

Written by Dannie, LBank Labs Research team

Introduction
-
Real world asset (RWA)
Real world asset (RWA) tokenization involves transforming the value or ownership of tangible real-world assets, such as real estate, stocks, art, jewelry, as well as intangible assets like intellectual property, copyrights, and patents, into digital representations that can be traded or transferred with improved efficiency and security.
This is a promising technology that has the potential to bridge the gap between traditional finance (TradFi) and the crypto world. By tokenizing real-world assets, it is possible to bring the benefits of blockchain technology to a wider range of assets, making them more accessible and liquid. This could have a significant impact on the way we invest, trade, and manage our assets in the future.
The total value locked (TVL) of all RWA projects is currently ranked 10th, over $1 billion.
The TVL of RWA projects has surged since April 2023, growing by approximately 60%.
The popularity for the term “RWA” peaked on June 4th.
-
DeFi Yield Crisis
Off-chain → On-chain
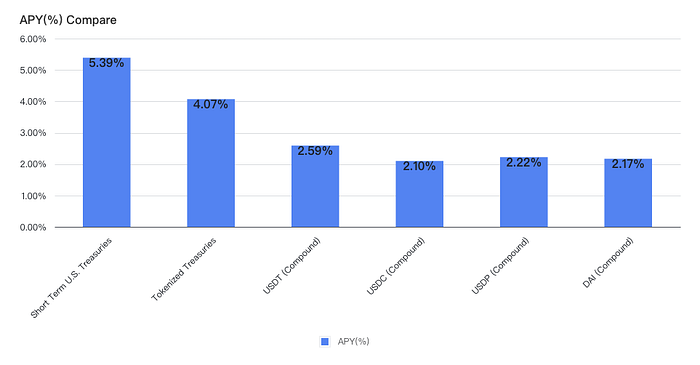
The 3-month U.S. Treasury bill yield has reached 5.39%, while the yield of web3 stablecoins is only over 2%. The yield of TradFi is significantly higher than the yield of on-chain crypto in the context of a sustained bear market and the Federal Reserve’s rising interest rates over the past year. Investors are more likely to pursue off-chain TradFi yields.
As DeFi infrastructure continues to mature and the cryptocurrency market faces a large outflow of funds, there is a growing need to allow on-chain crypto users to enjoy off-chain yields and provide crypto users with a wider range of investment options. This would benefit both on-chain and off-chain users, as on-chain users would be able to earn higher yields on their crypto, and off-chain users would be able to access new sources of capital.
On-chain → Off-chain
Traditional lending faces numerous challenges, driving an increasing demand for blockchain-based lending solutions. Some key challenges include:
- High transaction costs
- Lack of transparency
- Slow and inefficient processes
- Limited access to loan opportunities
This article discusses the following RWA subfields:
Tokenized Treasuries
On-chain Tokenized Treasuries can be categorized into two types:
- Major crypto projects manage their treasury funds strategically to balance risks and increase profitability. e.g., MakerDAO invests 500 million DAI in US Treasury bonds, Circle converts USDC reserves into cash and short-term US Treasury bonds, Tether holds over 100 billion USD worth of US Treasury bonds, and Mysten Labs uses a combination of cash and US Treasury bonds to manage their treasury funds.
- US Treasury bonds are known for their excellent liquidity and offering nearly 5% “risk-free” annualized returns, attracting a massive number of investors. As a result, some onchain projects act as a bridge for on-chain investors to invest in off-chain US Treasury bonds.
Here are four representative tokenized treasuries projects:
Ondo Finance
1. Funds
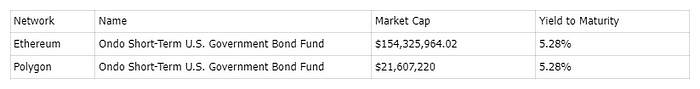
In early 2023, Ondo Finance launched a tokenized fund that allows stablecoin holders to invest in bonds and US Treasuries. The platform currently supports four investment funds: “the US Money Market Fund (OMMF, 4.5%)”, “US Treasuries (OUSG, 5.02%)”, Short-Term Bonds (OSTB, 5.39%), and High-Yield Income (OHYG, 7.33%). These investment funds are tokenized as RWAs.
On August 3rd, Ondo announced the launch of a new product called “USDY”, which offers an APY of 5%. USDY is secured by short-term US Treasuries and bank demand deposits, bringing institutional-grade low-risk yield opportunities exclusively to users outside of the United States.
