


Table of Content
1. Introduction: Beyond Scalability – The Evolution of Proof Systems for Enhanced Reliability
1-1. The limitations of existing ZK Proofs
1-2. Starknet: Setting the standard for next-generation Layer 2 with STARK Proofs
2. Starknet: A Trusted Rollup Solution with Optimized Performance and Usability
2-1. Starknet’s proven reliability with unique STARK technology
2-2. Advancing user-centric innovation: A faster, easier L2 experience
2-3. Enhancing Cairo development with SDKs and zkEVM
2-4. Building customized appchains with modular layers
3. Starknet Ecosystem: Scaling New Heights Through Technology and Usability
3-1. Paving the way to a global blockchain hub through ecosystem campaigns and Bitcoin integration
3-2. Key dApps and the evolving Starknet ecosystem
3-3. Tokenomics and community governance powering Starknet’s future
4. Final Remarks: Trusted Technology Driving Rollup Innovation
1. Introduction: Beyond Scalability – The Evolution of Proof Systems for Enhanced Reliability
1-1. The limitations of existing ZK Proofs
Ethereum has emerged as the second-largest Layer 1 ecosystem after Bitcoin, offering a diverse range of blockchain applications through its smart contract functionality. However, its scalability limitations have led to slower transaction speeds and prohibitively high gas fees, prompting the development of Layer 2 solutions. (Layer 2 solutions alleviate the computational burden on the main blockchain (Layer 1) by processing transactions on a separate network.) Among these solutions, rollup technology has drawn significant attention for its ability to process multiple transactions off-chain and record compressed data and verification results on-chain, delivering remarkable improvements in scalability. ZK rollups, in particular, leverage Zero-Knowledge Proofs to mathematically validate transaction authenticity, providing high security and real-time verification. These capabilities make ZK rollups a leading contender for enabling mass adoption within the Ethereum ecosystem.
SNARKs (Succinct Non-interactive Arguments of Knowledge) have been widely used as a Zero-Knowledge Proof method within ZK rollups due to their ability to achieve efficient verification and data compression. Many blockchain projects have adopted SNARKs for these advantages. However, SNARKs require a trusted setup, a process that involves creating public and private keys during an initial setup phase for transaction validation between provers and verifiers. While straightforward in design, this reliance on a trusted setup introduces centralization concerns. Should the private key be leaked or misused, fraudulent transactions could bypass verification, posing a significant security threat. Moreover, SNARKs are computationally intensive, relying on number theory-based cryptographic operations. As the volume of transactions increases, their processing speed slows, and verification costs rise, presenting a scalability bottleneck for large-scale transaction processing. To overcome these challenges, STARKs (Scalable Transparent Arguments of Knowledge) were introduced.
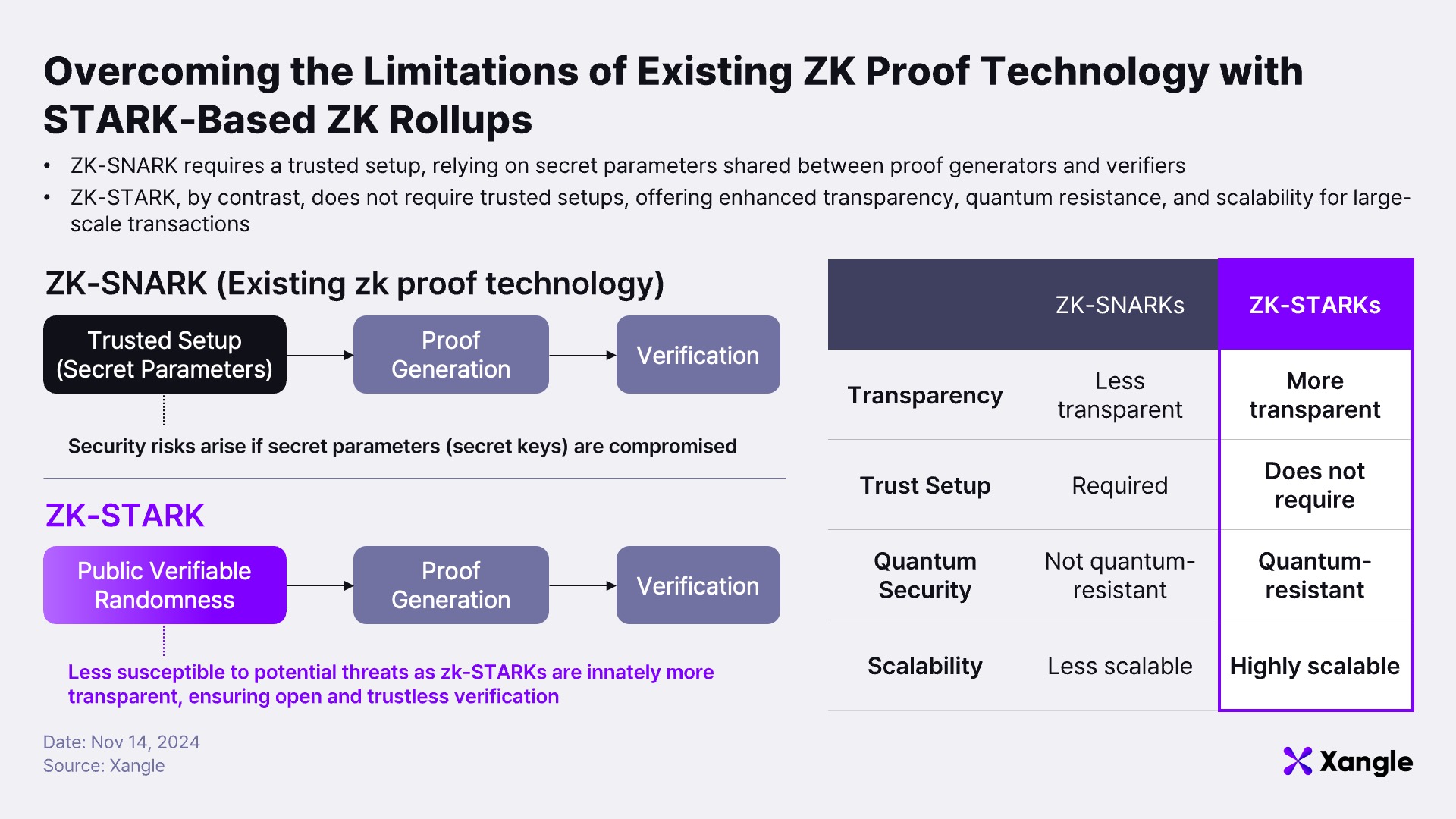
STARKs eliminate the need for a trusted setup by leveraging public parameters based on hash functions. Unlike SNARKs, STARKs do not require private keys and instead ensure data integrity and validity through hash functions and symmetric encryption. This design enhances both security and transparency, allowing verifiers to securely access the information needed without relying on centralized processes. Another key advantage of STARKs is their quantum resistance, making them impervious to potential future threats from quantum computing. While SNARKs are reliant on specific cryptographic techniques that may become vulnerable with advances in quantum computing, STARKs' hash function-based architecture ensures robustness even in a post-quantum environment. These attributes position STARKs as a highly secure and scalable solution capable of efficiently processing large-scale transactions while maintaining robust security. As such, STARKs are increasingly regarded as a foundational technology for addressing the blockchain scalability challenges of the future.
