

 Image Source: South Korean movie Parasite
Image Source: South Korean movie Parasite
Table of Contents
1. Intro
2. Inside Aptos: Technology and Features
2-1. Technology: High scalability achieved through efficient consensus and parallel processing techniques
2-2. Language: Building a stable and flexible development environment with Move
2-3. Ecosystem: Thriving with the Aptos Foundation’s all-out support
2-4. Tokenomics: Long vesting schedule and stable inflation rate
3. The Future Aptos Envisions
3-1. Growth Strategy (1): Future-proof Network via Upgradability
3-2. Growth Strategy (2): Ecosystem expansion centered on onboarding of Web2 companies
3-3. A longer-term plan to provide companies with dedicated blockspace
4. Gaming Sector Set to Lead Ecosystem Growth
4-1. Ecosystem growth driven by METAPIXEL
4-2. Gaming sector expected to drive a booming ecosystem
4-3. Burgeoning yet nascent, the prospect calls for a long-term observation
5. Appendix
Key Highlights
- Aptos is a PoS blockchain developed by the ex-Meta Diem team with a focus on speed and reliability. Aptos is designed to achieve a theoretical throughput of more than 100,000 and sub-second latency. It supports the Move programming language to provide a stable, fast, and flexible development environment.
- Technology alone is no guarantee of success. Aptos employs two key strategies to ensure sustainability and survive the L1 wars: 1) implementing a future-proof network via upgradability and 2) expanding its ecosystem through Web2 partnerships. This approach involves onboarding proven products and services and leveraging the intellectual properties and user bases of Web2 companies. It is also a bet on the blockchain industry’s future, which it predicts will be driven by global heavyweights, rather than Web3 startups.
- Aptos is likely to build its ecosystem around the gaming sector. It is one of the few public blockchains that is technically capable of supporting triple-A games. Aptos is also actively collaborating with METAPIXEL, leveraging their extensive game development expertise, to jointly build the necessary infrastructure and tools needed for Web3 game development. We expect that the features currently under development, including the token object model, proxy gas fee payment, VRF, and game SDK will streamline the onboarding process for game companies. Moreover, the highly awaited Gran Saga: Unlimited (GSU), which employs NPIXEL's prominent IP, is scheduled to launch in January next year.
1. Intro
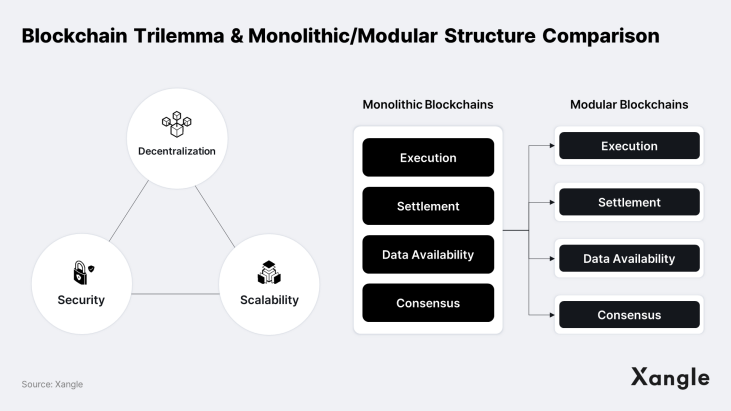
The ultimate goal of any L1 blockchain is to become a global database infrastructure capable of accommodating simultaneous access by tens of millions of users by solving the blockchain trilemma.That said, in the 13 years since Bitcoin's inception in 2009, no blockchain has yet resolved the trilemma. Existing blockchains have encountered limitations, often necessitating trade-offs such as compromising decentralization or experiencing slowdowns. These compromises have resulted in a range of issues such as network overloads, shutdowns, and excessive gas fees.
In response, the blockchain industry has proposed a modular architecture for several years now, different chains handle consensus, data availability, settlement, and execution separately. The primary advantage of a modular architecture is that each chain can specialize in a specific role, reducing the load on nodes and enhancing overall blockchain performance. Many blockchains, including Ethereum, Avalanche, and Cosmos, are currently aligning their roadmaps around a modular architecture.
Modularity has its share of limitations though. It can weaken interoperability and composability between dApps, fragment liquidity, and hinder user experience. Most importantly, modular blockchains are exposed to a wider range of attack vectors than monolithic blockchains, raising security concerns. Aptos is a new PoS-based blockchain designed under a monolithic architecture in recognition of such security challenges. It aims to provide a stable and fast blockchain infrastructure for users around the world, as befits its name meaning “The People.”
2. Inside Aptos: Technology and Features
2-1. Technology: High scalability achieved through efficient consensus and parallel processing techniques
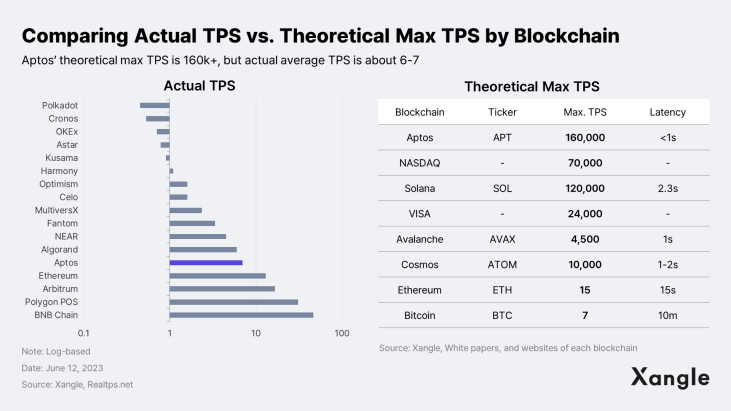
One major challenge for permissionless public blockchains is scalability. Scalability is primarily associated with the processing speed of a blockchain and is commonly measured by throughput* and latency**. Currently, demand for Aptos blockspace is relatively low, averaging 6-7 TPS, but the technology is theoretically capable of achieving 100,000+ TPS and sub-second latency. Considering that VISA and Mastercard process around 3k to 4k transactions per second, this is certainly an impressive number. Aptos' ability to achieve such high scalability is largely attributable to the adoption of technologies such as Quorom Store(Narwhal), State Delta Synchronization, Jellyfish Merkle Tree(JMT). At the core of it all lie its own consensus mechanism (AptosBFT v4) and parallel processing engine (BlockSTM).
