Table of Contents
1. The Rise of AI Agents and the Emergence of deAIOS
1-1. The rise of AI agents: Thinking and acting like humans
1-2. The emergence of deAIOS to overcome the limitations of AI infrastructure
2. 0G’s deAIOS: A Decentralized AI Operating System for AI and Crypto
2-1. Enhancing scalability and eliminating single points of failure with 0G
2-2. 0G Storage and Data Availability (DA): Secure Big Data Processing
2-3. Building a decentralized economy with the 0G service marketplace and alignment nodes
2-4. ERC-7857: Establishing a standard for AI agents
2-5. The role of 0G tokens within deAIOS
3. The AI and Crypto Ecosystem Growing on a Decentralized AI Operating System
3-1. Strategic moves to strengthen the AI agent narrative
3-2. Alliances to secure technological superiority of blockchain networks
4. The Path Forward for 0G
4-1. How AI agents innovate deAIOS, and how deAIOS boosts AI agents
4-2. The emerging DeFAI market and why 0G must take the lead
4-3. Practical challenges facing 0G
5. Final Thoughts
1. The Rise of AI Agents and the Emergence of deAIOS
1-1. The rise of AI agents: Thinking and acting like humans
In recent years, generative AI technology has advanced at an unprecedented pace, significantly enhancing AI’s ability to understand and generate human language. OpenAI’s ChatGPT reached 100 million monthly users within just six weeks of its release, setting a record as the fastest-growing application in history. Large language models (LLMs) such as GPT-4 have extended AI’s capabilities to complex problem-solving and even code generation, broadening the scope of AI applications considerably. Simultaneously, the rapid progress of large multimodal models (LMMs), which process various forms of input data to produce context-aware results, has brought AI agents into the spotlight. AI agents integrate LMMs as their core intelligence while autonomously carrying out tasks by leveraging multiple tools.
NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang, speaking at CES 2025 in January, highlighted the arrival of the AI agent era, emphasizing that AI agents—enabled by real-time inference and dynamic resource allocation—will be key to future innovation. As this trend gains momentum, the AI industry is expected to devote extensive resources and expertise to advancing AI agent technology and applying it to real-world services.
1-2. The emergence of deAIOS to overcome the limitations of AI infrastructure
Despite these rapid advancements, concerns over the centralization of AI infrastructure are growing. If the development and deployment of large-scale AI models and services remain concentrated within a handful of major tech companies, several critical risks arise:
- Bottlenecks and single points of failure
- Shortages and lack of transparency in big data storage
- Market distortions due to profit monopolization by big tech companies
Michael Heinrich, co-founder of 0G Labs, highlighted this issue, stating: “AI is controlled by a handful of companies. We hope they will operate AI in alignment with human values, but if they fail, the consequences could be severe.”
To counter these risks, efforts to build decentralized AI infrastructure have emerged in various forms. Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePINs) allow individuals to trade unused data storage and GPU power, creating a distributed marketplace for computational resources. Decentralized data marketplaces facilitate the exchange of domain-specific datasets and provide services for structuring and organizing data. Decentralized AI model training projects have also emerged, focusing on the development of specialized AI models tailored to specific applications rather than general-purpose large-scale language models.
However, since these decentralized infrastructure components operate independently, they fail to provide AI agents and AI models with a fully integrated environment where necessary resources and data can be seamlessly aggregated. In other words, while DePINs, decentralized data marketplaces, and decentralized model training initiatives each offer unique value propositions, they lack a unified framework to efficiently connect and manage the entire AI lifecycle—from data collection and model training to inference and result distribution.
To truly usher in the decentralized AI agent era, an integrated OS layer is essential—one that ensures both interoperability and security. Addressing this need, 0G Labs is developing the world’s first decentralized AI operating system (deAIOS). deAIOS functions as a comprehensive infrastructure layer that unifies existing decentralized AI infrastructure into a single ecosystem. It facilitates seamless access to computational resources, data, and tools required by AI agents, while ensuring a transparent Web3-based incentive system that fairly rewards all participants contributing to the ecosystem. By providing the most flexible and robust AI infrastructure available, deAIOS of 0G Labs aims to accelerate the growth of decentralized AI ecosystems while addressing the fundamental challenges of centralized AI infrastructure. As a result, 0G is not only introducing a new paradigm for decentralized AI but also attracting significant interest and anticipation from the market.
2. 0G's deAIOS: A Decentralized AI Operating System for AI and Crypto
0G deAIOS aims for the decentralization and democratization of AI and is currently developing the following six key components:
- 0G Chain: An optimized blockchain that supports high-performance AI and on-chain gaming through a modular expansion structure.