2. Flux Protocol
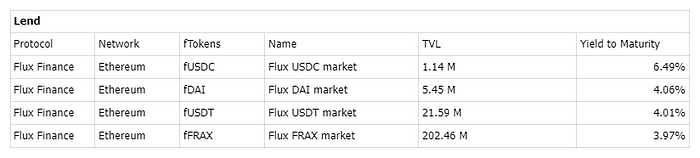
The Ondo Finance team also developed the decentralized lending protocol “Flux Finance”. The protocol offers a variety of tokens available for lending, with lenders providing USDC, DAI, USDT, and FRAX, and borrowers using OUSG as the only collateral asset. KYC-ed OUSG holders can deposit into Flux Finance for lending, while lenders can provide stablecoins to earn yield.
Users can only access and utilize these financial products after completing the KYC/AML process.
Background
The company has raised $34 million in funding from investors, including Pantera Capital, Founders Fund, Coinbase Ventures, and Tiger Global. The team members have extensive backgrounds in various institutions and protocols such as Goldman Sachs, Fortress, Bridgewater, and MakerDAO.
Keywords
- Compliance (AML & KYC)
- Institutional-Grade
- Restricted to qualified purchasers
- Redemptions are processed on banking business days
Business Structure
1. Ondo’s Tokenized Fund — OUSG is the most popular product
a. $OUSG investors send stablecoins to the fund’s Coinbase account, using the stablecoins to purchase $OUSG token.
b. The fund employs Coinbase to convert stablecoins into USD and transfers to Clear Street.
c. Clear Street is hired to provide primary brokerage services and to hold and trade the fund’s assets.
d. The investment manager instructs Clear Street (CS) to execute trades, settle transactions, and custody the fund’s assets in the CS account.
2. Flux Finance
To increase the utilization of $OUSG, investors can utilize their $OUSG holdings as collateral to borrow other tokens, such as $USDC, $DAI, $USDT, and $FRAX. They can earn interest in borrowed tokens through fTokens.
OpenEden
OpenEden is an on-chain U.S. Treasury bond protocol that enables users to invest in U.S. Treasury bills through the web3 native token, $TBILL, with an expected annualized yield of 5.3%, allowing holders of stablecoins to benefit from sustainable yields. By holding $TBILL, users can buy U.S. government debt without being restricted by U.S. trading hours, and have the flexibility to redeem $TBILL 24/7. T-Bill refers to a short-term debt issued by the U.S. government with a maturity of less than one year.
Background
In 2022, the OpenEden team was founded by Jeremy Ng and Eugene Ng, both of whom are former senior regulatory executives from Gemini exchange.
Keywords
- Ideal for B2B
- Redemptions 7/24 (typically takes 1–2 business days in TradFi)
- Institutional-Grade
- Compliance (AML & KYC)
Business Structure
OpenEden T-Bill Vault is a protocol that enables stablecoin holders to generate yields from their US Treasury bills investments. The majority of the assets are allocated to short-term US Treasury bonds, while a small portion of USDC is retained on the blockchain to facilitate instant withdrawals at any time. Users have the option to mint $TBILLs using their $USDC in their wallets, which they can then deposit into the vault to start earning yields.
Matrixdock
Matrixdock is a digital assets platform that provides institutional and accredited investors with transparent access to tokenized real-world assets (RWA) with an immutable record of ownership, daily Proof-of-Reserve and full bankruptcy remoteness.
The first product introduced on the platform is $STBT (Short-term Treasury Bill Token), which incorporates a risk-free interest rate based on the short term US Treasury bills. The underlying assets of $STBT consist of 6-month US Treasury bills and repurchase agreements collateralized by US Treasury bills. 1 $STBT is traded at the price of 1 USDC.
$STBT is an Ethereum-based token that complies with the ERC-1400 standard (security token), representing ownership of companies, debts, or other financial assets. The issuance and redemption of these tokens are managed by Matrixdock, and a contract whitelist mechanism ensures that transfers and trades are restricted only among authorized account holders on the Matrixdock platform.
As of August 2nd, the APY for investing in $STBT is 4.77%.
Background
Matrixdock is a digital assets platform launched by the Singaporean asset management company Matrixport.
Keywords
- Institutional and accredited investors
- Daily Proof-of-Reserve, secured with Chainlink
- Compliance (AML & KYC)
- ERC-1400
- Redemption: up to 5 New York Banking Days
Business Structure
- Investors provide $USDC or $USDT to the $STBT issuer, who mints the corresponding amount of $STBT tokens through a smart contract.
- The STBT issuer then converts the received $USDC into fiat currency.