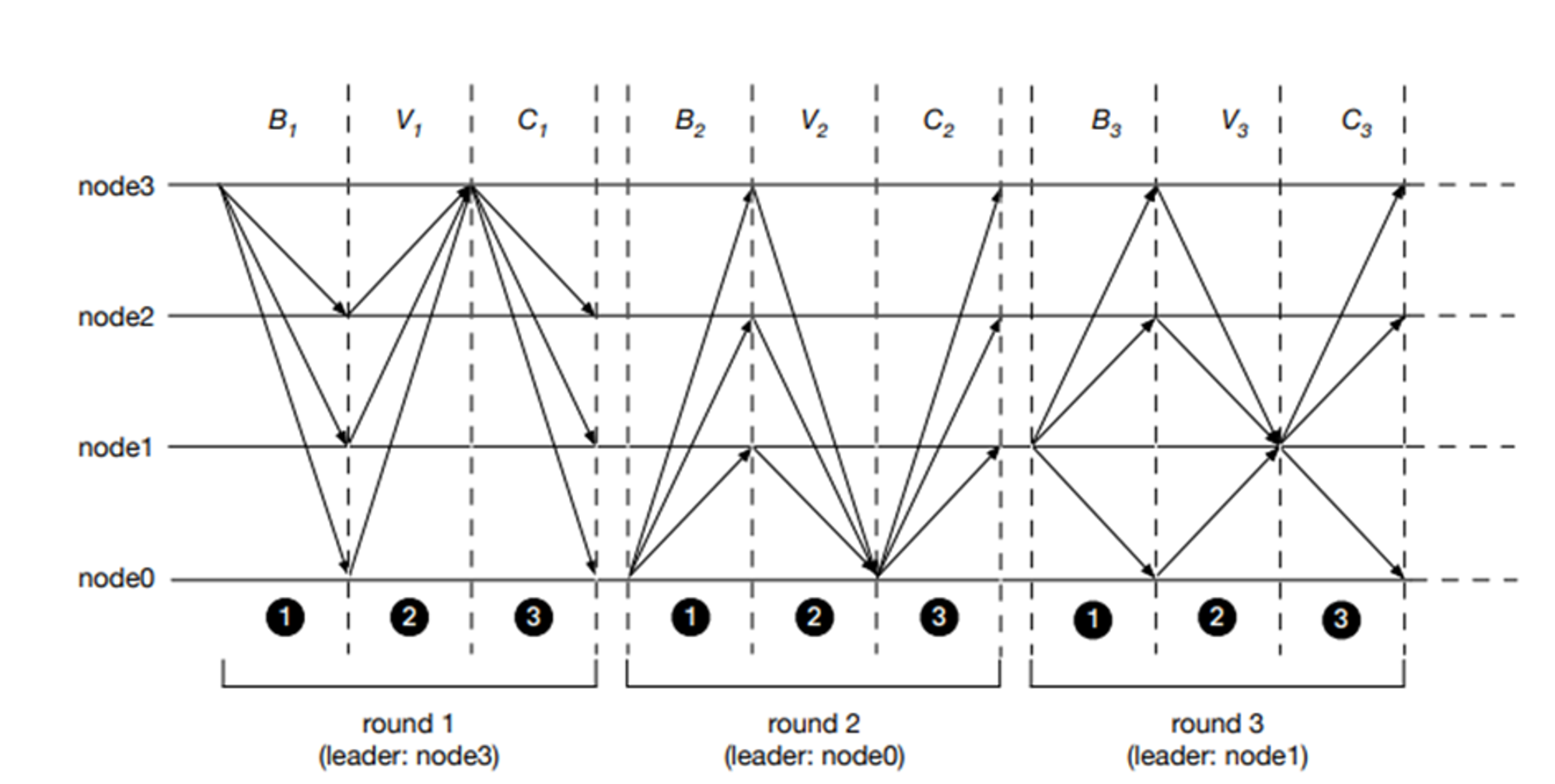
AptosBFT v4 is a consensus algorithm based on DiemBFT***, developed by Diem (formerly Libra), Meta’s former blockchain project. It is characterized by low network load and fast consensus speed, offering significant improvements over the previously prevalent PBFT consensus mechanism. The credits should be given to: 1) linear communication and chaining techniques that enhance latency and network efficiency, 2) a pacemaker that enables rapid synchronization between validators through efficient timeouts, and 3) a reputation system that analyzes the on-chain status to swiftly filter out unqualified validators during the leader node selection process. For more details about the AptosBFT consensus mechanism, please see Appendix 1.