- 0G Compute Network: A decentralized computing framework that matches and manages resources required for AI model computation in a decentralized manner.
- 0G Storage: A decentralized storage network designed to store and distribute large-scale datasets necessary for AI model training and inference.
- 0G Data Availability (DA) Layer: A data availability layer designed for infinite scalability.
- 0G Service Marketplace: A comprehensive platform for registering, hosting, and consuming AI services to foster a decentralized AI economy.
- 0G Alignment Node: A community-driven validation node that monitors participants in the ecosystem—such as storage, DA, and computation service nodes—and verifies AI integrity.
In traditional Web2 infrastructure, AI applications have been inherently dependent on centralized cloud services such as AWS, Google, and Microsoft. In contrast, 0G enables the complete on-chain operation of AI services within a decentralized Web3 environment.
2-1. Enhancing scalability and eliminating single points of failure with 0G
0G Chain is a Layer 1 blockchain built on the Cosmos SDK, but it is designed for full compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) using the Ethermint module. This allows 0G Chain to support smart contract languages like Solidity, widely used in the Ethereum ecosystem, and enables Web3 projects and existing decentralized applications (DApps) to migrate without requiring redevelopment. Additionally, through partnerships with interoperability protocols like Axelar, 0G aims to connect with non-EVM chains, fostering a broader multi-chain environment.
0G chain: The blockchain network underpinning deAIOS
0G Labs’ ultimate goal is to achieve horizontal scalability capable of handling the vast volumes of data and complex computations generated and processed by AI agents. To this end, the 0G Chain adopts a modular multi-chain architecture. While it currently operates as a single chain based on the Cosmos SDK, the long-term plan is to enhance scalability linearly by flexibly adding multiple parallel chains under its own consensus mechanism.
According to 0G’s technical documentation, this expansion strategy is made possible through a shared staking model. Each additional chain operates with an independent set of nodes responsible for consensus, while the 0G token stakes deposited on the Ethereum mainnet are delegated to these node operators, allowing them to participate in block production and validation. This approach resembles the security sharing concept of EigenLayer, yet it will be implemented under 0G Chain’s proprietary consensus mechanism. Notably, if an issue arises on any of the chains, the staked tokens on the mainnet face the risk of slashing, ensuring a security level comparable to that of the Ethereum mainnet.
 source: 0G Blog
source: 0G Blog
With this architecture, 0G Chain aims to achieve virtually unlimited scalability by continually adding parallel chains as needed. If successfully commercialized, this technology could significantly reduce bottlenecks in AI model training, on-chain inference, and large-scale data analysis.
In addition, 0G Chain is developing a Uni-Chain architecture in collaboration with multiple cross-chain protocols. This interoperability layer will facilitate seamless connectivity with various L1/L2 projects and Web3 services. Going beyond simple Ethereum compatibility, the goal is to remove barriers between chains, enabling AI agents to access and process distributed data and functionalities across multiple networks. Traditionally, fragmented blockchain ecosystems have made application integration difficult. However, 0G Chain seeks to eliminate not only on-chain/off-chain boundaries but also inter-blockchain barriers, allowing AI agents to aggregate resources from different networks and generate richer, more comprehensive responses.
