
Table of Contents
1. Algorand, the Blockchain Created by Silvio Micali, the godfather of cryptography
2. Algorand's Strengths: Robust Technology Contributing to an Enhanced UX
2.1. Dual Node Structure Improves Network Decentralization
2.2. Pure Proof-of-Stake System Enhances Algorand's Scalability
3. Algorand's Challenges: Collaborating with Less Sustainable Institutions and Countries, and Expanding the Ecosystem
3.1. Collaboration with Less Sustainable Organizations and Countries
3.2. Low Ecosystem Maturity
4. Algorand’s Resurgence: AlgoKit Facilitates Aggressive Marketing and Developer Onboarding
4.1. Aggressive Marketing and Expanding Target Market
4.2. Expanding Supported Languages and Simplifying Development Process with AlgoKit for Web2 Developer Onboarding
5. Notable DApps in Algorand
5.1. Folks Finance
5.2. Lofty AI
6. Closing Thoughts
1. Algorand, the Blockchain Created by Silvio Micali, the Godfather of Cryptography
Along together with Cardano and EOS, Algorand emerged as a prominent mainnet claiming to be a third-generation blockchain that could solve the blockchain trilemma. The project was founded by Silvio Micali, a distinguished MIT professor and a pioneering figure in cryptography. In 2012, he was honored with the Turing Prize for his groundbreaking contributions to Verifiable Random Functions (VRFs) and zero-knowledge proofs, which have now become widely used in the crypto industry. His profound expertise in cryptography has been instrumental in shaping Algorand's strong technical foundation.
However, Algorand's ecosystem growth has been slower than expected, despite its initial promising launch. Nevertheless, Algorand's technical strengths and the esteemed reputation of Silvio Micali have facilitated partnerships with various organizations and countries.
In this article, we will delve into a comprehensive analysis of Algorand’s technical strengths. Furthermore, we will examine the current challenges and explore potential opportunities that lie ahead for Algorand.
2. Algorand's Strengths: Robust Technology Contributing to an Enhanced UX
One of the key pillars of Algorand's strengths lies in its technical capabilities, which are backed by Silvio Micali's expertise in cryptography. This technical capability is a driving force behind Algorand's ability to provide a seamless user experience. In this section, we'll take a closer look at Algorand's technology.
2.1. Dual Node Structure Improves Network Decentralization
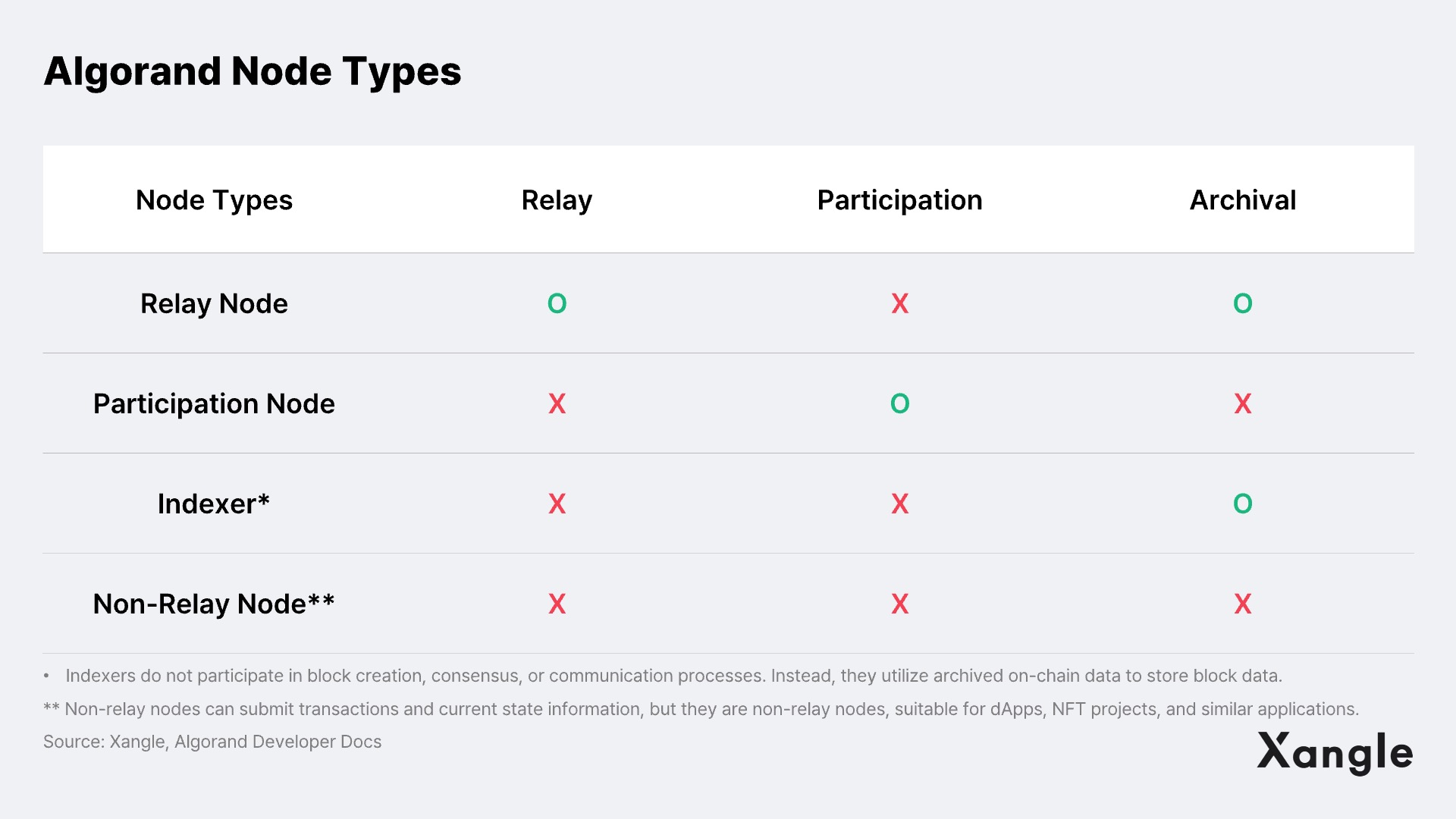
In its endeavor to solve the blockchain trilemma, Algorand adopts a structure that categorizes nodes based on their roles in relaying, participating in the consensus process, or archiving data. First, relay nodes do not partake in block creation and consensus. Instead, they serve as data interconnection points, relaying block data that has completed the consensus process at participating nodes. In other words, relay nodes are responsible for facilitating communication between nodes. They also serve as archives, storing blockchain data to speed up the process of block creation and consensus by propagating blocks between relay nodes.