AptosBFT Consensus Process | Source: LibraBFT
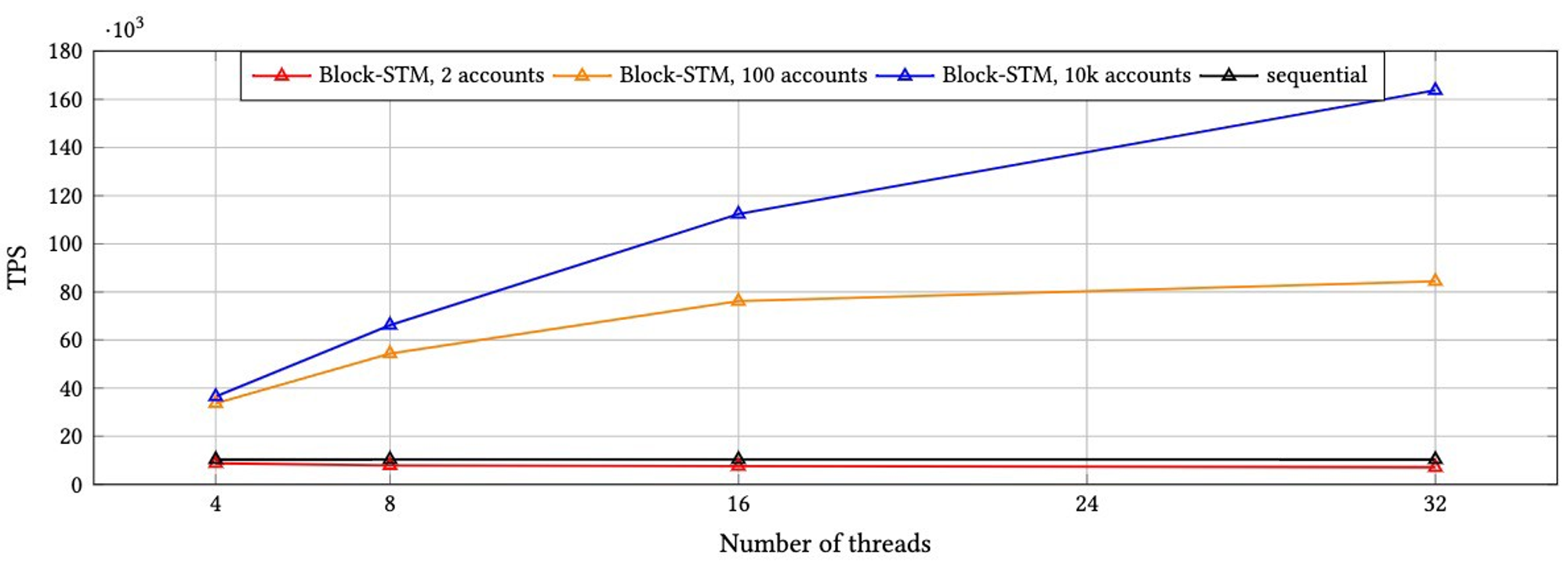
Next, BlockSTM is a parallel execution engine for smart contracts that utilizes Software Transactional Memory (a technique that extends the ACID properties of database transactions to parallel programming). Unlike the existing mechanism that requires transactions to be processed sequentially according to the block order, BlockSTM spreads out independent transactions into multiple threads and executes them in parallel. By pre-defining the order, it enables pre-execution, post-validation and consensus. This signifies that the introduction of BlockSTM can solve blockchain’s bottleneck problem and yield a breakthrough for transaction processing speed. The implementation of BlockSTM is described in detail in Appendix 2.
BlockSTM Performance | Source: Aptos Labs
*Throughput: The number of transactions a network can process in a second
**Latency: The time it takes for a network to finalize a transaction
***DiemBFT: A variant of Hotstuff, a blockchain consensus algorithm powered by Meta's technology
2-2. Language: Building a stable and flexible development environment with Move
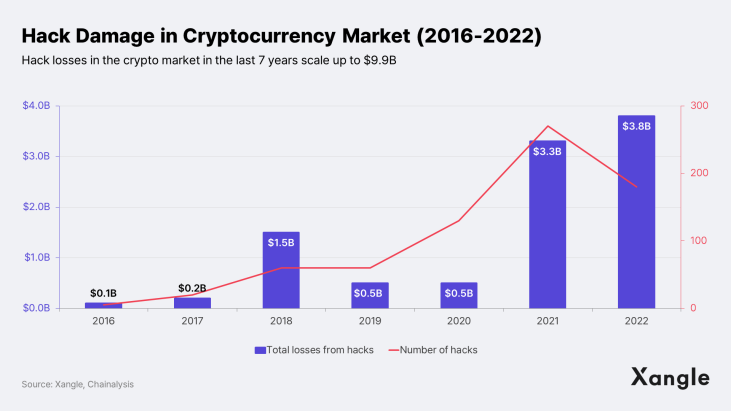
With Ethereum becoming a staple part in the crypto space, "EVM compatibility" has been a powerful narrative. And indeed, there are only a few non-EVM L1s, which don't use Solidity—namely Solana on Rust, Cosmos on Cosmwasm, Stacks on Clarity, and Sui and Aptos on Move. However, it became no secret that the EVM environment and Solidity are vulnerable to exploits. Numerous hacks have highlighted such vulnerabilities over the past few years. From 2016 to 2022, hacks have cost the crypto industry nearly $9.9B over the past seven years, according to Chainalysis.