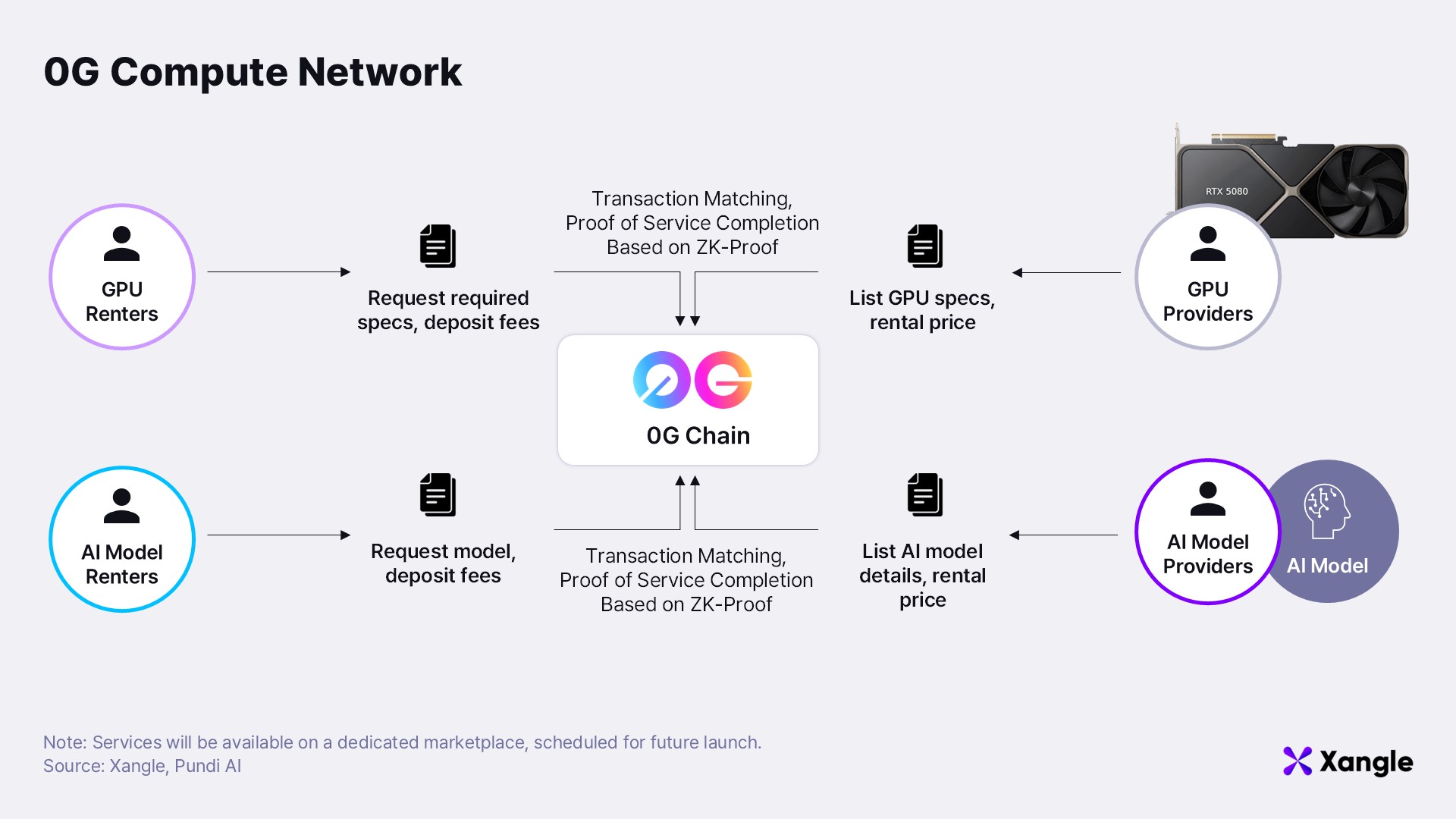
0G compute network: Supporting AI model inference and training
0G Compute Network, operated by 0G Labs, serves as a decentralized marketplace that matches the physical computing resources—such as GPUs and CPUs—required for AI model training and inference. Unlike traditional cloud services (e.g., AWS, GCP), where server overloads can cause performance degradation and skyrocketing costs, the distributed nature of 0G Compute Network ensures flexible, scalable handling of concurrent AI agent requests. Essentially, it functions as a global computational pool, aggregating idle GPUs and computing power from individuals and enterprises worldwide.
A key innovation of the 0G Compute Network is its smart contract-based automated settlement system. Users requesting AI services stake a predetermined amount in a smart contract before submitting their request. Service providers then process the request and submit a Zero-Knowledge Proof (ZK-Proof) verifying the computation’s validity. Once the proof is successfully verified, the smart contract automatically executes the settlement, ensuring transparent and trustless transactions between service providers and users.
Ultimately, 0G Chain aims to go beyond being a simple EVM-compatible Layer 1 and establish itself as a modular, multi-chain decentralized infrastructure designed for infinite scalability to meet AI workloads. When combined with the decentralized compute network, this ecosystem could significantly enhance trust, transparency, censorship resistance, and cost efficiency, solving challenges that centralized cloud providers have struggled with. This synergy aligns with deAIOS’s vision of an “on-chain AWS”, enabling AI agents to leverage vast computational resources with full transparency and cost efficiency.
However, several key challenges remain. The validator incentive structure and slashing mechanisms must be designed to function effectively in a multi-chain environment. Additionally, while the theoretical potential of the decentralized compute network is enormous—aggregating GPUs globally—major tech firms continue to monopolize GPU supply, which may limit the available computational power for AI training. For 0G to compete with established centralized cloud providers leading the AI space, it must secure sufficient node participation and ensure stable service quality to maintain long-term viability.