A participating node is a node that engages in block generation and consensus based on the stake it holds. These participating nodes are also connected with several relay nodes and relay the consensus processes to the relay nodes. Unlike relay nodes, participating nodes do not archive all block data. Instead, they store the 1,000 most recently created blocks to ensure accurate validation. Indexers and record submission nodes, on the other hand, do not participate in relaying and consensus; they can be set up for their specific purposes, such as on-chain data usage and transaction submission. The structure of relay nodes and participating nodes is illustrated in the figure below.

<Number of Algorand participating nodes and staking ALGO volume, source: Metrics.algorand>
In addition, node decentralization is achieved through Algorand Foundation. While theoretically all nodes can participate, Algorand is currently moving towards a model where participating nodes can participate autonomously, and the number of relay nodes is gradually increasing under the management of the foundation. Since its establishment, the Algorand Foundation has been committed to geographically distributing relay nodes, which are operated by universities, non-profit foundations, financial institutions, and various other entities across multiple continents and countries. The foundation is also gradually increasing the number of relay nodes through programs such as the Pilot Relay Node Program and the Community Relay Node Program. As of 2Q 2022, the Algorand Foundation reported a count of 120 nodes, with plans to further increase this number in the future. As of July 24, there were 1,332 participating nodes, and the number is expected to grow over time.
2.2. Pure Proof-of-Stake System Enhances Algorand's Scalability
Algorand uses Pure Proof-of-Stake to improve scalability. The core cryptographic technology employed in the Pure Proof-of-Stake is the Verifiable Random Function (VRF). A VRF takes user input and generates a randomly generated output (hash) value. The output is unpredictable from the outside, and anyone can verify the validity of the output at any time using the VRF's public key. In other words, randomness is used to cryptographically protect the selected user while still allowing others to verify the randomness.
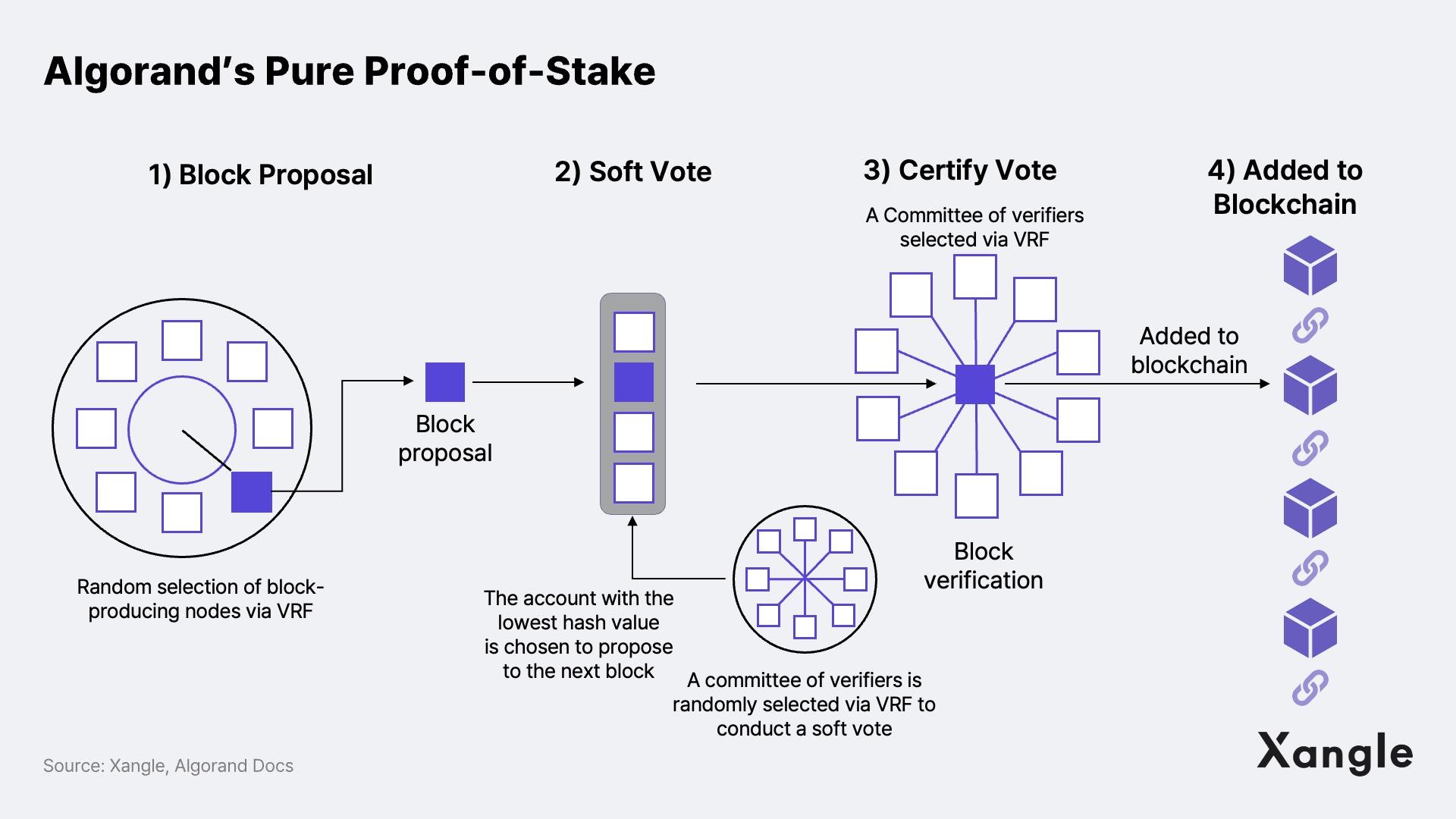
Proof of Stake consists of four steps: 1) Block Proposal → 2) Soft Vote → 3) Certify Vote → 4) Added to Blockchain. First, in the block proposal phase, nodes responsible for block generation and proposal are selected through the VRF. The selected node then proposes a block that records transactions and state values and propagates the proposed block with the VRF output, proving that the account is a valid proposer.