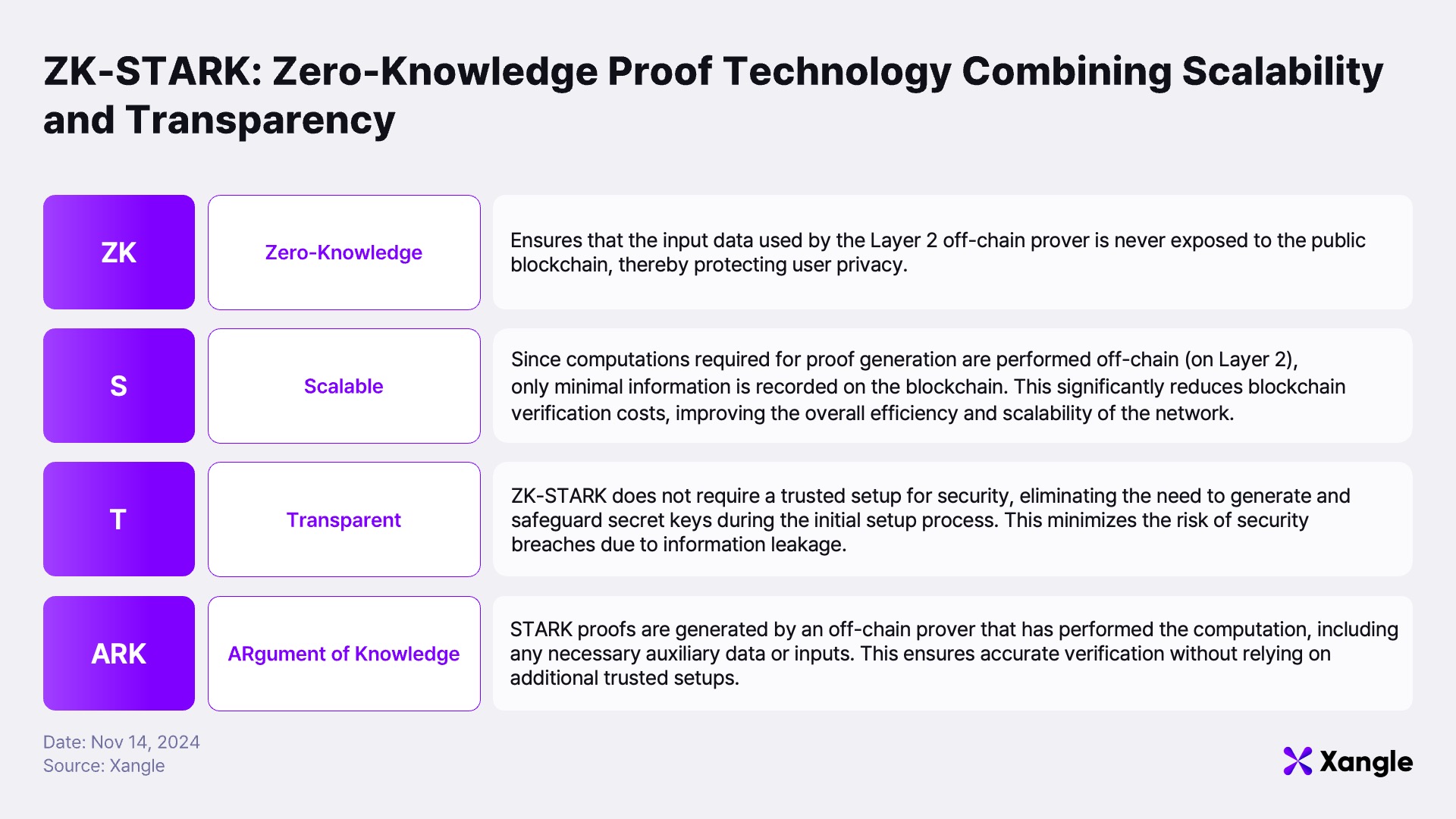
1-2. Starknet: Setting the standard for next-generation Layer 2 with STARK Proofs

Starknet is a next-generation Layer 2 solution built on STARK proofs, designed to simultaneously address Ethereum's scalability and security challenges. Notably, Professor Eli Ben-Sasson, the creator of STARK proofs and co-founder of StarkWare, has gained the trust of leading figures in the industry, including Vitalik Buterin, through his extensive research in ZK technology and cryptography. Leveraging its technical expertise and industry trust, StarkWare has secured $270 million across Series D funding rounds from top-tier investors such as Sequoia, Paradigm, and Pantera, solidifying its position as a leader in blockchain innovation. The company has also proven its capabilities by supporting app chain development for B2B services like dYdX and Immutable X, demonstrating its technology through real-world applications. StarkWare has since launched Starknet as a general-purpose ZK rollup solution, aiming to position it as the next-generation platform for solving blockchain scalability issues.