- The fiat currency is then entrusted to a third-party custodian, who purchases short-term bonds that mature within six months through a traditional financial institution’s US Treasury bond trading account or invests it in the reverse repo with the Federal Reserve.
TProtocol
TProtocol built on top of $STBT, using T-Bills as its underlying asset. Allowing retail investors to access the product. It provides DeFi-composable on-chain T-Bill tokens to meet the demand for risk-free yield in the DeFi ecosystem.
Background
Keywords
- $TBT → permissionless, retail investor friendly
- $wTBT → interest-bearing token
Business Structure
TProtocol has three types of tokens: $TBT, $sTBT, and $wTBT. $TBT is permissionless, allowing retail investors to participate. The design of $wTBT enhances the capital efficiency of rebasing tokens.
- $sTBT: it is a rebasing token whose price is always $1. $sTBT issued by Matrixdock. Only KYCed high net worth individuals or institutions are able to purchase.
- $TBT: it is short for T-Bill token, $TBT is fully backed by permissioned $sTBT. It’s a permissionless rebasing token. The minting and redemption price will always be $1. Retail users can mint $TBT with $USDC.
- $wTBT: it is a non-rebasing token that can be converted to TBT or the other way around. wTBT and TBT can be converted into each other without any fees. They are equivalent mathematically. It is permissionless. The purpose of wTBT is to enable TProtocol to be incorporated into existing DeFi protocols as most of the DeFi protocols do not support rebasing tokens. Currently, liquidity mining is supported on the Aptos, Optimism (OP), and zkSync networks.
Lending
RWA lending commonly features a default mechanism known as Tranche structuring. RWA protocols assume that defaults can occur at any time, especially in the case of credit loans, and therefore, it is necessary to design how asset losses will be allocated to the lenders in case of default. RWA protocols classify lenders and deposits based on their risk preferences. This RWA lending classification typically includes two main categories: senior tranches and junior tranches.
- Senior Tranches: Senior tranches represent a form of financing that can prevent losses but offers limited returns. Investors in senior tranches are prioritized in receiving repayments and are less exposed to potential losses. They are designed to be safer and cater to risk-averse investors who prioritize capital preservation.
- Junior Tranches: Junior tranches form a pool of funds that offer higher returns but are more susceptible to absorbing losses first in case of defaults. Investors in junior tranches take on higher risk and potentially higher rewards, but they are less protected compared to senior tranches.
TrueFi
TrueFi is an uncollateralized lending protocol powered by on-chain credit scores, maximizing capital efficiency for borrowers and earning rates for lenders. Currently, it focuses on providing uncollateralized lending services to crypto-native trading firms in stablecoins. TrueFi plans to gradually explore extending its services to companies and individuals in the future.
Background
TrueFi, a decentralized lending protocol, was developed by TrustToken, the same company that introduced the stablecoin TUSD. TrueFi has raised over $30 million in funding from various investors.
Keywords
- Credit risk management model
- Credit lending
- Targeting institutional and high net worth individuals.
- KTC & AML
Business Structure
- TrueFi DAO Pools
-Main participants:
- $TRU stakers: are responsible for due diligence, loan approval, and management, allowing them to earn high APY on their collateral and additional voting rewards. When whitelisted borrowers request a loan, TRU stakers bear the primary risk of defaults. Their staked $TRU will be the first to be reduced to compensate for the losses incurred by the lending pool in case of default.
- Lender/liquidity provider : In TrueFi, liquidity providers (LPs) deposit assets into the lending pool to earn interest. Liquidity providers can deposit stablecoins like $USDC, $USDT, $TUSD, or $BUSD into the respective pools and receive tfToken representing their principal and interest.
- Borrower: the main borrowers include crypto-native trading firms, trading platforms, market makers, DeFi projects, high net worth individual investors, and asset management companies. The majority of loans are provided to crypto-native trading firms and market makers. Future plans include expanding lending services to corporations and individuals.
-Risk management:
- $TRU stakers have the authority to vote on each loan, and for any loan to be approved during the voting round, it must receive more than 15 million votes, with at least 80% of the votes in favor of “YES.” After the “$TRU stakers Voting” is successfully passed, the Rating Committee makes the final decision on whether to disburse the loan.
- TrueFi stakers and TrueFi rating committee are responsible for risk management and use the “TrueFi credit worthiness score.”
- KYC: AML & KYC requirement. Applicants are required to have a minimum of $10 million in net assets with no debt.
-The default response strategy is as follows:
- The foundation’s 5 million $TRU tokens and $TRU stakers will absorb 10% of the losses incurred due to the default.
