of dYdX, perpetual futures DEXs’ narrative may not simply be a short-lived phenomenon after the FTX bank run. Besides GMX, GNS, and dYdX, various attempts aimed at solving transparency and centralization issues, such as Drift, Perpetual, and Cap, are increasingly popular, backing the trend to continue.
Maple Finance, the Largest Unsecured Lending Protocol
Maple Finance is a DeFi protocol that holds the largest market share in the unsecured lending market. Unlike Aave and Compound, it provides loans without collateral.

The goals it seeks to achieve with providing loans based on creditworthiness are liquidity expansion and higher capital efficiency. Most of all, Maple’s lending process is done on-chain, allowing for greater transparency and efficiency. After a borrower requests a loan, a designated loan pool approves transfer of funds, and the loan details, including information about the pool, loan balance, and interest paid, are recorded on the chain and transparently disclosed.
Although the absence of available details about Maple’s loan origination process (e.g., ID verification and due diligence) is concerning, the track records say otherwise. Of the 198 loans provided so far, 159 loans have been repaid with only 1 in default (a $10M loan to Babel Finance related to the Terra-Luna crash). What is also positive is that the project is ramping up risk management and credit analysis, publishing monthly business reports about liquidity pool and mandating user’s subscription to credit risk data platform Credora.
Unsecured loans like the products of Maple Finance are a double-edged sword. While such loans can facilitate credit expansion and capital efficiency by providing liquidity, imprudent lending and structured derivatives can cripple the entire lending market. Nonetheless, DeFi’s unsecured lending protocols are needed as part of the solution to CeFi’s single point of failure—which is the lack of transparency in the lending process, including sources of financing—and capital inefficiency and limited credit expansion of existing DeFi loan products. A rise in institutional demand and use will give a spur to the DeFi lending market. Currently, unsecured loans represent a single-digit percentage in the DeFi lending market, but the upside potential looks strong enough.
C. Decentralization: Liquid Staking
Growing Attention to Liquid Staking Since Ethereum PoS Transition
The FTX/Alameda crisis is a poignant example of the consequences an opaque and centralized operation can bring. As the risks associated with centralization can also arise from PoS blockchains, post-Merge Ethereum may face the same issues. As such, the importance of ETH staking as a representation of voting power and the level of decentralization of the network is rising. Moving forward, liquid staking services are expected to gain significant traction.
Decentralization & Rocket Pool

Launched in Sep 2021, Rocket Pool is a liquid staking platform that has lowered the bar for ETH staking not just for Ethereum stakers but for validator nodes as well. While nodes of most liquid staking services are given permission for operation, running nodes on Rocket Pool does not require permission and anyone with 16 ETH and RPL tokens are allowed to participate. A lower barrier to becoming a validator node can translate into a larger number of validator nodes, and this in turn can increase the level of decentralization of existing liquid staking and Ethereum network’s security.
Communities Seemingly Favorable to the Value of Decentralization

Interestingly, quite a few seem to agree with the idea. The post-Merge change in the amount of ETH staked was 45.7%, the sharpest increase compared to cbETH (41.5%) and Lido (10%). Further, in pursuit of greater decentralization, the 16 ETH requirement for node operation will soon be lowered to 8 ETH and then to as low as 4 ETH in the long run. This may boost demand for $RPL, which is considered key to both node operation and decentralization.
Lido, Too, Is Seeking Improvement

Lido, which has long been predominantly the no.1 Ethereum staking platform even before the Merge (representing 29.3% of Ethereum staked), appears to be going with the flow, adding decentralization features. A case in point is the dual governance model that leverages stETH, a token that represents an equivalent amount of ETH staked in Lido. Lido will start allowing stETH holders to have the right to veto governance proposals. Although the efforts have not exactly increased the size of the permissioned pool, Lido’s intention behind empowering LDO and liquid token holders seems to be focused on solving potential causes of concern—censorship and centralization. We will stay on the lookout for the values that Lido and Rocket Pool will create with decentralization and set them apart with from CEX’s centralized and unclear staking services.
D. Additional Momentum from TradFi’s Growing Adoption
As the fallout of the FTX fiasco and jitters about the legitimacy of Binance’s PoR ripples through the entire crypto industry, the uncertainty over centralized trusted entities is at its height. This could mean an opportunity for some—which are traditional financial institutions in this case. Once their adoption starts to accelerate, TradFi companies that have systems in place will likely lead the reorganization of the DeFi industry, expediting DeFi’s growth.
TradiFi’s Crypto Adoption Has Already Begun