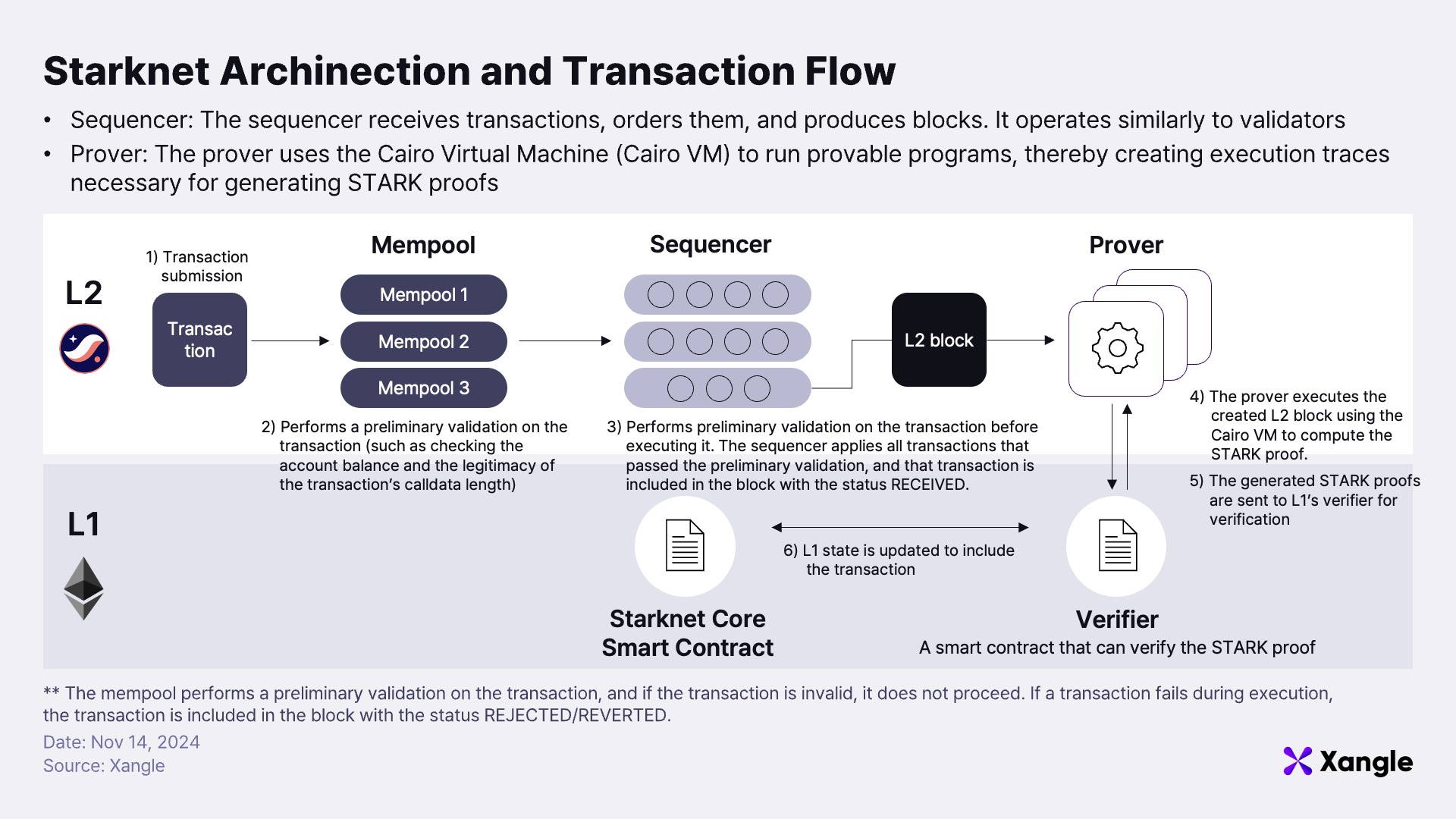
Starknet’s innovative architecture is specifically crafted to maximize STARK proof efficiency through seamless coordination between Sequencers and Provers. Sequencers validate and order transactions collected from the mempool, bundling them into blocks that are incorporated into the Starknet network. These blocks are then executed in the Cairo VM by Provers, generating STARK proofs. These proofs are sent to a Verifier smart contract deployed on Ethereum Layer 1 for final validation. Once validated, Starknet’s state is recorded via the Starknet Core smart contract, ensuring its reliability and security. This approach compresses transaction data off-chain while recording only essential information on Ethereum, thereby maximizing scalability and cost efficiency.
In addition, Starknet achieves multi-faceted optimization for ZK proofs. Its STARK proof methodology eliminates the need for trusted setups, providing a trustless validation environment capable of processing large-scale transactions rapidly and securely. The Cairo programming language, optimized for ZK verification, empowers developers to efficiently build smart contracts. This combination allows Starknet to achieve an impressive performance of up to 857 TPS (Transactions per second), placing it among the most efficient ZK rollups. By creating an environment that supports large-scale applications and a broad user base at low costs, Starknet is redefining scalability and reliability, positioning itself as the go-to next-generation ZK solution within the Ethereum ecosystem.
2. Starknet: A Trusted Rollup Solution with Optimized Performance and Usability
2-1. Starknet’s proven reliability with unique STARK technology
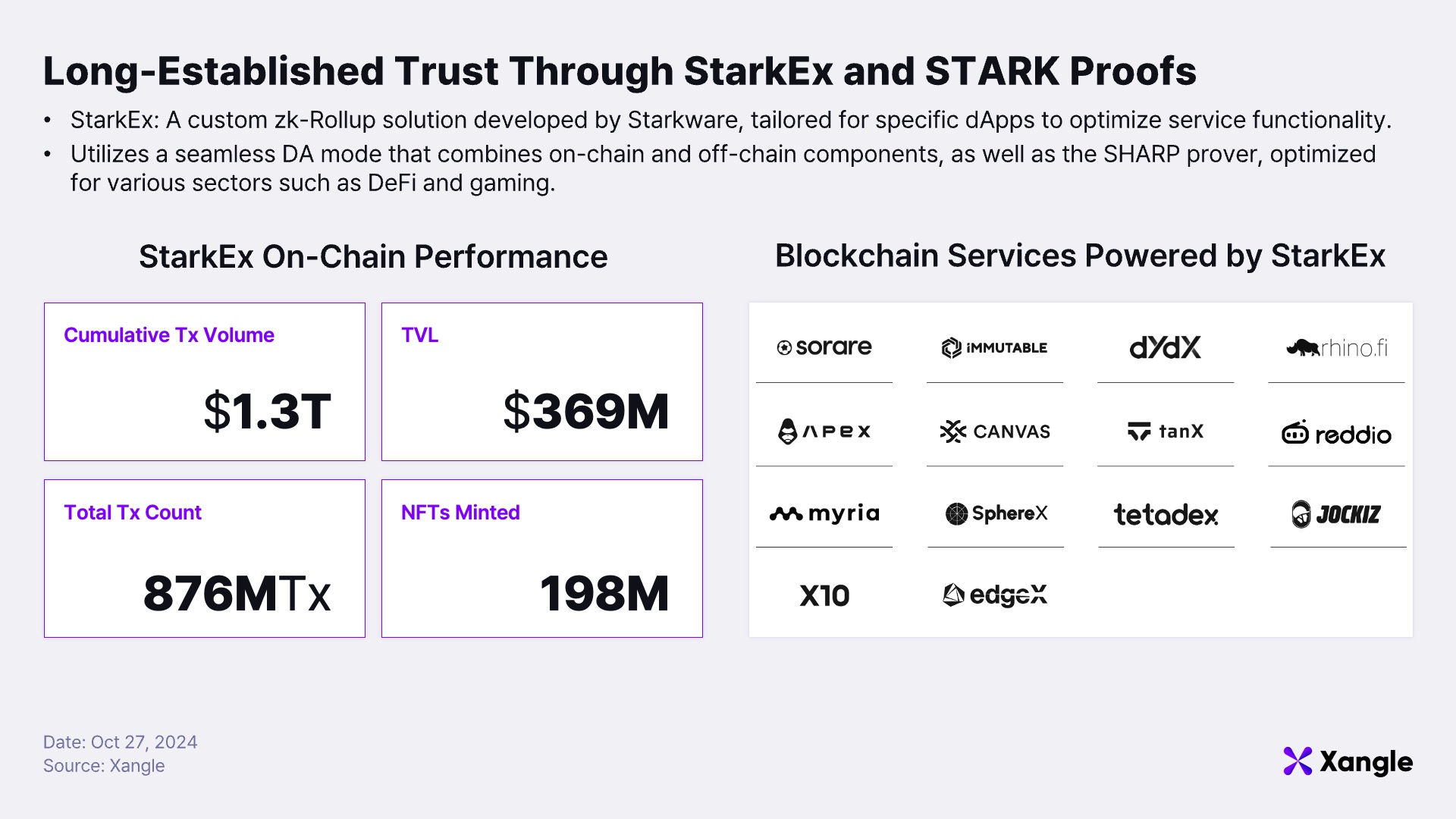
Even before launching Starknet, StarkWare had established itself as a trusted player in the blockchain industry through STARK proofs and a variety of scalability solutions. Among its achievements is StarkEx, a permissioned, application-specific scaling engine designed by StarkWare to provide optimized rollup solutions tailored to the unique requirements of individual applications. StarkEx has enabled major blockchain projects such as dYdX (derivatives trading), Immutable X(NFT minting and trading), and rhino.fi (a DeFi platform) to