- Liquidity providers will take the remaining default losses.
- Default events will be publicly announced, and all privacy options for borrowers will be revoked.
2. TrueFi Capital Markets
The key difference between TrueFi Capital Markets and TrueFi DAO Pools lies in the management structure. In TrueFi Capital Markets, the managers are third-party institutions. For Managed Portfolios, the qualification of the “Manager” is thoroughly reviewed. It also requires detailing the strategy and requirements for the proposed portfolio. The final decision on the approval of the “Manager” is made by TrueFi DAO.
$TRU (Incentive for staking)
- a portion of the protocol fees
- 10% of all interest
- Stakers may receive TRU rewards as incentive for staking, but as of May 2023 stkTRU rewards have also been turned off
Maple Finance
Maple Finance is a protocol that has been in development for three years, with its core business revolving around lending and institutional credit services.
- Lending services for $USDC and $wETH: the lending business is managed by independent centralized pool managers. These managers are responsible for overseeing aspects such as loan recipients, loan limits, interest rates, and strategies.
- Cash management: Maple Finance introduced a lending pool for investing in US Treasury bonds (1–14 day short-term Treasury bills) with an APY of 4.7%. The platform supports non-US DAOs, offshore companies, and other entities within the restrictions set by Maple Finance for investing funds in its designated pools.
- In order to reduce defaults, Maple Direct has been launched, focusing on providing financing solutions to Web3 enterprises that require compliant funding. The lending desk will offer loans in $USDC and $USDT stablecoins, and will accept $BTC, ether $ETH, and stake $ETH as collateral.
Maple Finance employs professional credit reviewers who conduct thorough credit assessments of borrowers. Its uncollateralized loans mainly target institutional borrowers and corporate entities. The platform offers multiple lending pools, each managed by credit professionals acting as pool delegates. These representatives are responsible for evaluating credit limits, negotiating loan terms with borrowers, and actively managing the loan portfolio.
Background
As of now, Maple Finance has successfully raised over $13 million.
Keywords
- Target institutional borrowers and corporate entities
- Uncollateralized loans
- Pool delegate
- The Maple team decides who can become a Pool Delegate
- Default rate: 2%
Business Structure
Borrowers create their profiles and submit their preferred loan terms and quote requests on Maple. Pool delegates review the proposed loan terms and conduct due diligence if they are interested. Both Maple DAO and pool delegates conduct thorough KYC and AML checks.
Key participants
- Borrowers: They are primarily institutional borrowers, such as hedge funds, exchanges, or market makers. These borrowers obtain uncollateralized loans based on their reputation and pay interest during the loan period
- Liquidity provider: Lenders deposit funds into the liquidity pool to earn interest. Lenders can claim the interest they have earned at any time, but they can only withdraw their principal after the loan is completed. The withdrawal period is currently set at 180 days.
- Pool Delegates: They are experienced financial professionals responsible for conducting due diligence on borrowers and leading the entire underwriting process. Pool Delegates are required to stake MPL (Maple token), and as a reward, they receive a portion of interest income and loan origination fees. All Pool Delegates must go through Maple’s rigorous whitelisting process. They also provide funding to the pool’s insurance to cover part of the risk. To ensure loan safety, Pool Delegates are required to stake a minimum of $100,000 worth of USDC-MPL (the native token of the project) as liquidity pool collateral, which will be used to repay the lenders in case of loan defaults.
Loan risks are managed by the pool’s delegates, who charge a certain management fee as compensation, while liquidity providers enjoy lending rates while assuming smaller default risk. 10% of the total interests go to Pool Delegates, and the rest to LPs (Liquidity Providers). Maple DAO controls the project’s funds.
$MPL (Incentive for staking)
- Transaction fee discount
- Community governance
- Dividends from lending interests
- Receive airdrop incentives
- Engage in liquidity mining
GoldFinch
Goldfinch Finance is an undercollateralized lending platform that provides borrowing entities with access to on-chain deposits. These borrowing entities can then use these deposits to provide loans to off-chain entities. Borrowers on Goldfinch Finance are either lending enterprises themselves or debt funds that provide loans to lending enterprises. Currently, the risk exposure to Goldfinch Finance is primarily focused on developing economies in Asia, Africa, and South America.
Background
Goldfinch has raised a total of $37 million in funding from three rounds of investment.
Keywords
- Credit loan
- Decentralized auditing (not yet launched)
- Institutional client composition: Emerging markets and debt funds.