Already, many of the world’s leading IBs have initiated cryptocurrency projects in 2022 and are making meaningful attempts in the DeFi ecosystem.
Recently, as part of a pilot program led by the central bank of Singapore, JP Morgan successfully executed foreign exchange and government bond trades against liquidity pools comprising Singapore government bonds, the Singapore Dollar, Japanese government bonds, and the Japanese Yen. Also, Singapore's largest bank DBS has become the first bank in Asia after Goldman Sachs and BNP Paribas to join Onyx, JP Morgan’s blockchain-based fixed-income trading network. Meanwhile, stablecoin issuer MakerDAO approved a proposal to collateralize a DAI loan with Huntington Valley Bank’s real-world assets. Apparently, global investment banks are attempting to connect real-world assets to the DeFi ecosystem and are leveraging blockchain to improve financial infrastructure and expand the range of products. (See The State of South Korea's Web3: Finance for more information).
4-3. Web 2.0 Companies Spearheading NFT Adoption
The NFT bubble has burst, after a peak in early 2022. The NFT trading volume has nosedived by more than 90% year-to-date while the NFT market cap, which used to hover around $40B, has plunged to $20B. The number of NFT buyers and sellers on a daily basis started this year with 40,000 but is slashed to below 20,000. Numerous NFT projects have lost steam and the falling prices of L1 coins like $ETH and $SOL more than halved the values of leading NFT projects. The sweeping downtrend has crushed the trading volume of the BAYC collection as well, which used to sit at around $420K based on FP (Floor Price—bringing it down by 79% to $85K in just half a year.

In the long run, however, NFT’s outlook remains promising. This time, the market is expected to take a slightly different path. Departing from the past trend where PFP projects used to be the most prevalent in the market, use cases of NFTs are expected to become more diverse from 2023. Apart from IP business like BAYC, NFTs will keep gaining ground in areas such as gaming, fashion, e-commerce, social, ticket, and ID verification (DID and Soulbound token). This is because, unlike fungible tokens, NFT’s true potential is unlocked only when it meets art, culture, and entertainment.

A. NFT-Gated Services for VIP Customers
Before the arrival of NFTs, Web2 companies could not figure out how to make use of the blockchain technology. Blockchain was in such a nascent state, and the values it promises to companies were vague. In this digital world where data can be replicated endlessly, the advent of NFTs has allowed users to claim and prove ownership of data just by connecting their wallets—and hence without procedural hassles. For companies, this signified a business opportunity in the blockchain market, which is NFT-gated service.
NFT-gated service is a service offered exclusively to specific NFT holders. It is applicable to a wide range of industries, such as fashion, merchandise, gaming, music and entertainment. For companies, an NFT holder means a potential customer of an NFT-gated service, which they could leverage to enhance branding, corporate value, and customer service. Yuga Labs’ BAYC is an iconic example of a successful NFT-gated service. The OG utility NFT showered its holders with exclusive benefits, including airdrops, merchandise, and IRL parties, maximizing customer loyalty as well as brand value. In just a year, BAYC eventually earned Yuga Labs a valuation of $4B from VCs like a16z and Animoca, placing the company’s worth on par with Supreme’s. Put another way, BAYC showcased what best fits NFTs.

In 2023, the NFT-gated service market is expected to see an explosive growth. Web2 companies have witnessed the successes of so many Web3 brands, including BAYC, Doodles, and Azuki. But even more noteworthy is the fact that global e-commerce platform Shopify added NFT-gated features in Jun 2022, reflecting customers’ strong demand for such options. Shopify is an e-commerce solution company offering a full suite of services for anyone looking to start an online shopping mall—ranging from website setup, inventory management, payment, delivery, marketing to data analysis. Most of their customers are small retailers, self-employed businesses, and SMEs. Shopify currently provides service to more than 4M businesses in 175 countries, posting a revenue of $5.2B (TTM) in 2022. The launch of NFT gating of a giant e-commerce enabler is expected to bring about a substantial increase in NFT use cases in the retail market.
Further, NFTs remove the hassles involved in brand collaboration. The existing gating that requires users to subscribe and log in to each website complicates collaboration. If brand A wishes to offer limited edition merchandise to the fans of brand B at a discounted price, it is difficult for brand A to figure out who the fans are. This is because brand A and B have separate membership DBs, and even if it is possible, the process of identification will be complex and time-consuming. This is where NFT comes in handy. For brand A, all it needs to do is to ask users to connect their wallets so it can verify if the users actually have brand B NFTs in their wallets. As such, starting this year, we expect to see a flood of collaborations leveraging NFTs.
B. Web2 Companies’ Entry Signaling the Dawn of Mass Adoption
While the 1st and 2nd generation PFP projects, i.e., CryptoPunks, BAYC, and Doodles, let the world know the existence of NFTs, mass adoption of NFTs will likely be led by global Web2 companies. As mentioned earlier, a lot of global Web2 companies have already entered the NFT market, citing various reasons, e.g., NFT-gating, new business, and marketing. Meta is prepping a service that allows users to easily mint and sell NFTs on Instagram; YouTube is set to unveil new creator tools to mint and sell video NFTs; and Nike went on to launch Web3 marketplace platform .Swoosh, following the rollout of PFP (Clone X) and virtual shoes (Cryptokicks). Collectible avatars have won Reddit more than 3M users and recently, Starbucks’ Odyssey Beta has gone live.