2-2. 0G Storage and Data Availability (DA): Secure Big Data Processing
For AI agents to navigate both on-chain and off-chain environments while executing complex decision-making, they require not only powerful computing resources but also fast, reliable, and secure access to massive datasets. However, existing centralized cloud solutions (e.g., AWS, Azure) come with significant cost, security, and accessibility challenges—from rising data upload fees to geopolitical access restrictions and heightened security risks.
To address these challenges, 0G Labs is building a decentralized data infrastructure through 0G Storage and the Data Availability (DA) layer. This aligns with the 0G Compute Network, which optimizes computational resources, while also overcoming the storage and distribution bottlenecks of traditional cloud services.
0G Storage: Addressing not just storage but fast retrieval and accessibility
 source: 0G Blog
source: 0G Blog
0G Storage is designed to eliminate single points of failure (SPOF) by sharding and distributing large-scale files—such as AI models, training datasets, and user-generated data—across multiple storage nodes. For instance, when a 10TB dataset is uploaded, it is split into smaller fragments and distributed across various nodes. Even if some nodes go offline, the entire dataset remains recoverable, ensuring high availability.
A defining innovation of 0G Storage is its Proof of Random Access (PoRA) consensus mechanism, which systematically filters out unreliable nodes and ensures that the network retains data integrity at all times. Since randomly selected storage nodes must immediately provide the requested data fragments to receive rewards, inactive nodes that merely store data without responding are naturally eliminated. Additionally, 0G Storage introduces a dual-lane architecture, which separates data verification from high-speed transmission. This structure is optimized for AI agents, allowing them to retrieve critical information with minimal latency.
By leveraging this approach, AI model parameters, massive text/image datasets, and other large-scale files can be securely stored and replicated across a distributed network—eliminating reliance on centralized cloud servers. Furthermore, since nodes participate in a decentralized marketplace and compete on storage pricing, the long-term cost of using 0G Storage has the potential to be lower than traditional cloud services.
0G Data Availability (DA): The backbone of a robust data infrastructure
 source: 0G Blog
source: 0G Blog
No matter how securely data is stored, it is meaningless if the network cannot guarantee its continuous availability and accessibility when needed. To solve this issue, 0G Labs operates a blockchain-powered Data Availability (DA) network, which periodically verifies and records data availability on the 0G Chain.
DA nodes leverage Verifiable Random Function (VRF) to conduct randomized audits of storage nodes, ensuring they still retain the necessary data fragments in a fully accessible state. If any anomalies are detected, they are immediately recorded on-chain for network-wide transparency. From the perspective of AI agents, this guarantees that all necessary data remains readily available at all times, significantly reducing the need for additional data validation processes during real-time inference or large-scale data analysis.
Furthermore, the 0G DA layer is designed to support multiple interconnected data availability networks, allowing seamless scalability even during high-intensity AI computations or sudden spikes in simultaneous requests. Unlike traditional distributed storage solutions (e.g., IPFS), 0G DA provides a more robust on-chain/off-chain integration model, ensuring that AI models handling large datasets operate without bottlenecks. Already, 0G Labs is collaborating with Ethereum rollup projects like Arbitrum and Optimism to explore using 0G DA as a scalable data layer for rollups. Additionally, several expanding dApp chains are paying close attention to 0G’s high-speed data availability features.
Ultimately, 0G Storage and 0G DA represent a fundamentally new approach to solving the bottlenecks, security concerns, and cost inefficiencies of centralized cloud services through decentralized networking. While it is true that cloud-based data centers—which aggregate massive GPU resources in a single location—can offer superior performance for large-scale AI processing, they are also vulnerable to single points of failure. As seen with ChatGPT’s occasional outages, when demand surges beyond capacity, centralized services experience severe bottlenecks and complete system downtime. In such cases, centralization exacerbates service disruptions, forcing companies to invest in additional infrastructure, leading to higher costs.
In contrast, 0G Storage and 0G DA distribute data storage, transmission, and verification across multiple nodes, ensuring that even if one server or data center becomes overloaded, the entire system remains operational. Instead of service-wide failures, 0G’s distributed architecture dynamically balances loads, preventing network congestion and enhancing service continuity. Moreover, since network nodes autonomously set their pricing and compete, long-term storage costs may be more competitive than centralized cloud providers. However, challenges remain: potential latency issues due to node-to-node communication delays and performance degradation from data fragmentation under extreme traffic conditions. Additionally, for 0G Storage to become cost-efficient, a critical mass of participating nodes and strong market competition are essential.