A single node is selected through VRF, though there is a possibility that multiple blocks may be proposed simultaneously due to concurrency issues or malicious nodes. To guarantee that only one block gets certified, the next step is to filter the number of proposals submitted in the soft vote phase down to one. First, a committee of 1,000 verifiers is randomly selected to conduct a soft vote using the VRF. The committee then compares the VRF hash values, and the account with the lowest VRF hash is chosen to propose to the next block.
Then the certify vote phase arrives with a new committee checking the block proposal for overspending, double-spending, or any other problems. Again, the committee members, who vote if the block is valid or not, are selected using the VRF. Once the block is considered valid as certified by the committee after a quorum is reached, the block is finally added on Algorand's blockchain.
Algorand’s consensus mechanism ensures instant block finality, with a block latency of about 3.3 seconds. Unlike other Proof-of-Stake chains that have to wait for the slots comprising the block to reach a checkpoint for block finality, a block is not generated in a slot in Algorand’s consensus protocol. Instead, it finalizes the consensus process block by block, which allows it to achieve faster finality compared to other PoS chains.
Another advantage of PPoS is that it does not necessitate node participants to lock up their tokens, eliminating the risk of slashing. However, from a protocol standpoint, the absence of token lockup can lead to increased selling pressure, and there is no mechanism in place to punish malicious nodes.
2.3. Participation Key and Rekeying
Algorand ensures the security of node participants and user convenience by employing participation keys and rekeying techniques.
First, Algorand provides a set of keys to node participants for voting and proposing blocks, and these are called participation keys. To take part in the consensus process, the account has to be marked online. However, this introduces a risk of having to reveal their account spending key to participate. To address this security concern, Algorand grants participation keys to participants in the consensus process. Participants generate and register for a participation key for a specific number of rounds, which allows them to generate a temporary key for each round and delete the temporary key used to participate after the process is complete.
Using participation keys offers significant advantages, particularly in protecting the tokens of node participants even if a participating node is compromised. In addition, participation keys and temporary keys for each round are deleted from the key file as each round is completed, ensuring continuous security of the blockchain and preventing attacks on previous blocks.
Rekeying, on the other hand, is a technique that allows users to change their private keys without changing their public address. This process uses Cryptographic Multisignature technology and involves the following steps:
- First, the user generates a new key pair (public and private keys).
- The user creates a transaction requesting a rekey to the Algorand network. This transaction includes the new public key.
- Network participants validate the key change transaction and cryptographic multisig. This verifies the validity of the transaction, and that the owner of the new key is the owner of the old key.
- Once the key change transaction is authorized, the old private key is replaced with the new private key.
Algorand streamlines the rekeying process to make it more convenient for users. Users can change their private keys simply by sending a rekey transaction without having to create a new wallet, even if their current private keys are exposed. This feature proves particularly beneficial for institutions and countries facing challenges in arbitrarily changing their public keys to maintain transaction continuity.
3. Algorand's Challenges: Collaborating with Less Sustainable Institutions and Countries, and Expanding the Ecosystem
3.1. Collaboration with Less Sustainable Organizations and Countries
Leveraging Silvio Micali's reputable background and technical strengths mentioned earlier, Algorand has adopted a strategy of attracting institutional and national demand to expand its ecosystem. Notably, Algorand has approached countries and institutions that were skeptical of PoW due to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) concerns by promoting a low-carbon green blockchain.
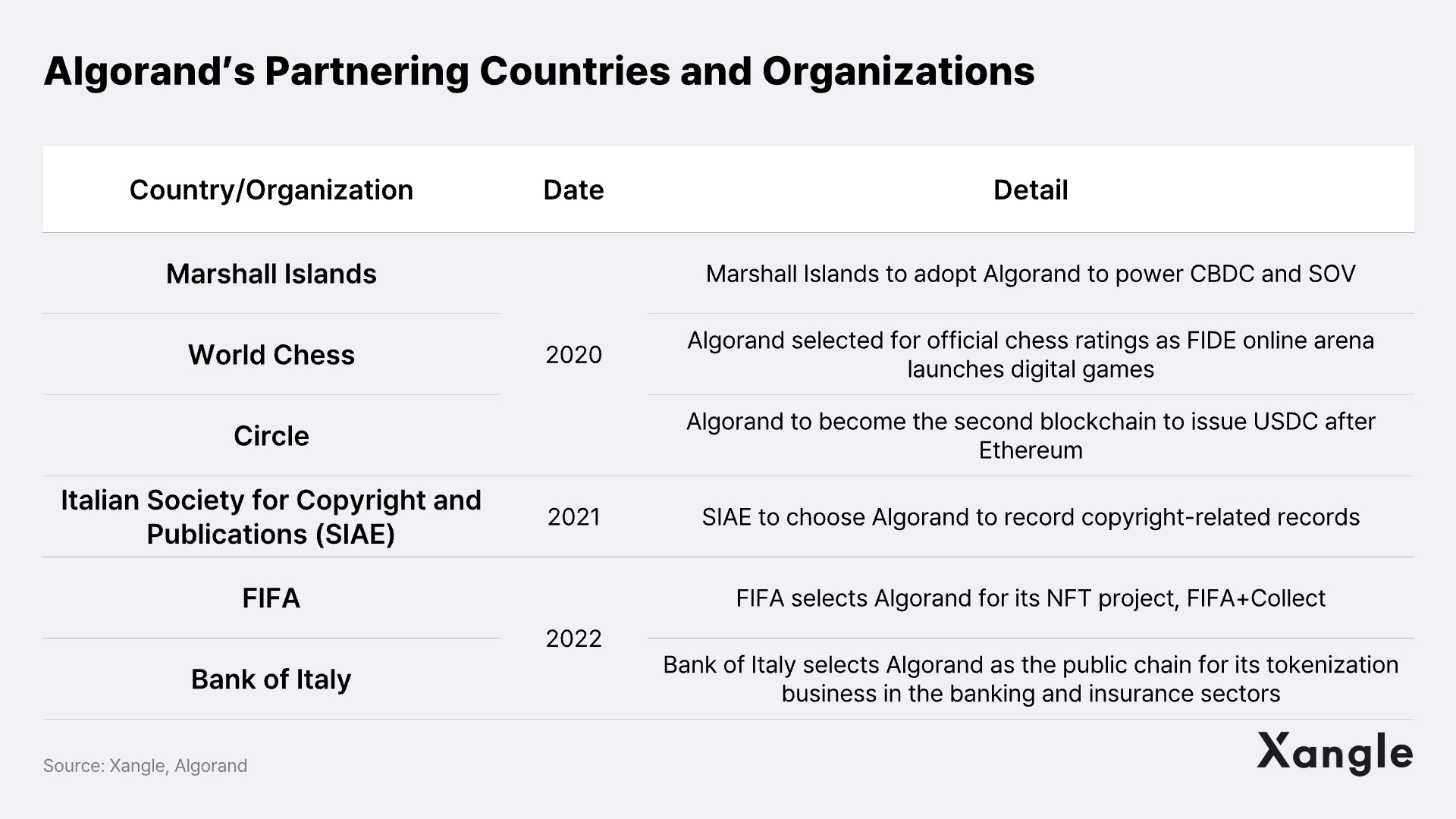
Through these efforts, Algorand achieved significant milestones, such as winning the Sovereign (SOV) project, a Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) project in the Marshall Islands in 2020, and became the second blockchain to issue USDC after Ethereum. Furthermore, Algorand entered into an agreement with the International Chess Federation's FIDE Online Arena to record games on the blockchain. In 2021, the Italian Society for Copyright and Publications (SIAE) chose Algorand to record copyright-related records. Moreover, in 2022, the Bank of Italy selected Algorand as the public chain for its tokenization business in the banking and insurance sectors. One of the most noteworthy partnerships is with FIFA in May 2022, FIFA announced a sponsorship with Algorand to launch the FIFA World Cup NFT project, FIFA + Collect. This initiative allows FIFA to create and sell “Moments” from previous World Cups, including the 2022 World Cup in Qatar.