Business Structure
— Deposit side:
- Junior Pool: Backers are responsible for providing funds for the Junior Pool and assess borrower credibility, conduct due diligence themselves, and can provide first-loss capital. It is a high-risk pool where losses are first absorbed in case of default, but backers can additionally earn 20% of the low-risk pool’s profits. Backers can expect an APY of approximately 15%-18%, plus an additional 20%, resulting in a total APY of over 40%.
- The senior pool is a low-risk pool that is funded by other liquidity providers. In the event of a default, the senior pool receives payments first. However, if the junior pool cannot fully cover the default, the senior pool will be affected. The APY for the low-risk pool is around 7.8%.
— Borrowing side: Borrowers, such as debt funds and fintech companies, provide their loan proposals and mainly avail USDC lending services.
— Key participants: Borrowers, Backer, Liquidity provider, auditor
— Risk management
— Auditor system
- The auditor verifies whether the borrower is who they claim to be without assessing their creditworthiness.
- Auditors need to stake $GFI to qualify for verification (to motivate them to do the right thing). Decentralized auditing is not yet released, core contributors play the role of auditors now.
- Once decentralized auditing is operational, it will be composed of an auditor pool. Auditors will be randomly selected from the pool, and at least 6 votes in favor with 0 votes against are required for approval. Auditors need to complete KYC and have a UID.
— Backers conduct due diligence themselves, and the high risk incentivizes them to be cautious.
— All borrowers are real-world entities that exist in the real world.
$GFI (Incentive for staking)
- 10% of interest
- governance token
Centrifuge
Centrifuge aims to lower financing costs for small and medium-sized enterprises and provide stable income sources for DeFi investors. As an RWA technology provider, Centrifuge offers lending tools for major protocols like MakerDAO and Aave. Tinlake, an application of Centrifuge, is a decentralized financing and lending platform controlled by smart contracts deployed on the ETH blockchain. Within Tinlake, enterprises can collateralize assets such as invoices, collateral, and media royalties to generate NFT tokens.
Centrifuge has its own substrate blockchain called Centrifuge Chain, which benefits from the security of the Polkadot network. Currently, Centrifuge has a total of 17 RWA asset pools. Each financing project creates a lending pool with different risks and returns. Centrifuge Chain successfully won the 8th slot auction of Polkadot in January 2022. Currently, the platform is deployed on the Ethereum blockchain, but there are plans to migrate it to its own independent blockchain.
Background
Currently, Centrifuge has raised over $10 million in funding.
Keywords
- Infrastructure
- Collateralized loan
- Compliance (Centrifuge has put considerable effort into compliance, adhering to the legal structure of asset securitization in the United States)
- Countries under U.S. sanctions are not allowed to invest in Centrifuge’s products.
Business Structure
-
Tinlake
Tinlake is a dApp from Centrifuge that allows entities to tokenize RWAs such as invoices and collateral loans into NFTs. These NFTs can then be used as collateral in Tinlake pools to access financing and liquidity from the on chain ecosystem. Borrowers can use physical assets as collateral to obtain stablecoins from on-chain investors.
For each Tinlake pool, the risk and return of the underlying physical collateral are effectively split to meet the needs of different investors. The structured products consist of two ERC20 tokens: $DROP and $TIN.
- $TIN, known as the “risk token,” represents the junior, floating-rate portion of the Tinlake pool. Compared to the DROP token, TIN token holders have lower priority in profit dividends from the asset pool but have higher exposure to both returns and risks. $TIN tokens typically have higher risk and higher returns.
- $DROP, referred to as the “yield token,” represents the senior, fixed-rate portion of the Tinlake pool. DROP token holders have priority in profit dividends from the asset pool but carry relatively lower exposure to risks, e.g., loan defaults. $DROP tokens have lower risk and lower returns.
2. Centrifuge Prime
Centrifuge has released Centrifuge Prime, a service and technology suite to help DeFi protocols support RWA. Centrifuge Prime includes a compliance legal framework designed for DAOs and DeFi protocols, a sophisticated tokenization and issuance platform, decentralized and objective credit risk and financial reporting, and a diverse range of asset classes and issuers, addressing issues related to KYC and legal recourse.
3. Relationship with MakerDAO
Centrifuge hosts multiple funding pools related to MakerDAO: The senior capital comes from Maker Vault, while the junior capital is provided by the asset Originator “BlockTower”, with $37.33 million and $97.17 million in each pool, respectively. The total funds related to MakerDAO in the Centrifuge ecosystem amount to approximately $161 million, representing 80% of Centrifuge’s TVL.