2-3. Building a decentralized economy with the 0G service marketplace and alignment nodes
0G Service Marketplace: The hub for decentralized AI services
The 0G Service Marketplace is a core platform designed to enable decentralized transactions and utilization of AI models and services. Here, service providers can register their AI models—including inference models, data processing models, and fine-tuning models—while specifying usage conditions and dynamic pricing (which fluctuates based on model complexity, resource demand, and verification options) through smart contracts. On the other hand, developers and DApp operators can browse and select the AI services they need, pay using tokens, and receive results once the provider completes the computation. The transaction is safeguarded through zero-knowledge proofs (zk-Proofs) and other verification mechanisms, ensuring that payment is automatically processed only when verification is successful. If the verification fails, the payment is canceled—protecting users from faulty or unreliable computations. This system guarantees a trustless and transparent AI service marketplace.
 source: 0G Docs
source: 0G Docs
While the marketplace currently focuses on AI inference services, it is designed to accommodate a broad spectrum of AI-related tasks, such as data preprocessing and fine-tuning. Before listing a model, providers must undergo GPU verification (e.g., verifying whether the stated NVIDIA GPU specifications are authentic) and complete a broker setup. Once these prerequisites are met, providers can officially register their AI models on the marketplace, where they can fine-tune details such as model type, verification method (OPML, TeeML, ZKML, and more), and pricing policies. Looking ahead, 0G Labs plans to introduce an ERC-7857-based NFT standard to tokenize AI agents, enabling secure ownership and transfer of AI models along with their parameters and state data. This would allow individual developers and small teams to launch their specialized AI models in an on-chain marketplace, facilitating transparent transactions and settlements via blockchain.
Another factor working in 0G’s favor is the rapid commoditization of large-scale AI models (LLMs), which is driving down AI service costs. As AI models become more affordable, more providers are expected to participate, leading to greater diversity of specialized AI models and fiercer price competition, allowing users to access AI services at more competitive rates. For instance, projects like DeepSeek have demonstrated that the cost of operating AI models tends to decrease over time. If this trend continues, the 0G Service Marketplace has the potential to establish itself as a central hub for the decentralized AI economy. Additionally, because key AI-related data—such as model weights, inference results, and payment records—are managed on-chain, the marketplace maximizes the advantages of decentralized cloud computing, fostering a globally accessible, trustless AI ecosystem.
Alignment Nodes: Community-driven validator for AI integrity
As the 0G ecosystem continues to grow, with various nodes, AI models, and AI agents interacting across the network, Alignment Nodes play a critical role in ensuring network integrity and security. These nodes act as key oversight mechanisms within the deAIOS (decentralized AI operating system) infrastructure, performing essential functions such as: Monitoring the state of storage nodes to ensure data availability and reliability, verifying the consensus process of Data Availability (DA) nodes, and validating computation results submitted by compute nodes. Moreover, Alignment Nodes help prevent malicious attacks that could compromise AI integrity. For example, they monitor and mitigate model drift (a decline in AI model performance caused by corrupted or low-quality data) and AI agent errors stemming from unreliable or adversarial data inputs.
To encourage community participation, 0G Labs launched an Alignment Node license NFT sale in late 2024, achieving significant success with the sale of over 80,000 licenses and raising approximately $28 million. The funds will be used to expand and enhance deAIOS, while license holders are granted the right to operate Alignment Nodes, contributing to network security and data integrity in exchange for periodic token rewards. To discourage speculative trading and prioritize genuine network participants, 0G Labs implemented temporary transfer restrictions on these NFTs, ensuring that license holders are committed to operating Alignment Nodes rather than seeking short-term profits.
By integrating Alignment Nodes with the 0G Service Marketplace, 0G is laying the foundation for a decentralized AI economy, where AI model and agent providers can engage in autonomous, trustless transactions and AI service quality and data integrity are ensured through community-driven verification. This marks a significant departure from the centralized AI monopolies of the past, where large corporations controlled AI model deployment and distribution. Now, even individual developers and small teams can launch their own AI services on a global scale, secure transparent compensation, and operate on equal footing with larger players. However, a key challenge remains: sustaining long-term incentives for node operators. The success of 0G’s decentralized AI economy will depend on how effectively 0G Labs continues to adjust and manage its reward distribution mechanisms. As a result, industry observers are closely monitoring how the team refines its incentive model to ensure stable and sustainable network growth.