<Example of an NFT Moment from the 2022 World Cup in Qatar, Source: FIFA+Collect>
However, the outcomes of the partnership have been mixed for Algorand, as it appears to have encountered challenges in sustaining collaborations with certain organizations and countries. For instance, the SOV (CBDC) project in the Marshall Islands has not seen any significant updates or progress reported since 2020. FIFA+Collect experienced a temporary surge in user engagement during the World Cup in Qatar, but this increased interest did not translate into sustained engagement in the long run. As for the collaboration with the Chess Association and the SIAE, there have been no recent updates or news since the announcement, making it difficult to confirm whether the data is actually being recorded on the blockchain as intended.
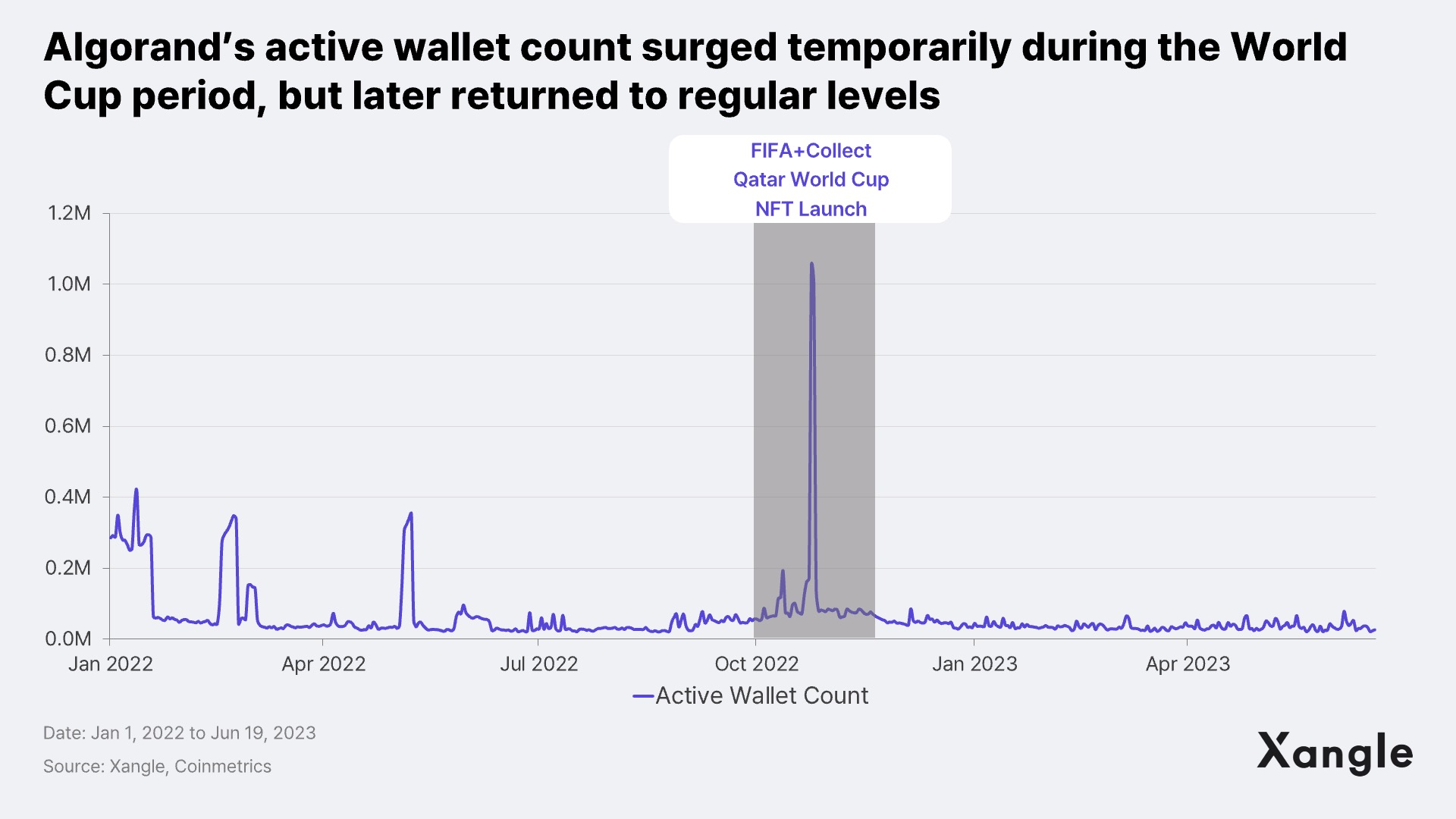
3.2. Low Ecosystem Maturity
Algorand is currently facing challenges in gaining traction among developers and users. Unlike other cryptocurrencies that have adopted widely accepted standards such as EVM and ERC-20 tokens, Algorand uses its own state machine, AVM (Algorand Virtual Machine), and ASA (Algorand Standard Asset). Instead of using Solidity, the programming languages used on Algorand are TEAL and PyTEAL, which are unique to the platform, making less familiar and accessible to developers.