Smart contracts are difficult to modify after deployment. This is why projects undergo multiple rounds of technology audits before releasing their dapps. Yet, the struggle is with the dynamic dispatch of Solidity contracts, as it is unpredictable what other unexpected variables might occur until execution. Amid the growing demand for a more secure programming language, developers are increasingly drawn to the security and benefits of Move and MoveVM .
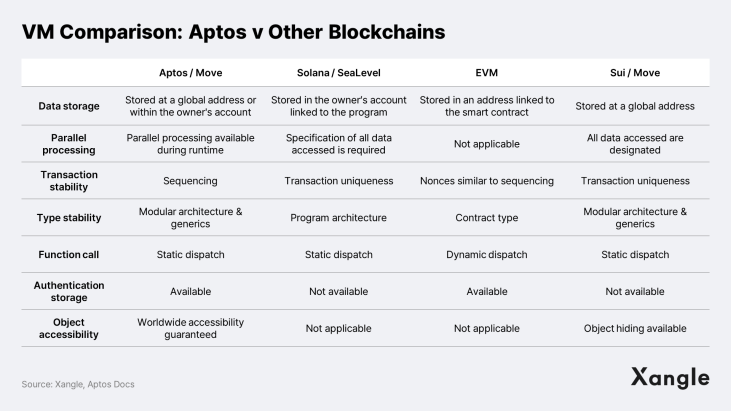
Move is an open source, Rust-based programming language developed by Meta. It is known for its superior stability to Solidity and can expedite the process from development and testing to deployment. This is attributed to the several key features of Move: It 1) supports first class assets to prevent arbitrary issuance and deletion of assets; 2) supports static dispatch to enhance code verification; 3) reduces validation time through prover; 4) ensures that codes work as intended by the developer; and 5) provides memory safety, similar to Rust, making it easier to manage memory. These features collectively make Move a reliable and fast development environment for developers.
2-3. Ecosystem: Thriving with the Aptos Foundation’s all-out support
Since its mainnet launch in October 2022, Aptos’ growth has been on a steady uptrend. According to Aptoscan, a total of 4 million wallets has been created, with an estimated 5-10 thousand new wallets created per day. The average number of daily transactions also remains strong around 500,000.
 Source: Coin98
Source: Coin98
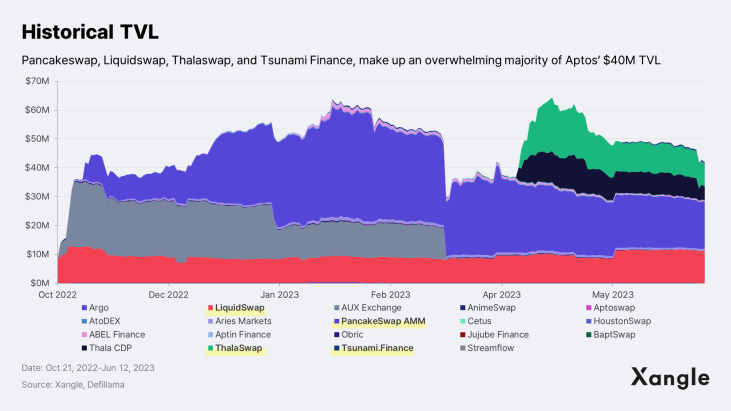
As of June 13, 2023, there were 275 projects onboarded in the Aptos ecosystem, with 113 NFT, 67 infrastructure and middleware, 46 DeFi, and 18 game projects. By TVL (Total Value Locked), three projects—Pancakeswap, Thala (Thalaswap, ThalaCDP), and Liquidswap—dominate the DeFi market, collectively accounting for 95% of Aptos' $44M TVL. In the gaming space, NPIXEL's Web3 gaming platform METAPIXEL is gaining significant traction in the Aptos ecosystem. In particular, Gran Saga: Unlimited, a blockchain-based MMORPG that incorporates the IP of NPIXEL's popular game Gran Saga, is one of the most anticipated titles. Further details regarding METAPIXEL will be discussed in Section 3-2
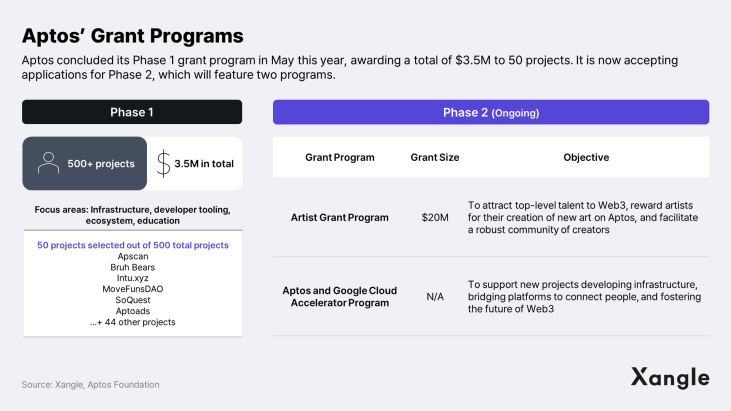
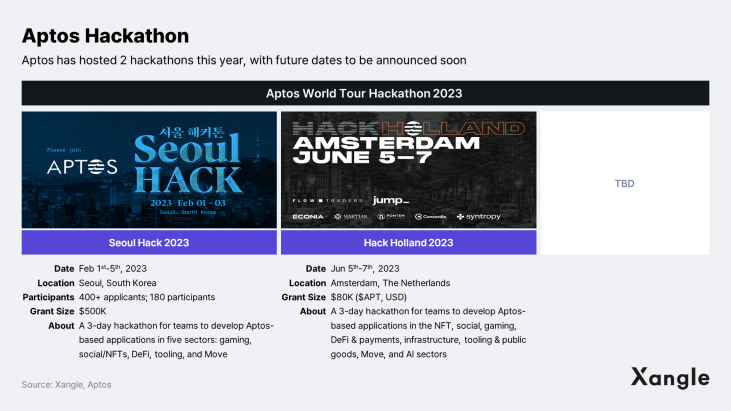
Despite the consistent growth of the Aptos ecosystem since the mainnet launch in October 2022, it remains significantly smaller than other prominent blockchains like Ethereum, Polygon, Arbitrum, and BNB chain. The ecosystem currently lacks killer dApps or high-profile NFT projects. The Aptos Foundation is well aware of this and is proactively running various grant programs, including hackathons, in response. Earlier this year, Aptos concluded its Phase 1 grant program, awarding $3.5 million to over 50 projects, including Apscan, Bruhbears, and Intu.xyz. It then launched the Phase 2 grant program, which consists of two categories: the Artist Grant Program and the Aptos and Google Cloud Accelerator Program. Applications are currently being accepted from a wide range of projects, and the total prize pool for Phase 2 is expected to be at least six times larger than Phase 1. Also this year, Aptos has successfully completed two hackathons, Seoul Hack and Hack Holland.