Having hundreds of millions or even billions of customers worldwide, the ripple effects of a global Web2 giant is so enormous that it is hardly comparable to that of PFP projects. The number of users who either bought or sold an NFT was estimated at 1.17M as of 3Q22. This stands in stark contrast to Facebook, amounting to a mere 4% of the MAU of the social media giant. Conversely, though, this also heralds a possibility where Web2 companies may drive an explosive growth of the NFT market.
Some of them are already reporting stellar results. The most prominent examples include Nike, Dolce & Gabbana, Tiffany, Gucci, and Adidas. Nike, in particular, generated $185M from 10+ NFT collections, including Clone X (PFP), MNLTH (shoes), Mint Vial (utility), and Cryptokicks (shoes)—with $93M from primary sales, $92.7M from royalties. In a way, a string of such successes is attesting to the profitability of NFTs to Web2 companies.

One area that is increasingly emerging as a noteworthy trend in the NFT market and attracting Web2 brands’ particular attention is “Phygital Goods.” The term “Phygital” is a synthesis of the words “physical” and “digital” that indicates an NFT that links a digital asset to a real-world asset. Nike’s CloneX Forging SZN1 collection that has recently closed the sale with a handsome revenue is a prime example of phygital goods. Nike sold 51,932 pieces of merchandise to 5,535 customers, raising $11.63M in revenue ($11.34M from primary sales and $287K from royalties).

Azuki is another project that is showing interesting attempts. In Oct 2022, it introduced Physical Backed Token (PBT), for which a chip is attached to a physical item to allow users to “scan-to-own” the item and enable an on-chain ownership verification. Azuki launched Golden Skateboard and Azuki X Ambush hoodie PBTs and raised more than $2.5M in revenue.
Meanwhile, the entry of Web2 companies into the NFT market may trigger a spike in M&A deals. For those companies with ample capital, there are few better ways than M&As to flexibly adapt to new technologies and market trends as well as increase profitability and get rid of competitors. As if to back this up, Yuga Labs, widely viewed as a leader in this space, acquired CryptoPunks and Meebits IP in Mar and WENEW and its 10KTF NFT collection in Nov, 2022.
C. NFT Finance Is Set to Bloom
Based on notional values, the global derivatives market is multiple times larger than the spot market. There is a myriad of derivatives, including forwards, futures, option swaps, and many more, not to mention the massive volume of transactions. This is because derivatives play a crucial role in the capital market, allowing participants to manage risk and tap leverage opportunities while providing liquidity to the market.

Starting this year, we expect an explosive growth of NFT financialization. Being less liquid than fungible tokens, NFT financialization may serve as a game changer for the growth of the NFT market.
The fastest growing areas in the NFT finance include lending, NFT fractionalization, and rental, while releases of other types of services, e.g., BNPL (Buy Now Pay Later), pricing, and appraisal, also continue.

Particularly noticeable among them are lending protocols like NFTfi, bendDAO, and jpeg’d. The cumulative NFT lending volume hit $530M as of Nov 29, 2022, up 1,350% YoY. The cumulative number of users has shot up 881% YoY to 27,000.

Notably, NFTfi (56.8%) and BendDAO (32%) are taking up 88% of the NFT lending market, and the models of NFTfi (peer-to-peer) and BendDAO (peer-to-pool) are becoming the standard in the NFT lending industry.

D. PFP’s Future Growth Strategy: OSMU, Utility Token, and IP Pipeline
Pokémon, the world’s largest IP, earned Nintendo $92B in cumulative revenue while Disney raked in $145B with Winnie the Pooh ($75B) and Mickey Mouse ($70B) alone. As of 2022, the estimated size of the global brand licensing market is tallied at $275B, and given the dominant share of PFP projects in the market, PFP still looks promising. The CAGR of the NFT market is estimated at 34.2% according to Emergen Research, a research and consulting firm focusing on the upcoming emerging industries. This implies that it is expected to grow from $20.9B in 2022 to $89.1B in 2027.

PFP projects like BAYC, Doodles, and Azuki aspire to become a global IP company. We speculate that the three overarching strategies of the top-performing PFP projects will be: 1) OSMU (One Source Multi Use), 2) native utility token, and 3) IP pipeline.
OSMU
OSMU stands for One Source Multi Use. It refers to a strategy that looks to maximize added value by leveraging an IP asset to produce various types of content, including movie, music, game, and animation (Please check Can Bluechip PFPs Become the Next Walt Disney? for more details). One of the companies best known for OSMU is the Walt Disney Company. Below is the “Synergy Map” Walt Disney sketched on a napkin in 1957. It gives a one-glace view of Disney’s core business strategies aimed at expanding the lines of business. It is a snapshot of how the company would bring its character assets to life and leverage them to enter various entertainment channels, such as Disneyland (theme park), merchandize, magazine, cartoons, music, to ultimately achieve that goal.