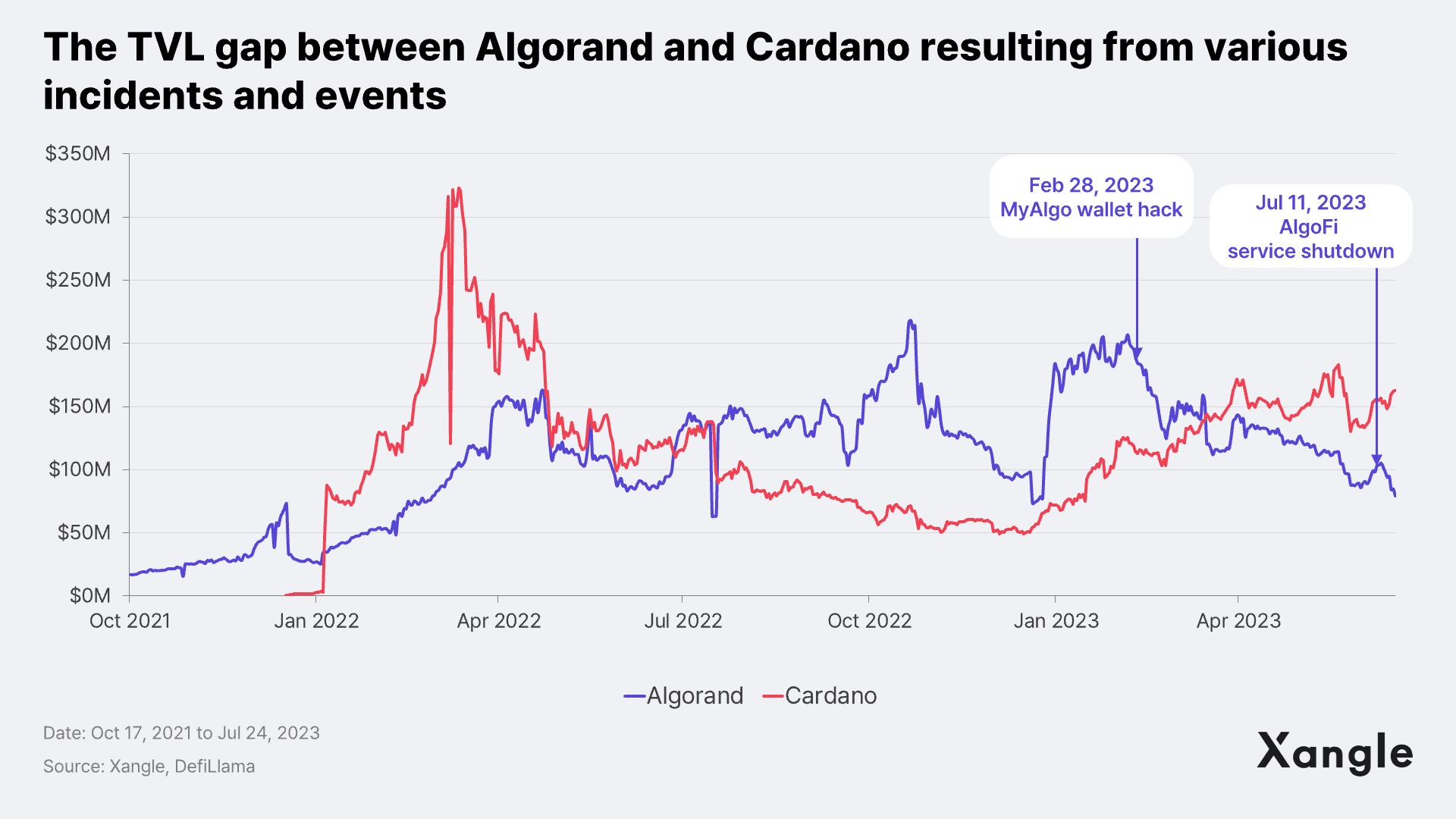
Comparatively, the DeFi ecosystem on Algorand lags behind its third-generation blockchain counterpart, Cardano, which has witnessed a substantial 300% year-over-year increase in TVL since 2023. In contrast, Algorand's TVL metrics have experienced declines due to various incidents, including the MyAlgo hack and the shutdown of AlgoFi. The shutdown of AlgoFi was particularly impactful, as it accounted for 55% of Algorand's TVL before the shutdown, significantly impacting Algorand’s DeFi ecosystem.