$CFG
- On-chain governance
- Pay for on-chain transaction gas fees
TradeFi
“TradeFi” refers to the use of financial instruments by companies to secure financing and facilitate international trade and commerce. It could be any financial tool that ensures a business has a steady cash flow. For example, invoice financing is considered a form of TradeFi.
Defactor
Defactor is bringing real-world assets to DeFi, or decentralized finance, and unlocking working capital for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) worldwide. Currently, the asset categories financed within the Defactor include invoices, trade, and inventory.
Background
Huawei has collaborated with Dogpatch Labs in Ireland to host the “Huawei International Scale-Up Programme,” and Defactor, as a local Web3 startup in Ireland, participated in this support program.
Keywords
- Only accept invoices, trade, and inventory as collateral
- To SMEs
Business Structure
Asset Originators (AO) need to apply on Defactor and submit relevant legal documents to prove the reliability of their assets. Defactor will assess the assets through its risk control system and audit committee, and provide four ratings: Prime+, Prime, Prime-, and SubPrime.
Users who are interested in providing liquidity funds as investors also need to comply with the platform’s KYC and AML requirements. After approval, they will be allocated a dashboard where they can allocate funds to selected liquidity pools with different risk profiles, supporting crypto payments.
Defactor only supports tokenization of three types of real-world assets:
- Accounts Receivable / Factoring (Note: Factoring is a financial transaction in which a company sells its accounts receivable to a third party at a discount).
- Trade Financing
- Inventory Financing
$FACTR (Incentive for staking)
- Asset Originators need to hold $FACTR to access the Defactor platform and its services. The token will be locked in smart contracts throughout the financing period to reduce circulation.
- Staking: Token holders who stake $FACTR will receive rewards.
- Buyback Mechanism: Defactor will allocate a portion of its income for regular buybacks of $FACTR tokens.
Polytrade
Polytrade aims to unlock liquidity that is locked in stalled invoices, thereby assisting global SMEs in improving their working capital. Additionally, the platform seeks to maximize the earning potential of stablecoins from on-chain users.
They achieve this by prepaying (using stablecoin payments) the invoices that SMEs enterprises receive from larger companies. Polytrade provides insurance coverage for each asset through insurance companies like AIG, Mercury, and Coface, ensuring protection for all its investors.
Background
As of now, Polytrade has raised over 5 million US dollars in funding.
Business Structure
Polytrade helps SMEs improve their working capital by purchasing their accounts receivable. Accounts receivable are the amounts that SMEs are owed by their customers (the core enterprises in supply chain finance are usually the key companies that play a central role in the supply chain and have significant influence on the operations and development of other businesses).
When an SME sells goods or services to the core company, the SME may not receive payment immediately. Polytrade purchases the SME’s accounts receivable at a discounted value, which provides the SME with early funding to address cash flow challenges. The discount amount represents Polytrade’s actual revenue.
$TRADE
- Staking rewards
- Usage rewards
- Settlement tool
Stablecoins
MakerDAO
1. Cost Reduction and Efficient Treasury Management
MakerDAO used to rely heavily on USDC as collateral for DAI issuance. This led to criticism that MakerDAO was bearing the centralized risk of USDC while Circle, the issuer of USDC, was profiting from the stablecoin issuance. MakerDAO has since reduced its reliance on USDC and increased its use of RWA as collateral. This has led to a reduction in USDC issuance and increased revenue for MakerDAO.
MakerDAO has established a complex legal framework to ensure that its purchase of US Treasury bonds complies with all applicable laws and regulations.
During periods when short-term US Treasury yields exceed 5%, Maker increases the DSR (DAI Savings Rate) to 3.49%. Stablecoin holders, including USDC, can exchange their stablecoins 1:1 for DAI through the PSM. Maker then redeems these stablecoins for USD to invest in US Treasury bonds and gain higher returns, potentially creating a win-win situation for both MakerDAO and stablecoin holders.
However, a drawback is that increasing the DSR also leads to higher loan rates, which reduces Maker’s competitiveness in the collateral lending market.
2. RWA lending — Collaboration with Centrifuge
Compared to purchasing on-chain US bonds, the volume of Real-World Asset (RWA) loans is relatively small, totaling $256 million.
—— Centrifuge offers a direct tool and marketplace for users in need of purchasing Real-World Assets.
- MakerDAO lends out DAI stablecoin.
- Borrowers deposit collateral into Vaults to obtain DAI loans.
- Collateral types include both cryptocurrency assets and RWAs.