2-4. Tokenomics: Long vesting schedule and stable inflation rate
Here are some key figures about Aptos' native token $APT:
- Maximum supply: ∞
- Total supply: 1,038,484,105 $APT (100%)
- Circulating supply: 200,288,451 $APT (19.3%)
- Inflation rate: 5.6% (decreasing annually, with a minimum of approximately 2.6%)
- Staking rate: 860,195,091 $APT (82.8%)
The $APT staking reward starts at 7% per year and gradually decreases by 1.5% annually until it reaches 3.25%. The initial inflation rate is estimated to be approximately 5.6% and is expected to decrease to as low as 2.6% over time. There are some overhang risks as more than 50% of the initial issue will be in circulation in about two years from now. However, with a long vesting schedule of 10 years, $APT's initial inflation rate is not considered high compared to other L1 tokens. For instance, the inflation rate of Ethereum, which used to hover above 10% from 2016 to 2017, has gradually descended to 4% after Merge, according to Xangle Analytics. Moreover, $APT’s inflation rate is lower than most other L1 tokens, which typically experience high inflation rates of over 10% in the early days of their mainnet launches (BNB: 16%, AVAX: 800%, MATIC: 80%, NEAR: 200%).
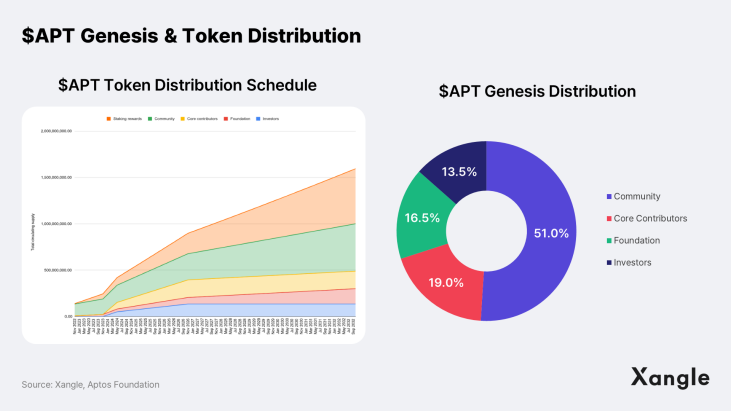
One thing that stands out is the staking rate. The $APT staking rate currently sits at around 82.8%, exceeding the percentage of the circulating supply. This is attributed to Aptos' design, which allows for staking of locked-up tokens. While some members of the community have voiced their concerns, assuming the inflation rate is not too high, the design may have a positive impact on the network in that: 1) the security of a PoS chain is proportional to the value of the staked tokens, and 2) protocols that wish to join the Aptos ecosystem can leverage the locked $APT to enjoy staking rewards.
3. The Future Aptos Envisions
Aptos' core strategy involves two key aspects: 1) ensuring a future-proof network via upgradability, and 2) attracting Web2 enterprises by leveraging extensive capital and network.
3-1. Growth Strategy (1): Future-proof Network via Upgradability
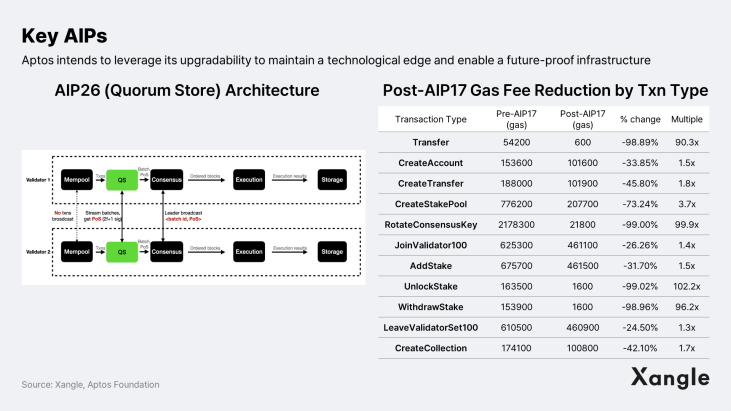
Aptos intends to leverage its upgradability to enable a future-proof network capable of accommodating a billion users. Future-proof is a term coined by Daryl Plummer, vice president and analyst at Gartner, at an IT symposium. It means to be adequately prepared despite future uncertainties. Unlike other blockchains such as as Ethereum, Solana, and Cosmos, whichy typically deploy major protocol updates every six months to a year, Aptos aims to become the most robust blockcghain in the long run through its fast and efficient upgrade system. Indeed, Aptos has passed 24 AIPs in the eight months since its mainnet launch on October 12, 2022, including core layer upgrades, i.e., AIP4, AIP17, and AIP26(Quorum Store), which Aptos says have the potential to increase network throughput by more than 3x and reduce gas fees by up to 100x. The frequent and consistent implementation of upgrades will be a vital part of Aptos' future-proofing of its network.