build independent rollup-powered service environments. For example, dYdX’s integration with StarkEx significantly reduced trading fees and minimum trade sizes while enabling instant trade execution and real-time balance updates, thereby delivering a dramatically improved user experience for decentralized exchanges. These success stories have demonstrated StarkEx’s ability to enhance scalability and security for applications. To date, StarkEx has facilitated over $1 trillion in cumulative transaction volume, processed more than 570 million transactions, and supported the minting of over 120 million NFTs, cementing StarkWare’s STARK technology as a proven engine for scaling and securing applications. With the launch of Starknet, StarkWare has extended its vision, addressing Ethereum’s scalability and security challenges using STARK proofs while building its own ecosystem. Starknet introduces features such as Native Account Abstraction and comprehensive support for developer tools and SDKs, overcoming limitations of both Ethereum and other Layer 2 solutions.
2-2. Advancing user-centric innovation: A faster, easier L2 experience
Starknet has garnered attention for processing up to 857 TPS, significantly expanding Ethereum’s capacity as a ZK rollup. The platform also prioritizes user experience, most notably by implementing Native Account Abstraction. Unlike Ethereum’s traditional account model, Starknet's accounts are inherently designed as smart (contract) accounts based on account abstraction. This innovation enables users to manage assets more securely and enjoy enhanced usability without relying solely on private keys and public key pairs.
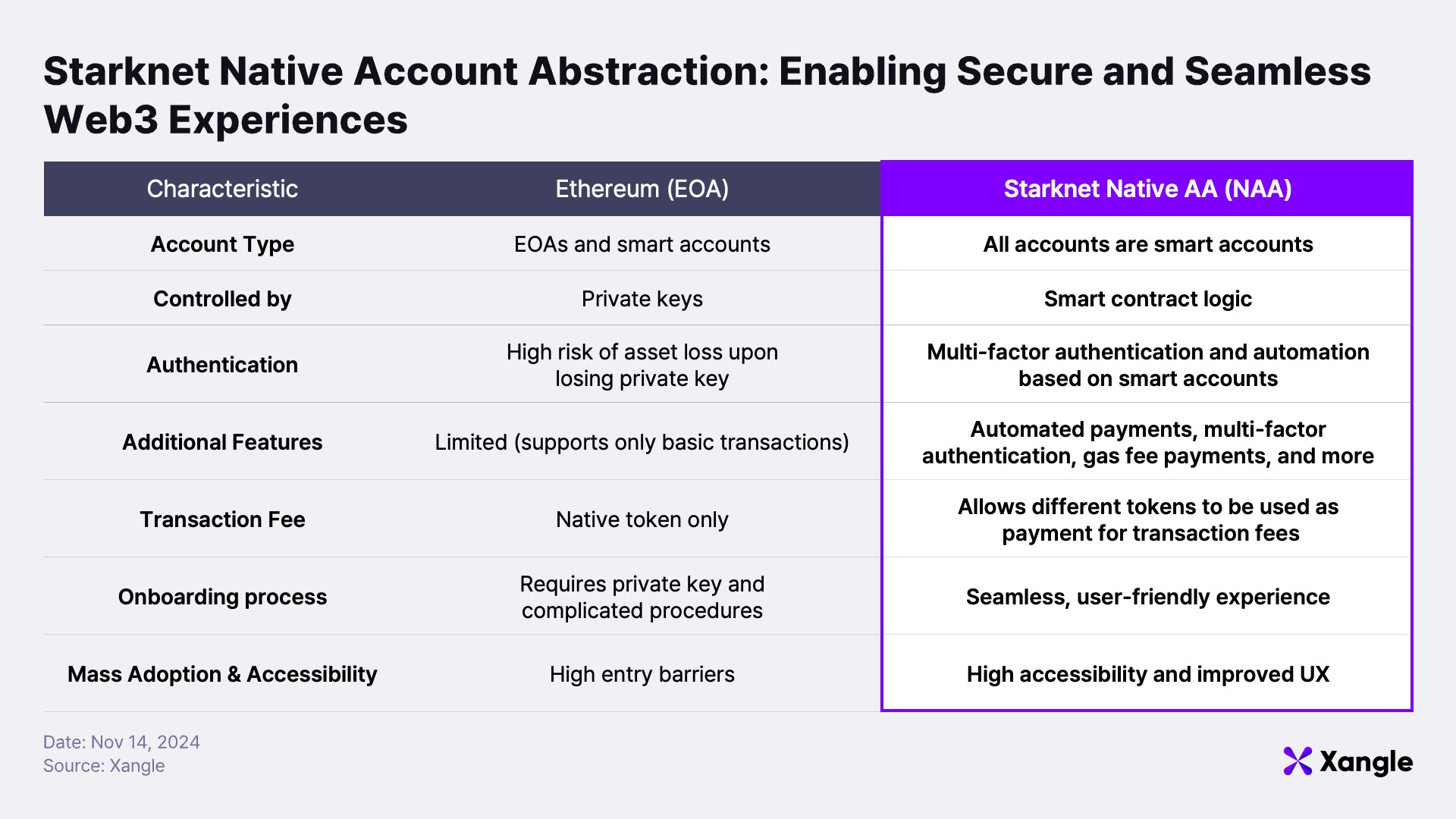
Under Ethereum’s conventional EOA (Externally Owned Account) model, ownership and authorization of accounts are tied to cryptographic key pairs. Private keys are mandatory for every transaction, requiring accurate signatures to move assets or verify ownership. In contrast, Starknet’s abstracted account model emphasizes account addresses over key pairs. Transaction validity is determined by confirming the originating account address, simplifying authentication processes while maintaining security. This model also facilitates advanced automation features, making it ideal for various applications.