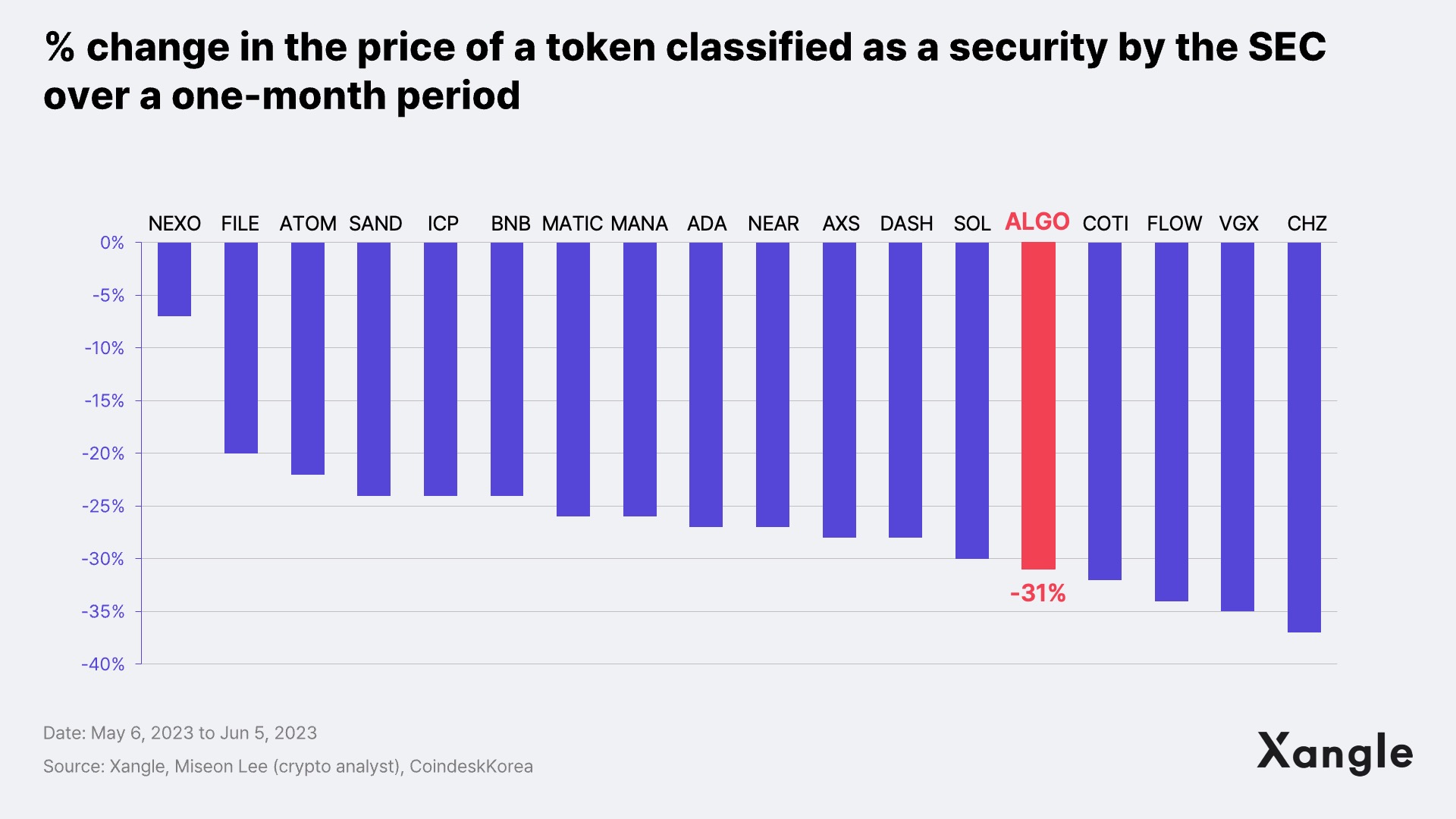
The NFT ecosystem in Algorand is even worse. Despite the presence of NFT projects such as PIXELS, M.N.G.O, and AlgoRaccoon, Algorand's total trading volume is currently at $39M, according to CryptoSlam. This volume is similar to Solana's 7-day trading volume of $42M. Even the highly anticipated FIFA+Collect is also underperforming, with a total volume of $552K. Adding to these challenges, Algorand recently received securities ruling from the SEC, causing a sharp decline in its token price and potentially exacerbating capital flight from the Algorand ecosystem.
4. Algorand’s Resurgence: AlgoKit Facilitates Aggressive Marketing and Developer Onboarding
4.1. Aggressive Marketing and Expanding Target Market
Lately, Algorand has recognized the significance of this bottom-up ecosystem and has taken a proactive approach to market itself. In a recent interview with Real Vision Crypto, Staci Warden, CEO of the Algorand Foundation, reflected on the company’s previous approach, where they believed that the strength of their technology alone would naturally attract developers and users. However, realizing the need for a change, the company appointed Jessica Tsai Chin, formerly from Nike, WhatsApp, and Apple as CMO, signaling the commencement of a marketing drive.
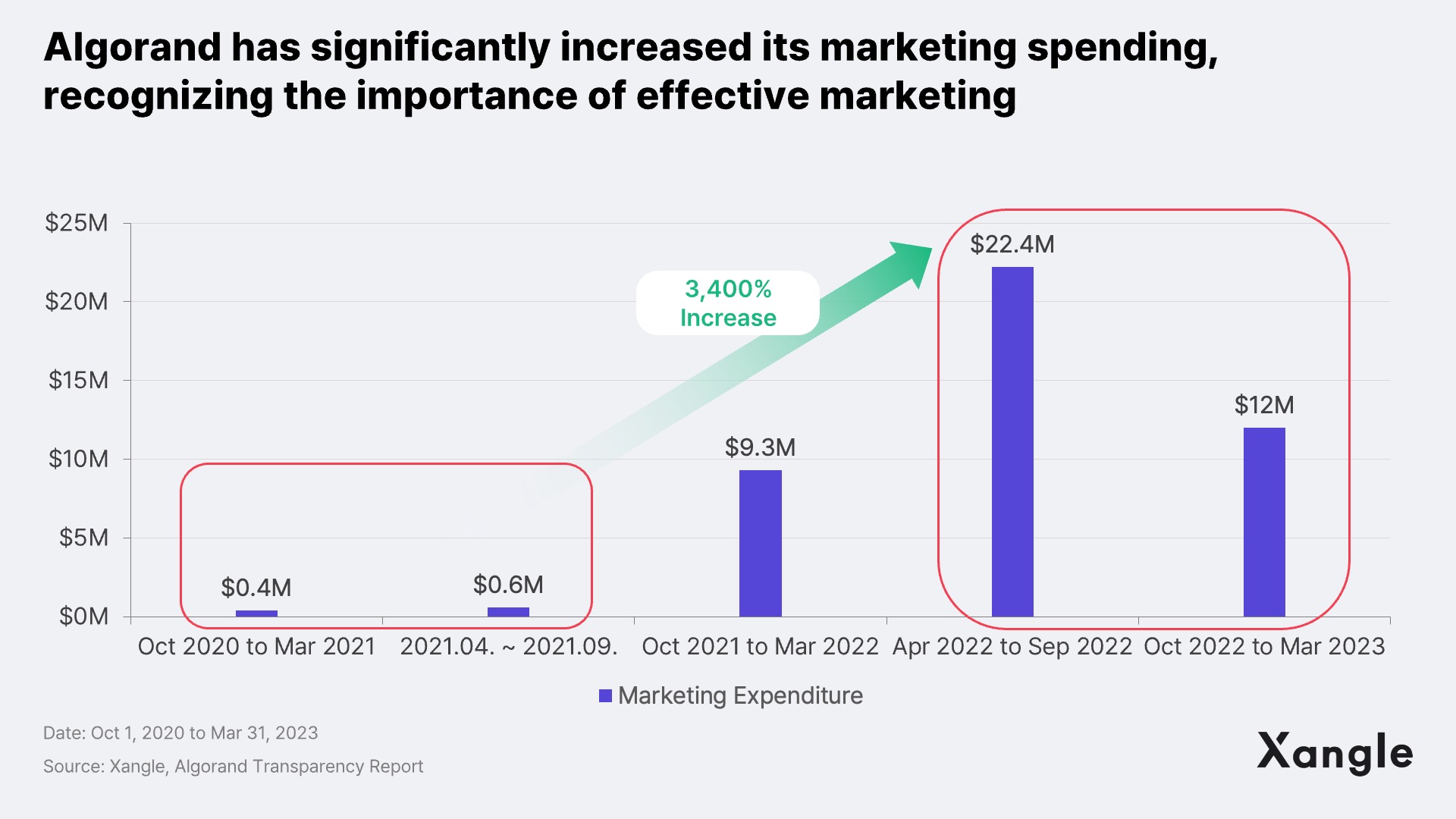
Algorand's recent focus on marketing is evident in its increased spending. Algorand publishes two transparency reports annually, and the latest report shows substantial growth in marketing expenditure, surging from about $1M in 2020-2021 to $34.2M in the most recent year, an increase of about 3,400%. According to my research, this significant investment is predominantly directed toward somewhat low-profile projects that Algorand considers promising.