 Source: Aptos Governance Forum
Source: Aptos Governance Forum
Implemented in March 2023, AIP17 is a proposal aimed at reducing transaction execution costs by separating the gas fee logic associated with storing and executing transactions. The idea was to assign absolute values to storage gas fees by transaction type while keeping the existing fee market mechanism for execution gas fees. This way, Aptos was able to reduce gas fees by approximately 99% for such types of transactions as UnlockStake, RotateConsensusKey, Transfer, and WithdrawStake. Quorum Store (QS), also known as AIP26, is a Narwhal BFT consensus specifically designed for Aptos' architecture. Its purpose was to solve existing consensus bottlenecks, such as wasted bandwidth for nodes during the block consensus process or duplicate propagation of the same transaction data. Aptos tested QS on previewnet and reported a more than 3x increase in network throughput. More recently, Aptos has been working on Shoal, a framework that will introduce pipelining and leader node reputation mechanisms. The introduction of Shoal is expected to reduce latency in Narwhal-based consensus algorithms like Bullshark, Tusk, and DAG-Rider by an estimated 40-80%.
Aptos is capable of supporting swift and immediate upgrades thanks to its modular architecture that enables protocol upgrades without requiring a hard fork, and an on-chain governance system that facilitates real-time release of upgrades. These features have ensured that Aptos has never experienced any downtime during AIP updates.
3-2. Growth Strategy (2): Ecosystem expansion centered on onboarding of Web2 companies
In contrast to the majority of L1s that prioritize Web3 projects for ecosystem development, Aptos' ecosystem expansion will revolve around large enterprises. This approach is driven by the goals of onboarding reliable products and services and bringing in IPs and user bases of Web2 companies. This is also reflective of Aptos’s bet that global companies, rather than Web3 projects, will ultimately lead the blockchain industry. Given the booming number of global companies entering the Web3 market, with big names like Nike, Starbucks, Adidas, Tiffany & Co., Gucci, Nexon, SK, and many more, Aptos' bet makes sense.
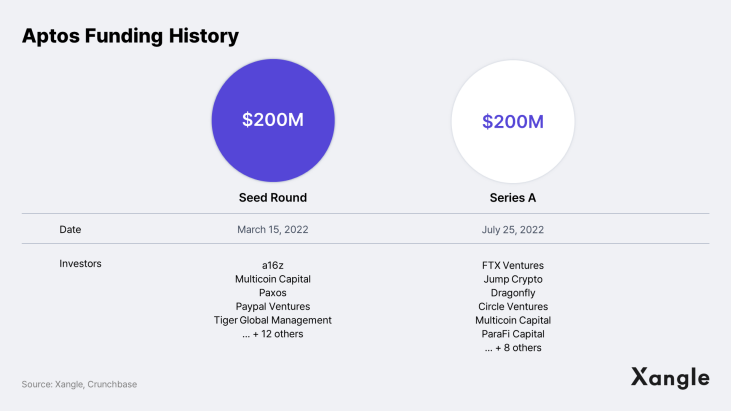
Aptos foundation is strategically leveraging its deep pockets and strong network to attract Web2 companies. In the last year alone, Aptos successfully closed two funding rounds (Seed, Series A) totaling $3.5M from top-tier investors such as a16z, Paypal Ventures, Apollo Global Investment, Tiger Global Management, Griffin Gaming Partners, Multicoin Capital, and Jump. Considering that Aptos has pledged to allocate 51% of the $APT issuance (valued at approximately $4B based on $APT FDV as of June 22, 2023) to ecosystem development, it appears to have secured enough capital to onboard partners.
Aptos co-founder Mo Shaikh has a strong network of contacts in Web2 companies, having worked at BlackRock, BCG, Consensys, and Meta. Another co-founder and CTO, Avery Ching is a former software engineer at Yahoo, Meta, Novi, and the Apache Software Foundation, and has a wealth of experience and connections in the tech space. Its experienced team and network of prominent investors will be invaluable in keeping companies onboarded.
Largely, Aptos foundation is targeting four key markets: 1) gaming, 2) finance, 3) media & entertainment, and 4) social networks. Aptos foundation is currently partnering with Mastercard and Google Cloud and has laid the foundation for growth, attracting investments from leading companies in the target markets to accelerate onboarding of a large number of companies. In the South Korean market, Aptos appears well-positioned to enter the gaming and media/entertainment markets given the investments it has received from Hashed, Irongrey, Hybe, YG, and its key partnership with NPIXEL.
3-3. A longer-term plan to provide companies with dedicated blockspace
Among the large Korean companies that have recently announced their entry into Web3, such as Nexon, SK Planet, Com2uS, Neowiz, and NPIXEL, only NPIXEL has opted for a monolithic blockchain. The rest of the companies chose L1s so that they can build their own blockchains, such as Polygon Supernet, Avalanche Subnet, and Cosmos Appchain. For those that are hesitant to build their own L1s, the primary advantage of these L1s is the availability of development infrastructure, such as SDKs, that streamlines the process of constructing mainnets.