Visa's experiment with Starknet's NAA
Visa, recognizing the potential of Starknet’s NAA, recently conducted an experiment on the platform to develop an auto-payment solution for self-custodial wallets. This solution enables users to securely hold assets while easily setting up automated payments, a functionality that is not supported on Ethereum. Starknet’s account model makes such innovations possible, overcoming the limitations of existing blockchain infrastructures and providing Web2-like user experiences.

Starknet’s development roadmap reflects its dual focus on enhancing performance and user experience. In Q3 2024, Starknet introduced parallel processing and block packing technologies, achieving 857 TPS and marking a significant milestone. These updates reduced block creation and finalization times while offering developers more flexible storage options and data structures, improving both blockchain efficiency and developer experience (DX). In Q4 2024, Starknet plans to roll out $STRK token staking and introduce Stateless Compression, a feature aimed at optimizing fees and enhancing decentralization. Looking ahead to Q1 2025, Starknet will implement Stateful Compression, further reducing fees and improving user experience (UX). Additionally, the platform will transition the Cairo programming language to LLVM to boost both performance and DX. By Q2 2025, Starknet aims to achieve 2-second block times, improving transaction processing speeds while introducing a decentralized sequencer architecture to enhance system stability and decentralization. Future updates will focus on gasless transactions and flexible data storage, continuously addressing user and developer needs to create a seamless blockchain experience.
2-3. Enhancing Cairo development with SDKs and zkEVM
Cairo, the primary development language of Starknet, is a smart contract programming language designed to maximize the potential of STARK-based technology. Cairo not only simplifies the implementation of complex program logic but also optimizes the proof generation process inherently through its built-in characteristics. This allows developers to focus solely on their core business logic without the need to address the complexities of proof optimization. Although Cairo is a purpose-built language for STARK proofs that requires new learning, its syntax, inspired by Rust, eases the onboarding process for developers familiar with low-level programming languages. This approach reflects StarkWare’s efforts to mitigate the learning curve for developers accustomed to non-EVM ecosystems, such as Solana and Cosmos, where Rust is commonly used.
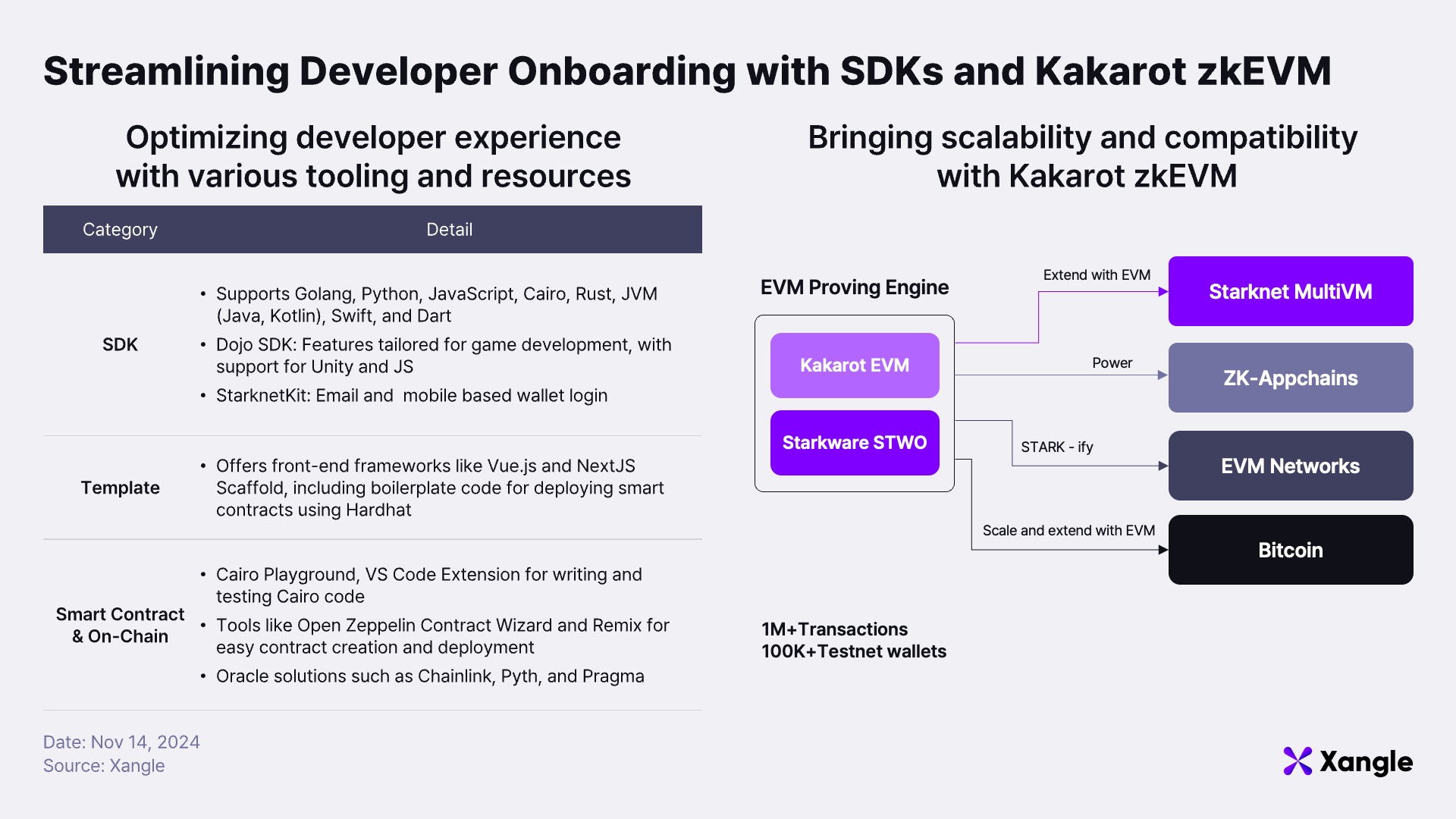
Starknet provides an extensive support system, including SDKs and development tools that enable seamless on-chain integration for developers unfamiliar with Cairo. These SDKs, available in multiple languages such as Starknet.js, Starknet.py, and Starknet.rs, support a broad range of popular programming languages, including Golang, Python, JavaScript, Rust, JVM (Java, Kotlin), Swift, and Dart. This diversity allows developers to build dApps using their preferred languages. Frontend and smart contract development are further streamlined with templates like Vue.js and Next.js Scaffold, while tools such as OpenZeppelin Contract Wizard and Remix simplify contract creation and deployment. Oracle solutions like Chainlink, Pyth, and Pragma provide reliable external data access for dApps requiring off-chain data integration.