Centrifuge charges a fee of 0.4% to assist these projects in obtaining loans. However, due to the higher possibility of default compared to government bonds, these projects carry a greater counterparty risk overall.
——Currently, MakerDAO’s Real-World Assets (RWA) are primarily divided into four categories:
- Real estate loans: RWA-001
- MakerDAO’s USDC holdings invested in projects custodied by Coinbase, with an APY of 1.5%: RWA 014
- Tokenized assets, such as real estate and structured credit: RWA 002
- Short-term bond ETFs: RWA 007
Even with collateral, there is still a risk of default. In the past week, the treasury managed by Harbor Trade has been in a state of suspension, with approximately $2.1 million of assets in default. In response to this situation, the MakerDAO community initiated a vote last week, which ended on 20th July, and the community unanimously agreed to stop providing additional loans to the credit pool managed by the financial technology company, Harbor Trade.
This shows that despite MakerDAO’s efforts to manage risks in its RWA portfolio, there can still be challenges and potential defaults associated with these assets. Proper risk management and community decisions are crucial to addressing such situations in the DeFi ecosystem.
$MKR & RWA lending
- Better decisions in the $DAI network -> higher interest generation -> purchase and burn more $MKR -> reduced circulating supply of $MKR -> $MKR appreciation ⬆️
- Mistakes in the $DAI system -> system incurs losses -> additional $MKR minted to cover losses -> increased circulating supply of $MKR -> $MKR depreciation ⬇️
When mistakes or unforeseen events occur, the Maker portfolio can face significant shortfalls. To cover these losses, new $MKR tokens are minted, which can lead to a decrease in the price of $MKR. Better lending decisions and increased demand for loans result in an increase in the price of $MKR held by its holders.
Real Estate
Propy
Propy is a blockchain-based real estate platform that enables buyers, sellers, their agents, and agents to conduct traditional real estate transactions entirely onchain. It allows for buying offers, payments, and contracts to be uploaded onto the blockchain. The platform has processed over $4 billion in transactions in collaboration with real estate partners across the United States, claiming to save 10 hours of paperwork for each transaction.
Key features of Propy include:
- Support for cryptocurrency and NFT-based real estate transactions, allowing properties to be bought and sold using digital currencies and in the form of non-fungible tokens.
- Simplification of domestic and international property buying experiences, eliminating fraudulent transactions, and reducing the need for third-party intermediaries in real estate transactions.
- The platform facilitates quoting, purchasing agreements signed through DocuSign, secure wire payments, and issuance of property deeds.
Propy has collaborated with the government office of South Burlington, USA, to transfer property ownership records onto the blockchain. This collaboration enables homeowners to transfer their properties to company names efficiently and entirely online, utilizing blockchain technology for swift and secure transactions.
Background
Keywords
- Using blockchain as a database
$PRO
- Paying platform fees
- Property transactions
Tangible
Tangible is a platform that allows users to purchase valuable physical commodities using the stablecoin Real USD. Tangible partners with world-leading suppliers to offer a variety of commodities, including art, fine wines, antiques, watches, and luxury items.
The platform provides a marketplace for issuing and trading TNFTs (Tangible Non-Fungible Tokens), which represent ownership of these commodities. Tangible Labs, the legal entity behind the project, facilitates the real-world purchase and custody of these commodities.
In real estate, for example, Tangible establishes Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs) for the acquisition and management of properties. These SPVs are dedicated legal entities created specifically for this purpose.
Background
Tangible was founded in 2021.
Business Structure
Purchase from Tangible (Top Figure)
- Users browse and purchase items on Tangible’s marketplace. Smart contracts process the item price, and storage fee where relevant.
- The TNFT is minted and sent to the user’s wallet, for safekeeping, trading, or selling.
- Concurrently, Tangible completes the purchase of the physical item from Tangible’s Supplier Partner.
- The purchased item is shipped to a Tangible Vault, where it is safely stored.
- During redemption, Tangible collaborates with logistics companies to ensure the safe transportation of the physical assets.
Secondary Market of Tangible (Bottom Figure)
- Users again browse and purchase items on Tangible’s marketplace.
- The existing TNFT is transferred to the purchaser’s wallet.
- Concurrently, USDC tokens are sent from the Buyer’s wallet to the Seller’s wallet. Smart contracts process the trading fee, item purchase fee, and storage fee where relevant. The item remains in storage unless the Buyer decides to redeem it.
- 33.33% of the Tangible DAO fees are used to buy and burn TNGBL tokens, and the remaining 66.66% is distributed in USDC to Tangible 3,3+ stakers.