Another similarity PFP projects share with Disney is the pivot of their OSMU strategy—character IPs. Much like the way Disney has built and grown its Mickey Mouse IP primarily on the foundation of movies and media, PFP projects are entering the fashion, merchandise, movie, music, and animation markets to strengthen their brands. Just like what Disney has done for decades, PFP projects will keep seeking content diversification as their OSMU push continues to develop.
Releases of Native Utility Tokens
For 2023, we project that blue chip PFP projects like Yuga Labs ($APE), DeLabs ($DUST) as well as Azuki, Doodles, and Moonbirds will launch native tokens to bind together their multiple lines of content produced under the OSMU strategy. Once launched, tokens can open up possibilities for better opportunities of financing, enhanced governance, and own payment system. For instance, such tokens can provide a sense of belonging to the members of the communities who cannot buy the NFTs, or be distributed as grants to holders wishing to start a business.
Expanding Universe to Build Up IP Pipeline
Similarly to Marvel’s Cinematic Universe, PFP projects are expected to continue launching separate sets of NFT collections that come under an overarching universe. Despite the underlying universe that they share in common, such collections should be able to present uniquely different stories and roadmaps. It’s as though superheroes like Iron Man, Spider-Man, and Thor have different storylines but would join forces in the Avengers to fight off a common enemy. This strategy will likely secure them pipelines while keeping the value of their original collections unharmed. DeLabs, the team behind the two leading NFT collections on the Solana platform, DeGods and Y00ts, is said to have adopted the strategy. On the contrary, sub-collections, such as BAYC-MAYC and WoW-WoW Galaxy, tend to exhibit limited scalability and entail a risk of diluting the value—hence, at most 1 or 2 collections are considered appropriate.

E. Polygon Expected to Steal Spotlight in the NFT Market in 2023
Most likely, the rise of Polygon will be salient in 2023. Polygon’s market will likely center around various utility NFTs launched by Web2 companies, rather than PFP collections. As already mentioned, many global Web2 companies, including Nike, Starbucks, and Reddit, are running NFT projects on the Polygon network. Starting this year, Instagram will allow users to mint and sell NFTs on Polygon.

There are several attributes that have turned Polygon into one of Web2 companies’ favorite blockchain networks. Polygon 1) can absorb Ethereum’s ample liquidity, 2) have massive financial firepower and a lot of in-house developers to be able to provide all-round support for the companies, and 3) retain pipelines of various L2 solutions (e.g., PoS, ZKEVM, Nightfall, Miden, Zero, and Supernet) that can satisfy a wide array of needs. Meanwhile, NFT trading on Polygon that had taken a nosedive since the beginning of last year has picked up since Aug 2022, placing Polygon in the fourth position among blockchain networks based on trading volume (with a 0.6% market share).

Royalties Are Vital for Resurgence of NFT Market
On-chain payment of creator royalties is not yet available in the NFT market. ERC721 and ERC1155 standards, which have served as the foundation for NFTs on Ethereum, can track owners, approve, and transfer, but do not have codes that mandate collection or distribution of royalties. For this reason, leading NFT marketplaces have either 1) eliminated royalties (e.g., Magic Eden, Looksrare, X2Y2, Sudoswap) or 2) blacklisted zero-royalty marketplaces or NFTs listed on such marketplaces (e.g., Opensea, Immutable). Royalties are a key conduit to attract more creators and expand the NFT ecosystem. They are at the core of the strength of NFTs and a due reward to NFT creators. Yet, Opensea’s decision to stick to royalty enforcement presumably aimed at nipping competitors in the bud is clearly ill-advised.
Making improvements in the protocols, such as EIP-2981, is considered an ideal solution to royalty payment. Indeed, NFT communities have hailed such protocol-level improvements since 2H 2021, when NFT marketplaces started to move away from royalties. EIP-2981 is a token standard compliant with the ERC721 and ERC1155 interfaces, where NFT smart contract mandates fees to be paid to creators every time NFTs are bought or sold. EIP-2981 is easier to implement for NFT marketplaces as it also covers off-chain activities