The Kakarot zkEVM offers scalability and compatibility for developers familiar with Solidity, enabling them to leverage Starknet without significant changes to their existing tech stack. Kakarot, an EVM-compatible virtual machine built using Cairo, allows smart contracts written in Solidity to run on Starknet without requiring additional learning or modifications. This compatibility enables seamless deployment of Ethereum or EVM-compatible contracts on Starknet, empowering developers to continue using familiar tools and workflows. Kakarot’s roadmap includes important milestones. In 2024, Starknet’s mainnet will implement MultiVM functionality, followed by the introduction of ZK-EVM appchains and block verification for Ethereum-compatible chains in 2025. By 2026, Kakarot aims to extend ZK-EVM technology to the Bitcoin network, further broadening its applicability across blockchains.
Kakarot zkEVM is designed with a modular architecture that facilitates easy maintenance and auditing while supporting scalability and EVM compatibility in diverse environments. When integrated with StarkWare’s STWO prover, Kakarot functions as a unified proving engine capable of delivering high-speed, cost-efficient ZK-proof performance. This combined engine supports not only Ethereum Layer 2 solutions but also multichain environments, zk-appchains, and even the Bitcoin network, enabling seamless interoperability across multiple networks. This infrastructure makes Kakarot zkEVM a compelling solution for scaling and securing decentralized applications across blockchain ecosystems. Its performance has already been demonstrated on testnets, processing over 1 million transactions and onboarding more than 100,000 wallets, underscoring its potential for widespread adoption.
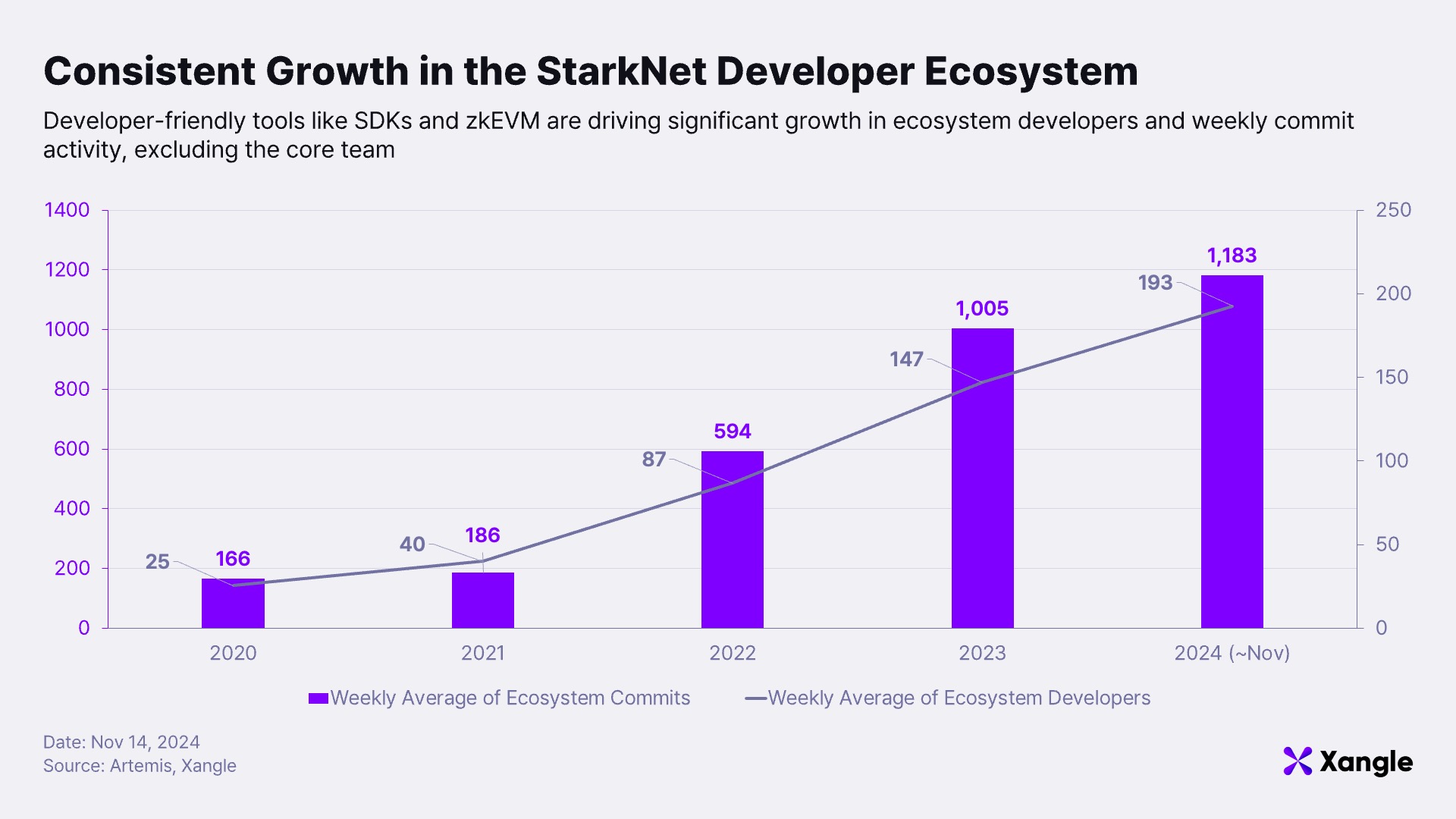
Starknet’s efforts to build developer-friendly infrastructure have translated into significant growth within its ecosystem. The average weekly number of developers has risen from 166 in 2020 to 1,183 as of November 2024, while weekly average commits have increased from 25 to 193 during the same period. These metrics highlight the robustness of Starknet’s builder ecosystem. With the progress of the zkEVM roadmap, it is expected that existing EVM-based applications, developers, and users will find it even easier to onboard onto Starknet.