2-4. ERC-7857: Establishing a standard for AI agents
0G Labs believes that a new type of NFT standard (protocol) is needed to enable the secure on-chain ownership and utilization of AI agents. Existing NFT standards, such as ERC-721 and ERC-1155, were designed primarily for static assets and do not account for the dynamic nature of AI agents, which continuously learn and incorporate sensitive model parameters and proprietary data. To address this, 0G Labs has introduced ERC-7857, an NFT standard that encrypts and protects the dynamic and sensitive information within AI agents while supporting decentralized transactions and ownership transfers.
 source: 0G Blog
source: 0G Blog
The proposed ERC-7857 standard is designed to represent AI agents as Intelligent NFTs (iNFTs). Traditional NFT standards, such as ERC-721 and ERC-1155, rely on external metadata storage and are therefore ill-suited for AI agents, which require continuous updates and learning capabilities. In contrast, ERC-7857 is specifically built to manage AI models, weights, and memory on-chain, ensuring that core AI data remains secure through encryption, ownership transfers include cryptographic verification of AI integrity, and changes in AI learning and state are recorded transparently on-chain.
Within this framework, an AI agent’s intellectual assets—including trained AI models, state data, and operational logs—are treated as dynamic metadata. These assets are encrypted and stored on-chain, with commitments (hashes) updated continuously, ensuring that AI learning and evolution are fully traceable on the blockchain, new owners can securely receive encryption keys to utilize the AI agent, and data integrity and ownership authenticity are maintained throughout transactions. In essence, ERC-7857 is an advanced NFT standard that incorporates privacy, security, and dynamic functionality, making it suitable for representing AI models as unique digital assets.
The adoption of ERC-7857 marks a significant shift, transforming AI agents from mere software applications into valuable on-chain assets. AI developers can tokenize and commercialize custom-trained AI agents as iNFTs, allowing buyers to securely acquire and utilize verified AI models. Smart contracts ensure data security and integrity, while AI agents can be synthesized and combined to create more advanced models. Additionally, enterprises can securely transfer proprietary AI agents between departments or partners while preserving data sovereignty.
Ultimately, the ERC-7857 standard serves as a key component of 0G Labs’ decentralized AI operating system (deAIOS), laying the groundwork for treating AI models as digital assets. By bridging AI and blockchain, this innovation opens new economic and technological frontiers, allowing both individual developers and large enterprises to maximize the potential of AI agents within a decentralized infrastructure.
2-5. The role of 0G tokens within deAIOS
In the deAIOS ecosystem built by 0G Labs, the 0G token serves a role beyond that of a mere gas token. To operate the data availability (DA) layer and decentralized storage in an infinitely scalable manner, 0G Labs has designed economic incentives to ensure that network nodes behave according to the protocol. The 0G token functions as the primary asset across the ecosystem, facilitating node staking, data upload and retrieval costs, AI model access, and governance participation.
AI agents or high-performance decentralized applications (DApps) that aim to store, analyze, and infer large-scale data through 0G infrastructure must pay node operators in 0G tokens. Storage nodes and DA nodes, which perform network validation and data integrity checks, are required to stake a certain amount of 0G tokens to operate and must pass periodic verifications (random challenges) to receive rewards. Nodes that fail to maintain data properly or disrupt consensus are penalized through slashing, losing their staked tokens, thereby ensuring reliable services without relying on trust.
This structure encourages nodes to compete voluntarily in a decentralized market, enabling users to utilize distributed infrastructure at reasonable costs. Notably, the 0G token is also used to publish AI models on-chain and to host large-scale data generated by Layer 2 or Layer 3 projects through the 0G DA layer. This ensures that the entire AI model training and inference process is transparently recorded on the blockchain, allowing developers to perform large-scale computations in a cost-efficient and verifiable manner compared to traditional centralized cloud solutions.
However, the initial plans announced by 0G Labs in 2024 are subject to change as the actual products and services are developed. For example, the token distribution model or specific staking mechanisms may be adjusted based on testnet results, tokenomics, and partnership dynamics. Nonetheless, the overarching vision of the 0G token providing liquidity and economic incentives throughout the decentralized AI operating system (deAIOS), serving as the key asset for AI model training, inference, and data management, is expected to remain unchanged.
3. The AI and Crypto Ecosystem Growing on a Decentralized AI Operating System
 Source: 0G blog
Source: 0G blog
0G Labs, developing a decentralized AI operating system (deAIOS), is working towards pioneering the on-chain AI landscape through its 0G chain, 0G compute network, 0G storage, and DA solutions. Beyond merely providing technological infrastructure, 0G is actively reinforcing the AI agent narrative while forging alliances with existing blockchain networks to ensure technological excellence.