Growing Adoption Changing Industry Terminology
As NFTs are increasingly adopted, the term “NFT” will very likely be replaced by easier-to-understand names. For non-crypto savvy customers, “Non-Fungible Token” is not immediately appealing or intuitive. Indeed, Nike, adidas, and Reddit have adopted “virtual creation,” “virtual gear,” and “digital collectible” to replace the term.
5. Inevitably Introduced, Regulations Will Support Mass Adoption in Long-Term
Governments and regulators are getting busy with the works under the undeniable grand cause calling for investor protection. The government-led crypto assets regulations are no longer avoidable. However, once a secure and stable system is established based on such regulations, investors will be able to use the blockchain services in a safe manner. Incorporating crypto assets into the regulatory fold would set off the flow toward the mass adoption of blockchains in the long run, fueling the blockchain industry to take another leap in its growth. The important thing in this regard is carefully looking through to see what kind of regulations would be introduced and what kind of impact and influence they would have on the blockchain ecosystem. Although most countries have yet to present definite regulations, we could explore the direction of the regulations with a focus on the European Union, the United States, and South Korea, which have relevant legislation proposed.
5-1. Introduction of Crypto Regulations Can No Longer Be Opposed
Initially, the blockchain ecosystem was built on the unique characteristic of “censorship resistance” that states “no entity can stop or restrict Bitcoin transactions.” Naturally, the ecosystem was mainly comprised of strong supporters of such an idea and responded with hostility whenever regulators made attempts to regulate crypto assets, or TradFi criticized the crypto scene. However, starting in 2022, we began to see some changes in the blockchain industry’s view on regulations, which used to be firmly based on humanism that value individual freedom. A series of incidences marked with greed and moral laxity, such as the LUNA, 3AC, and FTX debacles, destroyed the trust and confidence of the ecosystem overall, and eventually led the way for a call to self-examination and the need to introduce regulations.
A. EU – A Strong Regulation on Stablecoins Is a Given
MiCA, the First-Ever Regulatory Framework for Crypto Assets → a Cornerstone for Regulatory Introduction World-Wide
Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) is a regulatory framework in the works to be adopted for the first time in the world by the European Union (EU). The lawmakers tried to get comprehensive coverage of the agenda affecting the industry overall, including the categorization of crypto assets and authorization and supervision of crypto asset service providers (CASPs). If the vote in February 2023 passes the proposal, MiCA is scheduled to go into effect in 2024. It is a meaningful step as it signifies the end of a complex legislative system that differs by each EU country and the establishment of an EU-level regulation with a simplified process. Moreover, as it will be the first-ever legislation of its kind to be adopted and enforced, MiCA will also act as the cornerstone for crypto asset laws to be set up in other countries.

Crypto Assets to Be Regulated Differently by Type; Prohibition of Interest Payable to Potentially Impact Stablecoins and DeFi Negatively
MiCA divides crypto assets into security tokens, utility tokens, asset-referenced tokens (ARTs), and electronic money (e-money) tokens and applies varying regulations accordingly. At the core of the regulations are the asset-referenced tokens and e-money tokens, both of whose prices are pegged to certain “values.” (This regulation does not cover Bitcoin, NFTs, and central bank digital currencies (CBDC), and security tokens are regulated under EU’s Markets in Financial Instruments Directive and Regulation (MiFID/MiFIR).)
According to the definition above, stablecoins are highly likely to be placed in either ARTs or e-money tokens categories. Stablecoins are a major type of asset widely used across most of the crypto industry, such as DeFi, and enjoy a dominant sway over the crypto asset market. MiCA seeks to mitigate and control the potential risk of impact they may have over other values (currencies, in particular) by applying strong regulations on this asset group.
In particular, articles 36 and 45, “Prohibition of Interest” and “Prohibition of Interests,” prohibits the issuers and CASPs of the tokens mentioned above from providing any interest. This means that stablecoin holders will no longer be able to earn any interest (staking rewards) from depositing their stablecoins. One of the reasons stablecoins have enjoyed such high demand was the fact that the token holders could generate stable income from deposit interests based on their stable prices. However, if this regulation is enacted and interests can no longer be earned, the demand for stablecoins would drop, which would lead to weaker profitability and higher liquidity risk, potentially making huge damages to DeFi protocols.
Strict Rules to Be Applied on Crypto Asset Issuance and Operation

Since the crypto asset market today does not have any regulation on issuing tokens and drafting whitepapers, it is very difficult to secure and confirm the identity of the body operating the projects or the reliability of the whitepapers. However, MiCA is here to change all that. It seeks to resolve such issues by applying strict regulations on the matter. MiCA stipulates that any crypto asset projects whose whitepaper does not comply with the form set forth by the competent authorities shall not be able to obtain the approvals necessary for trading said assets. MiCA regulations on white papers are expected to filter out only the “genuine” projects from the vast sea of scam projects in the market. Furthermore, issuers of crypto assets will be strictly regulated by the competent authorities. The qualifications and obligations for each type of issuing body are stipulated in the proposal, ensuring some transparency to the investors who had no option but to depend on the goodness of the project owners’ hearts for information. However, the regulatory grip is tightly wound on the key target assets, ARTs, and e-money tokens, restricting the issuance of these tokens to those with authorization from the competent authorities and central banks. This is likely to raise some controversy as involving such a strong government control goes directly against the idea blockchain initially sought after: decentralization.
B. U.S. – Supervisory Authorities to Be Strengthened across the Market