Algorand has also been actively utilizing a grant program called AlgoGrant, and a key strategy in 2023 involved the establishment of a direct investment entity known as Algorand Ventures. Instead of providing grants to dApps, which can lead to problems such as rug pools, Algorand aims to address these concerns by securing a stake in the project through direct investment and addressing the capital liquidity problem of the project together. In particular, the company has recently been expanding its footprint in Asia rather than North America, where regulatory constraints may hinder operations. Algorand Ventures is actively supporting startups in Asia by launching the APAC Accelerator program, which runs from September 2022 to March 2023. Through this initiative, Algorand aims to foster the growth and development of promising startups in the region.
4.2. Expanding Supported Languages and Simplifying Development Process with AlgoKit for Web2 Developer Onboarding

<Algokit, developed for the convenience of Algorand developers, Source: Algorand Developer Portal>.
In March 2023, Algorand introduced a developer tool called AlgoKit to make onboarding easier for developers. Algokit is specifically designed to address issues around complex developer experience in web3 by streamlining the setup process and providing various libraries and templates that people can use to easily build Algorand dApps. This approach allows existing Web2 developers to work with Algorand’s platform using familiar languages without having to learn unfamiliar languages.
AlgoKit also streamlines the development, testing, and deployment process in Web3. In contrast to other mainnets, where deploying a dApp involves developing a contract, testing it on a testnet, and subsequently deploying it to the mainnet for final testing, AlgoKit offers a more efficient approach. It enables developers to test and deploy directly on the Algorand mainnet by temporarily opening an isolated space known as the "local net." In other words, AlgoKit simplifies the otherwise complex process of testing on both testnet and mainnet.
Algorand is anticipating onboarding Web 2 developers with these advantages. According to Algorand's July announcement, AlgoKit has been downloaded over 9,200 times since its March launch, with nearly 8,000 developers already onboarded. Although this figure is relatively small compared to the estimated 200,000 Solidity developers, it's worth noting that Algokit has only been available for three months, indicating potential for growth in the future.
5. Notable DApps in Algorand
In this section, we'll explore some of the notable dApps in Algorand's ecosystem. While there are no killer dApps in Algorand yet, there are several dApps that hold significant value and importance for the Algorand Foundation. Two prominent dApps in Algorand are Folks Finance, the current DeFi leader in the network, and Lofty, a real estate tokenization project.
5.1. Folks Finance
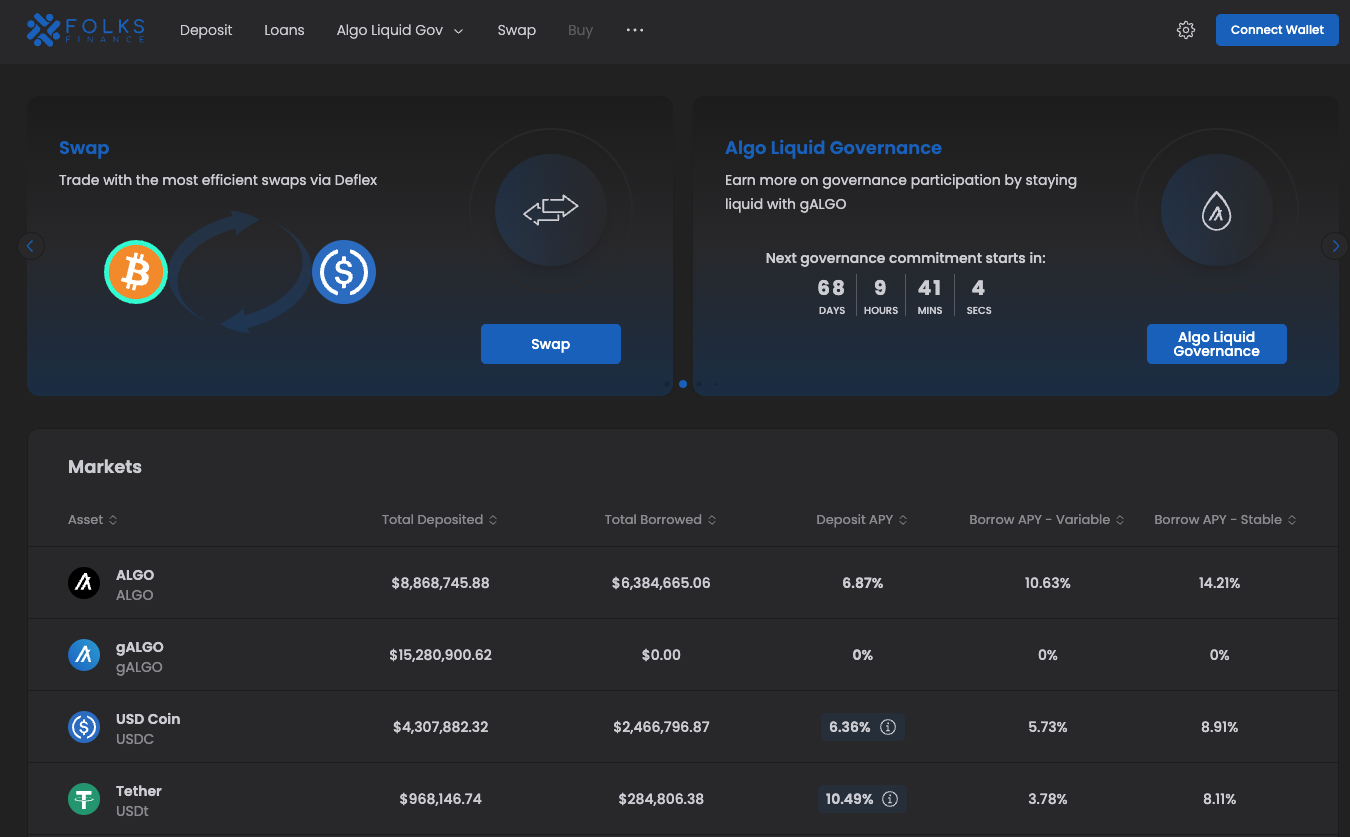
Folks Finance is Algorand's flagship DeFi project, especially after AlgoFi’s shutdown. Folks Finance functions as both a DEX and a lending platform. One of the distinctive features of Folks Finance is its utilization of gALGO and xALGO tokens. gALGO represents a securitized version of ALGO, and users have the ability to exchange ALGO for gALGO, which can be used in DeFi applications, providing opportunities to earn staking and DeFi rewards simultaneously. xALGO has the same reward acquisition method as gALGO, but it is converted to BRC-20 and can be connected to PancakeSwap on Binance Chain.