3-1. Strategic moves to strengthen the AI agent narrative
As discussed earlier, AI agents are emerging as a next-generation trend in both the crypto industry and the global IT market. To establish this AI agent narrative within the blockchain ecosystem, 0G is taking several strategic steps.
On the partnership front, 0G collaborates with various AI-focused projects to implement on-chain AI agents. For instance, its partnership with Talus enables secure storage and distribution of AI models and datasets on 0G storage, minimizing latency for AI agent operations. Another collaboration with Theoriq focuses on building a decentralized AI hub where multiple AI agents can cooperate on tasks or autonomously respond to user requests, enhancing security and transparency compared to centralized clouds.
Additionally, 0G partners with AI-centric protocols and decentralized computing projects (such as ORA, Spheron, and ionet) to source GPU/CPU resources globally, enabling distributed AI inference. This underscores 0G’s evolution into a full-stack blockchain infrastructure tailored for AI services, integrating large-scale computation, extensive data storage, and scalable DA solutions—differentiating itself from traditional chains focused solely on consensus and transaction processing.
3-2. Alliances to secure technological superiority of blockchain networks
0G also collaborates with various blockchain projects to showcase the technical capabilities of its infrastructure, including its chain, storage, and DA (Data Availability) layers. Rather than being merely a “chain for AI,” 0G extends its reach by enabling multiple L1 and L2 ecosystems to leverage its DA solutions, storage lanes, and compute networks, fostering mutual benefits across the Web3 space.
In practice, 0G has formed partnerships with leading L2 projects such as Polygon, Arbitrum, Fuel, and Manta Network to co-develop DA solutions that allow these networks to securely store and utilize large-scale data on-chain. For instance, when Arbitrum utilizes 0G’s DA functionality, it can upload transaction data in a lightweight manner while ensuring it remains verifiable at any time. This results in significant advantages in terms of gas cost reduction and scalability. Additionally, from a cross-chain perspective, 0G provides decentralized storage and DA infrastructure that enables secure recording and transfer of assets and information across different chains, establishing a robust interchain data exchange environment.
Ultimately, through these extensive alliances and initiatives, 0G is redefining its identity beyond that of a single blockchain or standalone AI project. Instead, it is emerging as a critical data and computation layer in the cross-chain and multi-chain era, as well as a key enabler of AI-driven innovation. Its vision for an infinitely scalable storage and DA layer reflects an ambitious strategy to integrate seamlessly with numerous chains and protocols, facilitating the realization of on-chain AI. This, in turn, represents a calculated move to establish itself as the definitive hub when AI and decentralized data become foundational pillars of the Web3 landscape.
However, as most current partnerships remain focused on infrastructure and technical integration, a key challenge lies in fostering user activity and activating diverse on-chain assets within the 0G ecosystem. For AI agents to seamlessly integrate into Web3—across automated DeFi operations, on-chain gaming, and NFT/DAO ecosystems—improving user experience (UX) and strengthening ecosystem support will be essential. While 0G has successfully laid the foundation for on-chain AI infrastructure, achieving true mass adoption of its decentralized AI operating system will ultimately depend on expanding user-centric services that cater to real-world demand, such as DeFi and on-chain entertainment.
4. The Path Forward for 0G
4-1. How AI agents innovate deAIOS, and how deAIOS boosts AI agents
AI agents require a wide range of infrastructures and tools to function effectively. To flexibly assemble these resources while also adhering to the principles of decentralization for on-chain activities, a modular platform like deAIOS becomes indispensable. In other words, by integrating distributed storage, compute power, and a DA (Data Availability) layer under one unified system, deAIOS provides the scalability and transparency needed for AI agents in a way that traditional centralized approaches cannot.
Conversely, deAIOS is designed with economic incentives and decentralized mechanisms so that a “flywheel effect” can emerge as AI agents are actively utilized and developed. For example, as more alignment nodes and storage nodes join the network, data management and model verification become more robust, allowing AI agents to operate more reliably. And as the number of AI agents and their users grows, the natural result is an increase in node participation and liquidity, which amplifies the overall network effect. Consequently, on-chain AI agents can expand using deAIOS’s decentralized infrastructure, while deAIOS itself builds a richer ecosystem based on the traffic and demand generated by those AI agents.
This kind of reciprocal synergy between on-chain AI agents and deAIOS forms the core of 0G’s vision for an on-chain AI ecosystem. By leveraging the economic incentives and verification mechanisms of a decentralized AI OS, AI agents—requiring diverse resources and tools—can advance toward an even more flexible and transparent AI environment.