The main motivations for building own mainnets are having 1) network control and 2) own blockspace. In the former case, Aptos can be a viable option depending on the size and business model of a company, as it eliminates the burden of operating a mainnet, including time, cost, and development resources.
In the latter case, monolithic blockchains may not be the immediate choice for companies with a significant demand for dedicated blockspace. This is because monolithic blockchains operate with a structure where all participants must compete for the same resources. While it is worth noting that Aptos’s high scalability allows all services to share the same blockspace, potential risks surrounding building one’s own blockchains, such as fragmentation of security, reliability, liquidity, and data availability, should not be overlooked as well.
Monolithic blockchains are also responding in their own ways to meet companies’ demand for dedicated blockspace. In this regard, Solana introduced Stake-weighted PoS in the second half of last year, offering an alternative to provide and guarantee network bandwidth in proportion to the $SOL staked. Aptos is taking a different approach by incorporating sharding into its solution. A demo version will be released within the next 6 months to a year.
4. Gaming Sector Set to Lead Ecosystem Growth
4-1. Ecosystem growth driven by METAPIXEL
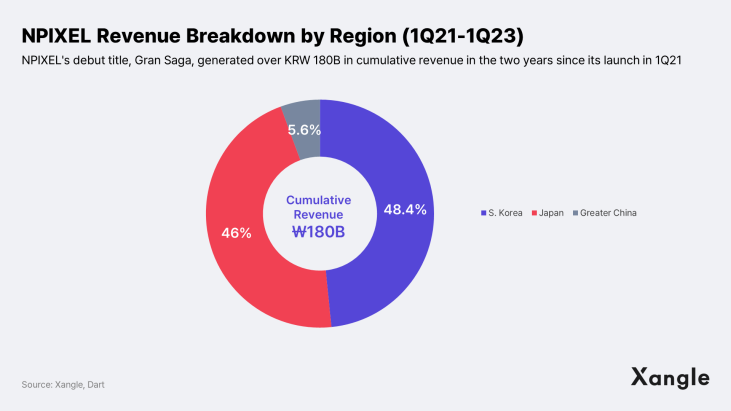
As part of a strategic partnership with NPIXEL forged in November 2022, Aptos will exclusively onboard games produced by Meta Headquarters, NPIXEL's blockchain division. Founded in 2017, NPIXEL is a Korean game developer that became a unicorn in the shortest period of time in the gaming industry by raising KRW 100 billion in Series B investment in 2022. One of its flagship games is the globally popular mobile game Gran Saga, which boasts 4.2 million downloads, KRW 180 billion in cumulative revenue, and $200 monthly ARPPU (Average Revenue Per Paying User). Next year, NPIXEL will launch Chrono Odyssey, an open-world MMORPG that is expected to establish itself as a significant addition to the company’s IP lineup.
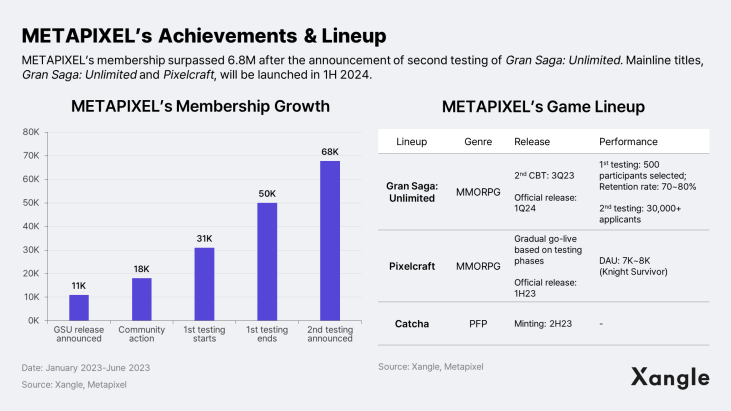
METAPIXEL is a blockchain-based gaming platform operated by Meta Headquarters. Its first game, Gran Saga: Unlimited, is set to launch in January 2024. As an extension of NPIXEL's flagship IP, Gran Saga: Unlimited saw an impressive retention rate between 70% and 80% among the 500 participants during its first Closed Beta Test (CBT) in March this year. The second CBT, scheduled to open in July, will provide even richer content to a total of 8,000 gamers, and the number of applicants has already exceeded 30,000. METAPIXEL will collaborate with 100 influencers with an average of 20,000 followers in the upcoming second CBT, and the test is expected to act as a powerful driver for bringing users into the METAPIXEL ecosystem.
 Screenshot of GSU's 1st CBT | Source: METAPIXEL
Screenshot of GSU's 1st CBT | Source: METAPIXEL
In addition to Gran Saga: Unlimited, METAPIXEL is developing and operating Pixelcraft and Catcha projects. Pixelcraft is a 2.5D hyper-casual pixel art RPG game that is expected to go live in the first half of next year. Knight Survivor, a mini-game within Pixelcraft, is generating KRW 1.5 million in daily revenue and has 7-8 thousand average Daily Active Users (DAU). This is a significant number, considering that The Sandbox has an average DAU of 200-300 as of June 22. The success of the game has helped METAPIXEL reach 80,000 subscribers in about half a year from January to June 2023 and could act as a trigger for further growth in the Aptos ecosystem.