2-4. Building customized appchains with modular layers
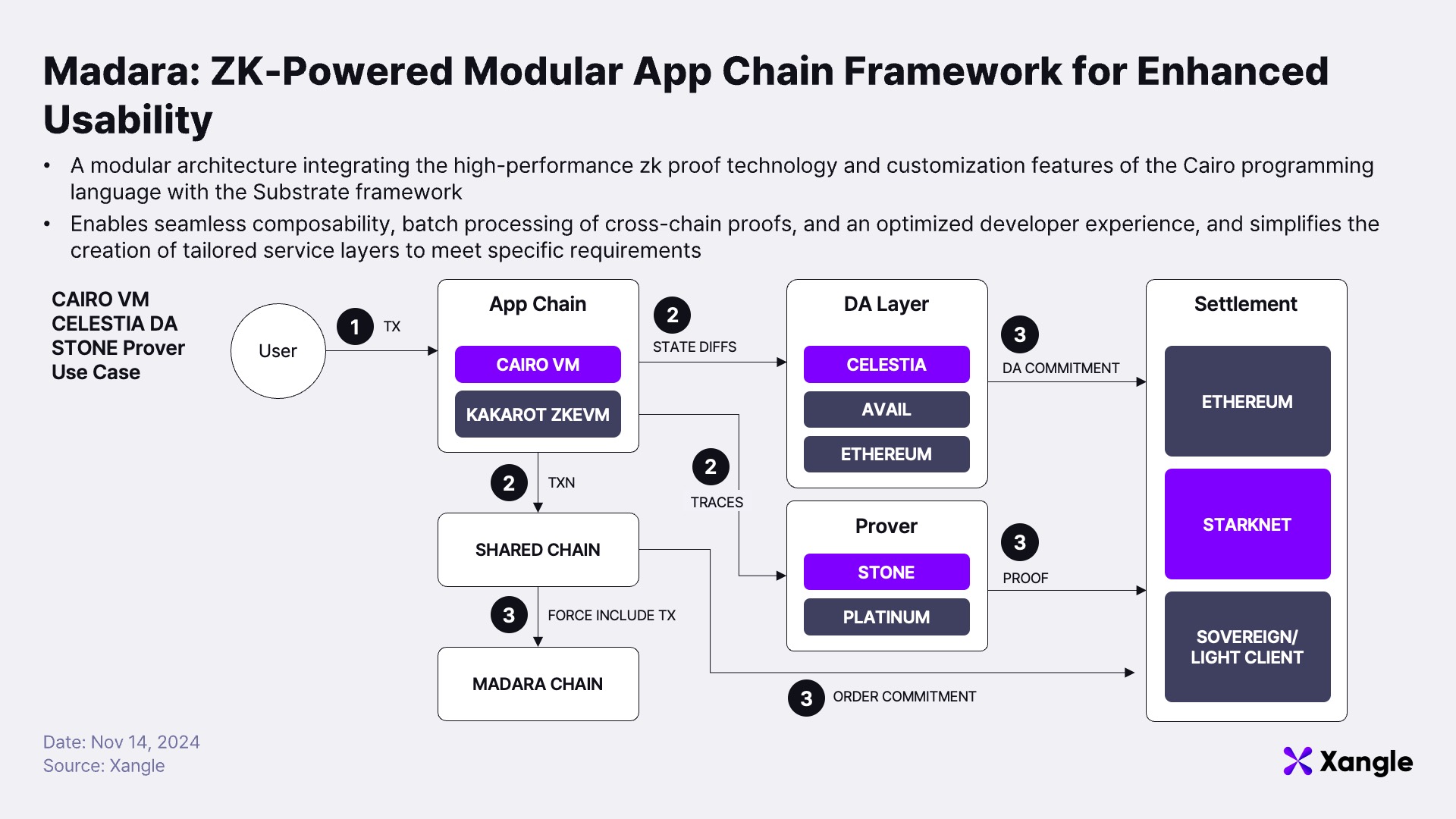
Starknet introduces the concept of appchains and L3s, enabling developers to create independent and tailored blockchains optimized for specific projects. At the forefront of this initiative is Madara, a modular appchain framework designed to provide robust customizability and ZK-proof capabilities using the Cairo programming language. Inspired by the Substrate architecture employed by Polkadot, Madara is designed to maximize flexibility and scalability. Madara allows developers to freely configure key blockchain components, including the appchain virtual machine (VM), data availability layer (DA Layer), prover layer, and settlement and consensus layers. It supports various VM options, including the Cairo VM, and integrates with multiple DA layers such as Celestia and Avail, ensuring reliable and flexible network data management. Additionally, provers like STONE and PLATINUM enable batch proofing across chains, significantly reducing verification costs. For settlement, developers can leverage a dual-layer approach using Ethereum and Starknet, optimizing security and reliability for specific applications.
This modular architecture allows Madara to address scalability challenges while providing custom configurations tailored to application-specific needs. Its ability to meet demands such as data availability, reduced verification costs, and cross-chain composability makes it particularly well-suited for industries like DeFi, gaming, and financial services, which require high transaction throughput and real-time responsiveness. As Web2 services in these sectors increasingly transition to Web3, appchains are becoming a preferred solution. Madara’s efficient ZK-proof functionality and flexibility make it easier for applications to create optimized chain configurations, potentially driving further growth of the Starknet ecosystem.
3. Starknet Ecosystem: Scaling New Heights Through Technology and Usability
3-1. Paving the way to a global blockchain hub through ecosystem campaigns and Bitcoin integration

Starknet has been actively strengthening its developer and user base through large-scale ecosystem campaigns such as DeFi Spring and Catalyst. The grant program is divided into two primary categories: the Seed stage and the Growth stage, offering tailored support for projects at different stages of development. Of particular note, the Catalyst program operates with a budget of approximately 20M $STRK. This approach supports the discovery of new projects and the advancement of existing dApps, enhancing the diversity and vitality of the Starknet ecosystem. These initiatives serve as a driving force for Starknet’s evolution into a more comprehensive and inclusive blockchain ecosystem.
In addition to Ethereum, StarkWare is also pursuing the expansion of Starknet into the Bitcoin network through the implementation of OP_CAT. This functionality, which was deactivated in 2010, allows for the introduction of complex scripts and smart contracts on Bitcoin. Once reactivated, StarkWare plans to integrate STARK proof technology into Bitcoin, enhancing scalability and security while enabling safe asset transfers between Bitcoin and Starknet. To support this endeavor, StarkWare has allocated $1 million for OP_CAT research, aiming to expand its user base beyond Ethereum into Bitcoin’s ecosystem. As Bitcoin holds the largest market cap and exerts significant influence globally, this initiative positions Starknet to play a leading role in the nascent Bitcoin Layer 2 ecosystem, unlocking substantial growth potential.