While MiCA decides the future course of crypto asset regulations in Europe, it would be up to i) the Ripple lawsuit, and ii) the DCCPA legislation to steer the course, during which the turf war over who will take home the jurisdiction for crypto asset regulation is expected to continue between the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC).
SEC vs. Ripple Labs: The Suit to Define Security Tokens
2023 will be the year that we see the end of the over-two-year-long lawsuit between the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and Ripple Labs on whether Ripple (XRP) violated the Securities Act. The SEC has been claiming that they are able to determine whether a crypto asset should be classified as a security using the Howey Test, and pointing out that several crypto assets indeed fall under securities. SEC had named nine cryptocurrencies, including Amp (AMP) and Rally (RLY), as securities last July, and is conducting investigations into Yuga Labs, the issuer of BAYC NTFs. The lawsuit, which started with the SEC filing legal complaints against Ripple Labs for violation of the Securities Act in December 2020, is waiting for the final verdict expected to be delivered in March 2023, with both parties having submitted their closing arguments for the summary judgment.
We need to keep a close watch on how this plays out since there is a great chance that the outcome of this lawsuit is going to be the guiding rule for determining whether a crypto asset should be treated as a security going forward. Particularly important to note is how the court will rule on Ripple Labs’ argument that there is no investment contract, to begin with, since there is no contract, no Ripple issuer obligations, and no token holder rights. If the court were to side with the SEC, the interpretation of the law would be that de facto investment contracts do exist, even if they may not necessarily be written down on documents. In that case, the ruling would open up the possibility of treating crypto assets issued based on whitepapers as securities even without any specified contracts between the issuers and investors, which ties up a whole lot more of crypto assets to be subject to be judged whether they should be considered securities.
Faith of DeFi to Be Determined by DCCPA Legislation
The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) is currently working toward defining cryptocurrencies as commodities and claiming the supervisory authority over the market through the Digital Commodities Consumer Protection Act (DCCPA) proposed last August. (For further information on the DCCPA bill, please refer to the Xangle report on the matter.)
The DCCPA is often dubbed a “DeFi Killer” because there is a strong likelihood that the “digital commodity trading facility,” as defined in DCCPA, will include decentralized exchanges (DEXs). Not only is the definition of “digital commodity trading facility” broadly defined as “facilities that execute trading of digital commodities,” but it also fails to include any distinction between the centralized exchanges (CEXs) and decentralized exchanges (DEXs), such as whether assets are exchanged through smart contracts or existence of any intermediary trustee. This means that there is a good chance that DEXs may become subject to numerous compliance mandates, starting with the requirement to register with the CFTC.
U.S. Senator Debbie Stabenow, one of the lawmakers to have tabled the DCCPA bill, has recently revealed that an investigation into the DCCPA bill has begun again since the FTX debacle. Some even argue that the bill needs to be drafted again, focusing more on protecting the customers, because FTX was heavily involved in DCCPA. For more rational and reasonable regulations over the market, we await a phased introduction of rules, starting with those areas with technical feasibility after sufficient and thorough research and consideration.
C. South Korea – Prepping Up Regulations Focused on Investor Protection

Bills to Protect Investors and Guidelines from the Policy-Making Authorities
As for Korea, it seems that the movement toward investor protection will be led by the digital asset legislation set forth and guidelines on crypto assets provided by government agencies. For one thing, it is expected to take quite some time before we see a comprehensive bill like MiCA in Korea. A proposal for addressing investor protection and regulating unfair trades must be discussed first, based on which a regulation on non-security tokens, tentatively called the “Digital Asset Bill,” would be enacted.
Policy authorities stated that they plan to distribute various guidelines to fill the void until the legislation is enacted. Financial Services Commission (FSC) announced the plan for those tokens currently issued and have characteristics of securities to be classified as security tokens to be subject to the rules of the Capital Markets Act and is scheduled to release the “Guideline for Determining Security Tokens” in January 2023 to aid with such efforts. Financial Supervisory Service (FSS) has also announced plans to ramp up disclosure requirements and distribute audit guidelines to address issues related to crypto assets such as accounting, footnote disclosures, and external audits.
Anticipating Pilot STO via “Guideline for Determining Security Tokens”
All the securities issued and circulated in Korea are regulated by the Capital Markets Act. Likewise, any token classified as securities under the guideline for determining security tokens shall also be subject to the Capital Markets Act, making it only natural to assume that the issuance and circulation of such tokens should follow the existing securities issuance and circulation system, unlike the other non-security tokens. Leveraging the existing infrastructure, the system of issuing and circulating security tokens would flow as below:

Many securities firms have been known to be in preparation for security token issuance business in line with the regulatory direction. Once FSC presents the market with the guideline for determining security tokens, we can anticipate pilot security token offerings (STOs) to be carried out by these securities firms.
Stronger Footnote Disclosure and Introduction of Digital Asset Bill
The regulators are making the moves to improve information transparency and prevent unfair trades by making footnote disclosures mandatory and enacting the Digital Asset Bill. The FSS has forewarned compulsory footnote disclosures for legal persons to provide information on crypto assets to their investors in a transparent manner. For this, FSS plans to newly include a paragraph on disclosure requirements in the accounting standard and publish requirements on footnote disclosures, which will include the details below:

On top of stronger footnote disclosure requirements, preparations are also underway for a bill. There are 16 crypto asset-related legislation currently pending at the National Assembly, which are expected to be put together as a Digital Asset Bill, centered around two bills introduced by representatives Yun, Chang-hyun last October and by Baek, Hye-ryun in November, respectively. A closer look into these bills reveals that they both prioritize protecting investors and preventing unfair trades. The key agenda of the bills are as below:

With mandatory footnote disclosure requirements and regulations against unfair trading enforced in the crypto asset market. as with the traditional financial market, we would be able to create a safer environment for investors. Our experience of a series of incidences, such as the fall of Terra, Luna, and Wemix, heightened interest in investor protection. Now, it is time for the regulations to match our expectations with rational and reasonable rules.
D. Introduction of Regulations Will Eventually Lead to Blockchain Mass Adoption
As we could see in our earlier exploration into the direction of the crypto asset regulations in the EU, US, and South Korea, the policymakers of each country are working toward introducing legislation with strong control. In terms of introducing constructive crypto asset regulations, it would be problematic to insist on a TradFi-esque regulatory structure forcing complete and total supervision and oversight. However, going to the other extreme and blindly asserting the principles of decentralization and non-intervention will not help either. With that in mind, the Xangle Research Team presented some core principles essential for introducing crypto regulations. (For more details about each of the principles, please refer to the Xangle report.)
- Internationally recognized and understood crypto taxonomy
- Clear distinction and understanding of TradFi and DeFi
- Mandatory disclosure requirements for crypto assets
There is no denying that the key regulations as of now are rather thin in terms of such perspective as above. Once the regulations are enacted, it will raise many questions in regard to conflicts with the values blockchains have been pursuing, such as the weakening of DeFi and diluted decentralization, in particular. The difference in opinion in such areas will need to be mitigated through continuous discussion with the industry participants. However, the introduction of regulations is not only inevitable but also necessary because it lays the foundation for the safe and efficient use of the technology. Only with this sound basis will we be able to alleviate uncertainty, provide clear guidelines for businesses, and ultimately ensure investor protection. No matter how innovative a technology may be, it is worthless if it is too difficult for businesses to utilize or not chosen by the public. We anticipate that these regulations will lead us to blockchain mass adoption in the long term.
5-2. Difficult Time for Exchanges as Well: Every Exchange for Itself
Crypto exchanges enjoyed a boom in 2021 with a rise in transaction amounts and a hefty sum in transaction fees. However, in 2022, transaction volume was hit hard by the uncertain macro environment, coupled with various other issues, with the profit also nearly halving. Furthermore, last November, the market witnessed the major and innate limitation of crypto exchanges displayed with the bankruptcy of FTX, the largest crypto company to become insolvent.

With the Crypto Winter dragging over a longer period of time with the FTX debacle, bringing the trading volume down along with it, the profitability of crypto exchanges is expected to continue to worsen. As stagnant market drive users to flock to those exchanges with greater liquidity, the phenomenon of the rich getting richer and the poor getting poorer will become more prominent. Exchanges will seek to survive the competition by making continuous cost reductions. Moreover, with the accelerated introduction of government regulation expected to head toward the exchanges, they also need to plan out measures against them. In addition to the government-implemented regulations, exchanges are expected to voluntarily fortify their investor protection measures with the “Proof of Reserves (PoR)” at the core.
A. Exchanges Switch on Their Survival Mode as Wealth Becomes More Polarized
The drop in the trading volume overall chopped down the revenue for exchanges, also deteriorating their performances. To cope with the situation, exchanges sought to save costs by laying off their employees. Coinbase, a large-scale U.S. exchange, suffered losses for three consecutive quarters with a YoY 54% revenue reduction last 3Q, coupled with fixed operating expenses continuously flowing out. Coinbase let go of as many as 1,160 employees in an effort to save their costs.

The situation is more dire for small-to-medium exchanges. It is not just a matter of cutting back on cost but their survival itself. According to Cryptowisser, 344 crypto exchanges went out of business over the last five years, and the list of closed exchanges is mostly filled with small-to-medium exchanges.
Why are more exchanges going out of business when the crypto asset market continues to grow? It is because i) the trading volume is concentrated on large-scale exchanges, ii) DEXs, where KYC is not required, have positioned themselves as an attractive alternative, and iii) the operation of small-to-medium exchanges are limited by the regulations.
Having ample liquidity is a huge leg up for exchanges since smooth transactions and low slippage are considered advantages. Based on the such network effect, large-scale exchanges are absorbing not only the trading volume but also the users new to the market itself. Binance in the global crypto market and Upbit in the Korean crypto market have been expanding their market share based on this. (Please refer to the charts below.)

Moreover, decentralized exchanges (DEXs) that do not require KYC while providing many different token pair options, would have accelerated small-to-medium exchanges’ narrowing position in the market. DEX trading volume grew rapidly to reach 30% of CEX spot trading volume at peak and an average of 11%.

Lastly, with crypto asset-related regulations being set up, exchange report requirements were also introduced. In many cases, small-to-medium exchanges could not fulfill such requirements, leading to a restricted operation of their businesses. Exchanges faced with such hurdles suffer a massive drop in their profitability and even fear for their very survival.
In Korea, the bipolarization of the crypto exchanges took a turn for the worse when the revision of the “Act on Reporting and Using Specified Financial Transaction Information” was put into effect last September, which stipulates that the real-name bank accounts must be secured as a part of the reporting requirements for exchanges in the Korean Won market. The top 5 exchanges that have partnered with commercial banks in the TradFi market and continued operating in the KRW market have grown up with the crypto market in 2021 and recorded operating profits. However, exchanges operating in the coin market recorded operating losses. In the Korean market, the competitiveness is significantly lagging behind the KRW market exchanges, so it would be very difficult to keep operating the business.