5.2. Lofty AI
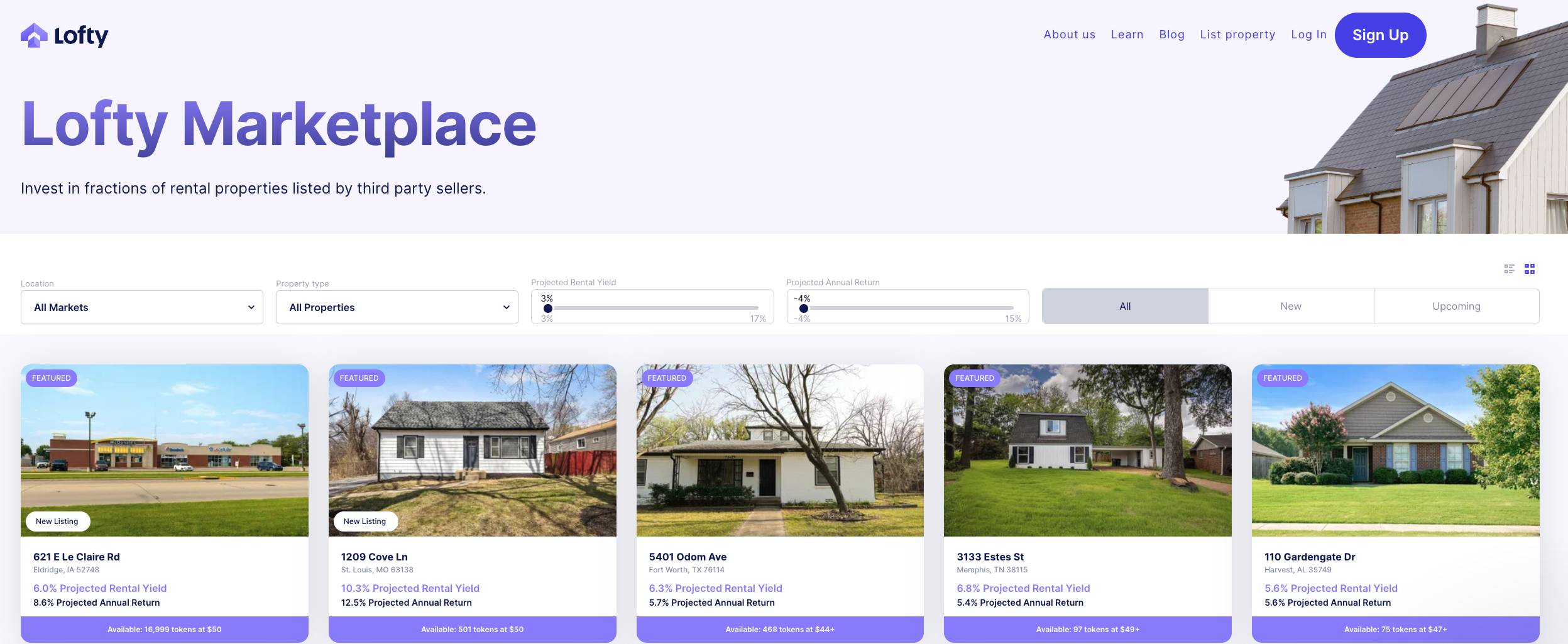
Lofty AI is a real estate fractional investment platform based in the U.S. launched on the Algorand blockchain. Serving as a real-asset-based DeFi platform, Lofty AI allows users to make fractional investments in real estate properties vetted by a proprietary algorithm and on-site team. In 2019, Lofty AI received investment from Y-Combinator, a well-known Silicon Valley accelerator. Despite the lack of real-asset-based DeFi projects, Lofty AI has managed to achieve an impressive TVL of $26M.
6. Closing Thoughts
In this article, we delved into various aspects of Algorand, covering its strengths, challenges, responses, and promising dApps in the ecosystem. To recap, Algorand is a blockchain with strong technical capabilities. Its decentralized nature, supported by a dual-node structure, ensures impressive speed with a 3.3-second finality achieved through PoS. The platform also facilitates user-friendly experiences for individuals, institutions, and countries by implementing participation keys and rekeying. Despite these technical strengths, Algorand has encountered some hurdles, particularly in maintaining sustained collaborations with institutions and countries, and the Web3 ecosystem is still in its early stages. Nevertheless, Algorand is not without opportunities for Algorand. It is strategically shifting its target market to Asia and has undertaken aggressive marketing efforts. The launch of AlgoKit to help onboard Web2 developers further demonstrates its commitment to fostering accessibility. As the platform evolves, it will be intriguing to see if Algorand can capitalize on these opportunities and potentially emerge as a prominent player among third-generation blockchains.