Currently, Tangible mainly deals with four categories: gold, wine, watches, and real estate. For transactions and storage of gold bars. Regarding real estate, Tangible creates native Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs) specifically tailored to each property. These SPVs manage the properties by seeking tenants, collecting rents, or overseeing maintenance. All properties are leased, and rental income is paid to TNFT holders in the form of USDC.
Tangible Fraction
Tangible allows large assets to be divided into smaller fractions (ERC-721), enabling more investors to purchase a portion and share ownership of the asset.
- Original TNFT: At the beginning, there is a complete TNFT representing a specific tangible asset, such as a piece of jewelry or a real estate property.
- Tangible Fractions: The original TNFT is divided into smaller fractions, for example, splitting it into 100 portions, with each fraction representing 1% ownership.
- Transferred to buyers’ wallets: These divided Tangible Fractions are then sold to different buyers. Each buyer purchases a portion, for instance, buying 5 fractions means they own 5% of the asset. The purchased Tangible Fractions are transferred to the respective buyers’ digital wallets.
- Original TNFT locked: To ensure transparent and reliable transactions and ownership of Tangible Fractions, the original TNFT is locked in a smart contract vault. At this stage, the original TNFT cannot be redeemed or sold.
- Redemption or sale: To redeem or sell the original TNFT, all Tangible Fractions must be collected, meaning all buyers collectively hold 100% ownership. Once all Tangible Fractions are gathered, the original TNFT can be unlocked, allowing changes in ownership or the option to sell.
Tangible Fractions offer a flexible investment approach, enabling investors to purchase different proportions of the asset based on their preferences.
Token
- $TNGBL: Staking $TNGBL allows users to earn rewards.
- $TNFTs: Tangible Non-Fungible Tokens represent ownership of tangible assets. They can be traded and transacted on the secondary market.
- $USDR Stablecoin: USDR is a stablecoin used on the Tangible platform. It is pegged to the US dollar, ensuring a fixed value. Users can use USDR to purchase goods and conduct transactions.
Synthetic Assets
Synths & RWA
Synthetic assets are included within the category of RWAs. If equity-based RWAs become popular, they may resemble SNX (Synthetix), which imitates stock prices using oracle price feeds. Similarly, RWAs can cater to speculative investment demands through tokenized securities and oracles. Nevertheless, unlike RWAs, synthetic assets do not facilitate the actual transfer of funds between on-chain and off-chain.
Synthetic assets act more like a trading tool, reducing barriers to investing in various financial market assets. RWAs are currently perceived as more stable and may not offer extremely high returns compared to other investment tools.
Synthetix
A Synthetic Asset is an investment product that mimics the performance of other financial instruments. We don’t need to physically own the underlying asset; instead, you invest in a product that tracks the price of that financial instrument.
Business Structure
Advantages:
- Synthetic assets offer more flexibility since they are derived products linked to the prices of other assets. For example, they can provide inverse products, where the synthetic asset price rises when the price of the underlying asset falls. This allows for hedging or taking positions in both directions without needing to buy or sell the actual asset.
- Synthetic assets can enable users in one region to access financial products from another region. Additionally, they can make high-entry-barrier investment products more accessible by utilizing synthetic assets.
Disadvantages:
- Failures of off-chain oracle systems that provide price data can be a concern for synthetic asset platforms, as accurate and timely price feeds are crucial for maintaining the peg.
- Sharp fluctuations in the collateral assets can lead to impermanent loss for liquidity providers in synthetic asset protocols.
- Some synthetic asset platforms may have a lower leverage ratio, e.g., 0.25x, which might not suit all trading strategies or risk appetites.
- High collateralization ratios might be required to ensure stability, which can limit the capital efficiency of traders and liquidity providers.
The four main categories of Synths are as follows:
- Fiat Currency Synths:
- Precious Metals, Stocks, and Forex Synths
- Cryptocurrency Synths
- Inverse Cryptocurrency Synths
STO & RWA
STO (Security Token Offering) is another subset of RWA. RWAs involve the tokenization of real-world assets and bringing them onto the blockchain, while STO specifically refers to fundraising through the issuance of security tokens representing ownership in a company or other traditional financial instruments like bonds.
RWA products offer a more diverse range of options, varying degrees of returns cater to different risk preferences.
RWA has more opportunities for two main reasons:
- Current stagnant market conditions are causing lower returns for investors in blockchain, leading to a demand for higher risk-free returns.
- In 2018, DeFi infrastructure was not as well-established, lacking essential components like reliable oracles and token standards.
Token Summary
The following is a summary of token statistics related to RWA.