In 2023, with the crypto market rebound uncertain, exchanges are expected to focus on cost saving by tightening their belts. In particular, the small-to-medium exchanges with lower competitiveness than the large exchanges or major DEXs would be hit very hard. They would have to do everything possible to survive.
B. Still Far from Getting Results from New Businesses in 2023
Today, most of the revenue for most crypto exchanges is incurred from transaction fees. As of 3Q 2022, the revenue from transaction fees takes up 85.4% of Coinbase’s, 98.7% of Dunamu’s, and 100% of Bithumb Korea’s revenue. With such a high level of dependency on the transaction fees revenue, the exchanges’ profits are directly impacted by the crypto market’s environment.
To overcome such issues, exchanges are taking on the strategy of diversifying their source of revenue. However, it would be difficult to expect any specific results in 2023. For example, Coinbase is trying to lower its dependency on the revenue from fees by launching a subscription service (including USD 0 transaction fee and 24/7 customer service). However, the subscription services without the blockchain rewards only amount to 2% of the total revenue for now.

Major Korean cryptocurrency exchanges, such as Upbit, Bithumb, and Korbit, are also seeking breakthroughs to improve their revenue structure which is heavily based on fees, including launching NFT businesses. However, these are all newly invested businesses that will take some time for us to see significant results. Even the DeFi services currently in operation are expected to be regulated due to the GOFi and Genesis incidents, making it difficult to expand the business in the near future.

C. Compliance Is Not an Option but a Must for Exchanges
As the confidence in the ecosystem overall crumbled down with the Luna and FTX incidences, the need to introduce regulations for exchange businesses is heightened. Considering the similarities between how cryptocurrency and securities transactions are structured, some of the regulations in place to stabilize the traditional financial market may be similarly applied to the crypto market. One of the key regulations is the introduction of a license. As countries start to adopt a registration system for exchanges, those without a license are being banned from operating in that country. Exchanges without any specific headquarter location, and therefore free from regulations of a single nation, such as Binance, are taking on the strategy to localize by directly building exchanges locally, getting licensed (Binance.US in the U.S.), or acquiring already licensed companies (acquiring Sakura Exchange BitCoin in Japan).

In addition to the strong government regulations, cryptocurrency exchanges are taking matters into their own hands and starting voluntary regulations, launching their own systems. First, exchanges are launching the Proof of Reserves (PoR) system to prove their financial soundness. Since the main reason FTX ended up bankrupt was poor management of their assets, they are voluntarily disclosing their financial information and emphasizing that there is no issue in protecting assets of their investments. Today, the PoR system is officially launched on Binance with KuCoin, Bitfinex, OKX, Bybit, and more onboard.
The Korean exchanges were not as badly hit by the FTX bankruptcy as other businesses overseas since they have been announcing quarterly external audit results in accordance with the Specified Financial Transaction Act. However, Korbit has disclosed the assets held by the exchange to verify asset management in real-time. Whether by choice or mandate, introducing regulations for cryptocurrency exchanges is inevitable.

Closing Thoughts
This isn’t the first time the market has experienced a crypto winter, but as the research for the 2023 outlook came to a close, our team agreed that this time just hits differently compared to the 2018 crypto winter. In 2018, Bitcoin and Ethereum were the only two prominent projects, and Bitcoin’s survival was questioned by many. However, the 2022 crypto winter is substantially different from 2018.
First, Bitcoin has established itself as a financial asset and gained significant traction in institutional adoption. Fast and cheap Layer 2’s and the monolithic blockchain infrastructure emerged as solutions to the blockchain trilemma, a lingering problem for most developers. The DeFi platforms surged up immensely in 2020 and have crossed $200B, an all-time high for the industry, and became blockchain’s killer dApps. The NFT market has made records as the NFT craze in 2021 attracted a wave of NFT holders to NFT marketplaces. Furthermore, blockchain games combining both NFT and DeFi technologies have raised the level of blockchain content to another level. Though controversial, the building blocks for crypto regulation have been introduced – U.S. regulators are planning to introduce new crypto guidelines that would eliminate uncertainties while ensuring stability, which will, in turn, bring in more institutional investors.
Xangle’s macroeconomic projections for 2023 indicate the road to recovery will be challenging. However, the direction of blockchain infrastructure development and blockchain content will remain unchanged, backed back massive capital injection from investors and strenuous effort by everyone involved in tackling challenges and delivering services for users. Xangle’s first outlook was produced in line with that direction. As much progress was made in the NFT and Defi sectors during the recent crypto winter, we hope to see the launch of many new services that the users will choose.
As antifragile as it is, the crypto market will stay resilient and grow even stronger in the face of hardships. It always has.