4-2. The emerging DeFAI market and why 0G must take the lead
The rise of DeFAI (Decentralized Finance + AI)—the convergence of AI and decentralized finance—is another major opportunity 0G aims to seize. Across the industry, expectations are growing that AI agents will revolutionize asset management, investment strategies, and credit assessments by automating these processes while maintaining transparency and verifiability on decentralized networks—surpassing the capabilities of traditional financial systems.
For 0G, the expansion of the DeFAI ecosystem presents a significant advantage, as its infrastructure is uniquely optimized for AI-driven decentralized applications. Recognizing this potential, 0G is actively working to secure an early foothold in the DeFAI space, establishing an $88 million ecosystem fund and launching incubation programs for DeFAI startups. Through strategic partnerships with leading venture capital firms, 0G is fostering the integration of cutting-edge AI and crypto innovations within its ecosystem.
Ultimately, as DeFAI matures and AI agents begin to autonomously conduct high-frequency trading, algorithmic investments, lending, and insurance on-chain, scalable and trustless infrastructure—such as that provided by 0G—will become indispensable. The synergy between AI agents, on-chain finance, and decentralized storage/DA solutions is poised to create profound industry-wide transformations, the full impact of which remains difficult to quantify. However, 0G is already recognized as the most systematically prepared player in the space, positioning itself as the backbone of this decentralized AI-driven financial revolution.
To date, 0G deAIOS has emerged as one of the most ambitious projects bridging AI and blockchain, securing the top ranking on the Kaito dashboard—a testament to the industry’s growing interest. By consolidating the vast data processing capabilities, real-time inference, transparent governance, and infinite scalability required by AI agents into a single unified framework, 0G is laying the groundwork for the AI agent era. Moving forward, the project is set to amplify the AI agent narrative, forge extensive alliances with global blockchain initiatives, and aggressively expand into emerging AI-powered financial sectors such as DeFAI. Through these efforts, 0G is poised to become the core infrastructure accelerating on-chain innovation at the intersection of AI and crypto. This is the vision behind 0G’s decentralized AI OS, and as the AI agent revolution gains momentum, all eyes are on what 0G will do next.
 Source: KAITO Connect
Source: KAITO Connect
4-3. Practical challenges facing 0G
As previously mentioned, 0G faces several immediate, practical challenges that must be addressed.
First, building an entire high-performance AI model—especially large-scale LLMs—directly on-chain remains difficult at this stage. As a result, the immediate priority should be optimizing support for fine-tuning and seamless integration of AI agent frameworks. By enabling AI services to function efficiently with moderate computing resources, 0G can gradually expand its network of participants, including nodes and developers.
Second, on-chain engagement is still largely limited to infrastructure and technical stacks, meaning there is a pressing need to strengthen the broader ecosystem with user-centric assets, applications, and DeFi solutions. For the vision of a decentralized AI operating system to take shape, users must be able to leverage AI agents in tangible ways across DeFi, NFTs, and on-chain gaming. Providing concrete services that cater to these needs will be essential.
Third, long-term incentive design is critical. Sustaining an ecosystem with adequate storage and computational nodes requires continuous rewards not only for alignment nodes but also for validators. This necessitates a well-coordinated approach that integrates smart contract-based tokenomics with sustainable node operation policies, in addition to securing funding from capital markets.
5. Final Thoughts
0G's vision for a new era of on-chain AI
The concept of a decentralized AI operating system is an innovative endeavor that 0G has pioneered. Merging AI with blockchain to create an infinitely scalable storage and data availability (DA) layer, decentralized computing, and transparent governance is an ambitious challenge—one that still has a long way to go. Along this journey, technical hurdles and the operational dynamics of partnerships will continue to be tested.
Nevertheless, the potential for AI and crypto to mutually reinforce each other is becoming increasingly tangible. 0G has already secured over $358 million in funding, underscoring strong market interest. Moreover, it is actively exploring various scenarios where AI agents could be applied across the Web3 ecosystem, including DeFAI. If a decentralized AI OS successfully gains traction, it could fundamentally reshape the way AI is utilized on-chain, while simultaneously ushering in a pivotal transformation within the crypto industry.
deAIOS, the system 0G envisions, represents a bold attempt to transcend the limitations of centralized AI infrastructure and fully integrate AI with blockchain. The speed at which the on-chain AI era unfolds will depend on how effectively 0G balances capital, technology, and strategic partnerships. With this perspective in mind, we look forward to witnessing the evolution of 0G’s decentralized AI operating system and its impact on the future of AI and blockchain.