3-2. Key dApps and the evolving Starknet ecosystem
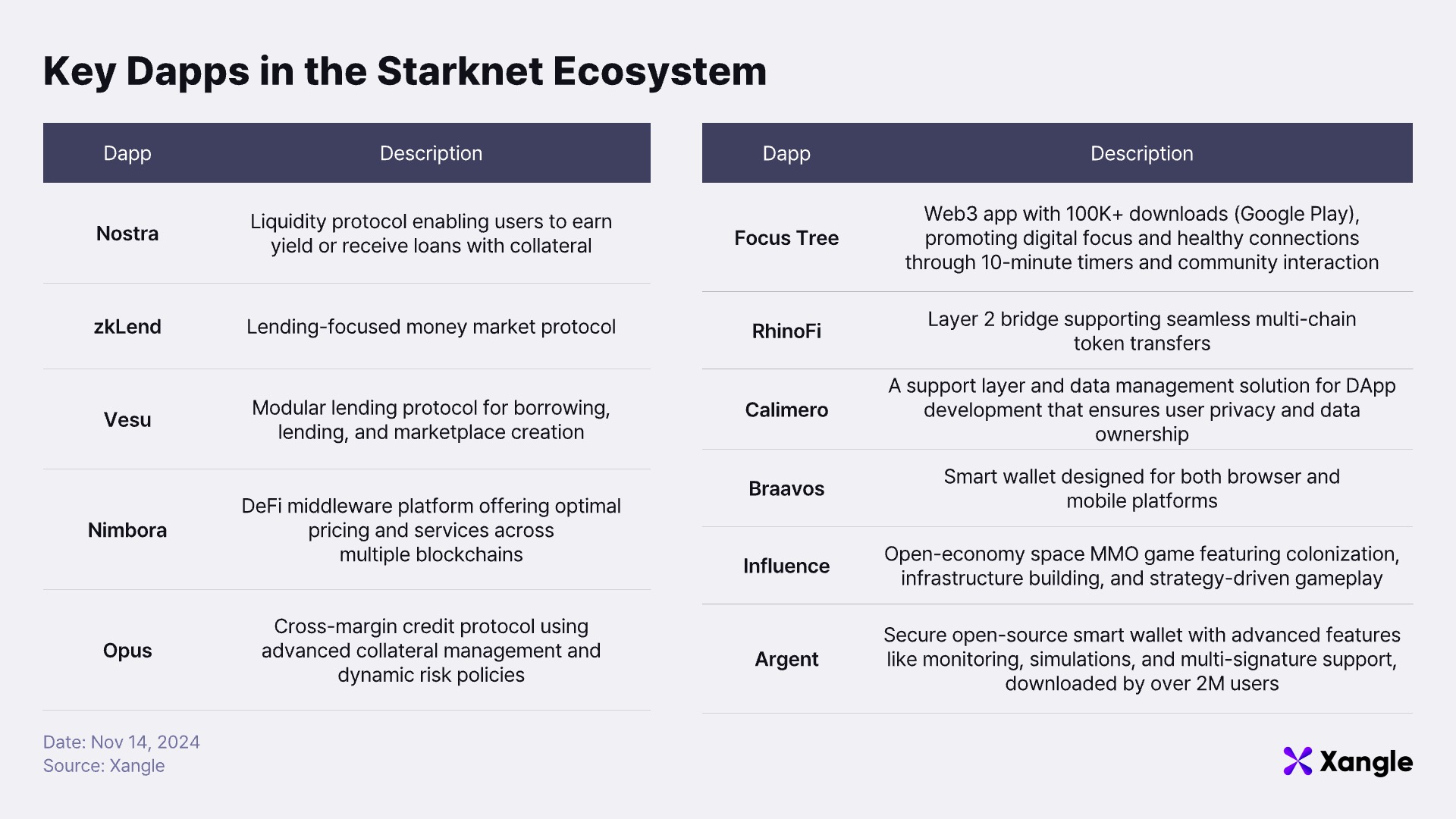
Starknet’s dApp ecosystem is currently centered around DeFi applications, largely due to the onboarding of numerous DeFi projects through two iterations of the DeFi Spring program. However, Starknet is actively diversifying its ecosystem. Through initiatives like the Gaming Committee, it is attracting gaming projects, while consumer applications like Focus Tree are bringing real-world utility to Web3 by helping users enhance digital focus. Privacy-focused solutions like Calimero, which leverage ZK technology, and smart wallet solutions powered by account abstraction (AA) enhance user experiences with high security and advanced functionality, creating a more attractive environment for both developers and users.
Nevertheless, support for Starknet from major multichain products remains limited. This is likely due to the stabilization and implementation phases required for ZK technology before achieving broader adoption. Additionally, Starknet’s primary programming language, Cairo, presents an initial onboarding challenge for developers. However, Cairo’s Rust-like syntax offers a significant advantage, enabling developers from Rust-based ecosystems like Solana, Aptos, and Sui to adapt quickly. Designed as a ZK-optimized language, Cairo is expected to deliver faster and more efficient performance compared to EVM-based frameworks. If Starknet successfully expands its collaboration with the Bitcoin ecosystem and continues leveraging ecosystem campaigns, it holds the potential to build one of the largest Bitcoin-integrated ecosystems. Over the long term, it will be important to monitor whether Starknet leverages its technological capabilities to secure unrivaled competitiveness in the ZK Rollup space in terms of liquidity and user base, while also fostering sustained growth of its developer ecosystem**.**
3-3. Tokenomics and community governance powering Starknet’s future
Starknet’s tokenomics model is designed to ensure long-term ecosystem growth and stability. The introduction of the $STRK token this year has become a critical element of network operations. Recently, through Starknet Improvement Proposals (SIP), a community-driven governance mechanism, the staking feature was approved and is scheduled for official implementation on the mainnet on November 26, 2024. This staking feature is a notable advancement, expected to enhance network security and encourage active participation from token holders. Once implemented, Starknet will be the first Layer 2 solution to offer direct staking functionality.

The launch of Starknet Staking
Participants in staking can choose to act as either validators or delegators. Becoming a validator requires a minimum stake of 20,000 $STRK, while delegators can delegate their $STRK tokens to validators to participate in the network. Delegator rewards are distributed based on the amount of staked tokens and the fee policy set by the validator. This system not only provides additional incentives for long-term $STRK holders and validators but also contributes to the network's stability by encouraging greater validator participation. Moreover, it is expected to enhance the token's value stability by fostering a committed and active community.
4. Final Remarks: Trusted Technology Driving Rollup Innovation
Starknet has established itself as a next-generation Layer 2 solution, leveraging its proven STARK-based zero-knowledge proof technology to address Ethereum's scalability challenges. Unlike other proof mechanisms, STARK proofs do not require trusted setups, offer quantum resistance, and deliver exceptional security and efficiency for processing large-scale transactions. These unique advantages have cemented Starknet and its developer, StarkWare, as highly regarded players in the blockchain space. However, achieving long-term ecosystem growth will require Starknet to further expand and capitalize on initiatives like Catalyst and DeFi Spring while forging successful partnerships. The recent initiative to expand into the Bitcoin network represents a significant opportunity for Starknet to grow beyond Ethereum and establish itself as a global blockchain hub. By combining its proven technical capabilities with ecosystem expansion efforts, Starknet has the potential to solidify its position as a leading rollup solution, driving innovation in the blockchain industry.