4-2. Gaming sector expected to drive a booming ecosystem
The gaming sector will likely be the primary catalyst for the exponential growth of the Aptos ecosystem in the foreseeable future. Aptos stands out as one of the few public blockchains that has the technical capabilities to support triple-A games. Aptos is also collaborating with METAPIXEL, leveraging their extensive game deveopment expertise, to build the necessary infrastructure and tools required to streamline the process of developing and launching Web3 games.
Speed and reliability are likely the top priorities for game companies when selecting a blockchain platform to build their projects on. Depending on the extent to which the in-game experience is implemented on-chain, a fully on-chain MMORPG with blockchain technology applied to all goods and items would involve processing thousands to tens of thousands of transactions per second. Currently, there are only a few blockchains that can handle such high performance requirements, and Aptos, with its 100K+ TPS and sub-second finality, is a natural choice for game companies. Plus, the stability and expressiveness of Move will also play a role in attracting game companies.
Moreover, Aptos Labs is working closely with METAPIXEL to prepare various game-related infrastructure and tools to make it easier for both game developers and gamers to onboard to the blockchain ecosystem. Currently, one of the biggest challenges in developing blockchain games is a poor development environment. Aptos and NPIXEL are working together to develop standardized implementation values for a smoother Web2 to Web3 transition for game companies. The initiative involves introducing various features that cannot be implemented with EVM and is expected to lay the groundwork that will serve as a major selling point for attracting game companies in the future. Some of the most notable examples include:
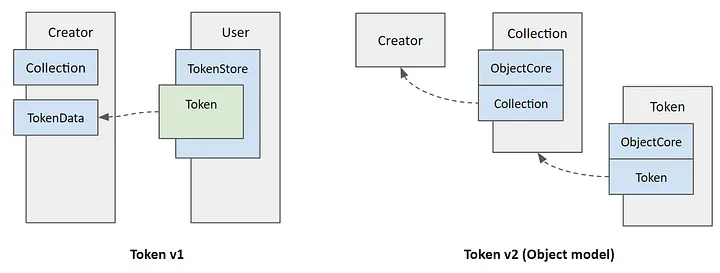
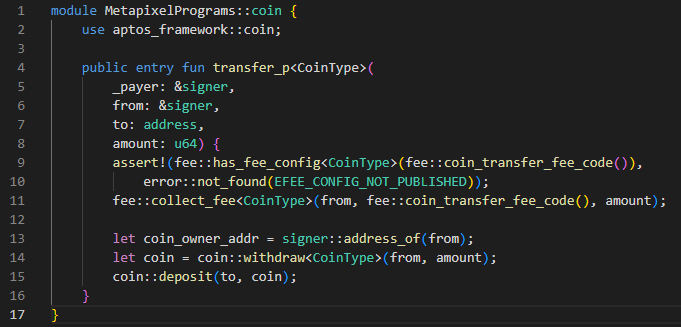
- Token Object (AIP11): METAPIXEL has improved the following areas by transitioning from Aptos's initial Token v1 model to the Object model (Token v2):
- NFTs represented on the same level as user accounts: For more intuitive and straightforward handling of resources, NFTs are identified by 32-byte addresses, just like user accounts.
- Enhanced ownership identification: The owner field of an object makes it easy to identify the owner of an NFT. It simplifies the ownership verification and transfer process, facilitating composability.
- Efficient storage usage: Grouping objects and related resources, along with the previously defined ObjectCore, enables efficient use of storage space, thereby reducing storage costs.
- Dynamic, Flexible NFTs: With the Token Object model, game assets can be dynamically and flexibly managed. A single Token object can be used to mint game NFTs, grant Soulbound status, and upgrade attributes.
 Source: METAPIXEL
Source: METAPIXEL
- Proxy gas fee payment: To enable user experience comparable to Web2 games, Aptos is building an open-source, proxy gas fee payment system. The system incorporates two key features: 1) multi-agent transactions that activate multiple actions in a single transaction and 2) a remote-signing process that remotely signs gamers' transactions.
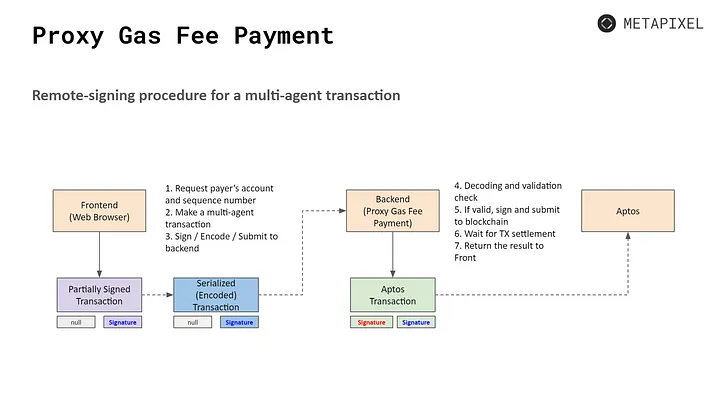
 Source: METAPIXEL
Source: METAPIXEL
- Verifiable Random Function (VRF): One of the biggest benefits of bringing blockchain technology to gaming is transparency. METAPIXEL and Aptos Labs have developed VRF to increase the transparency and reliability of the gacha system.
- Stackable (TBD): A new token standard is under development to implement semi-fungible NFTs similar to ERC1155.
- SDK: Aptos is planning to develop an SDK that will simplify the process of building games on top of its network.
4-3. Burgeoning yet nascent, the prospect calls for a long-term observation
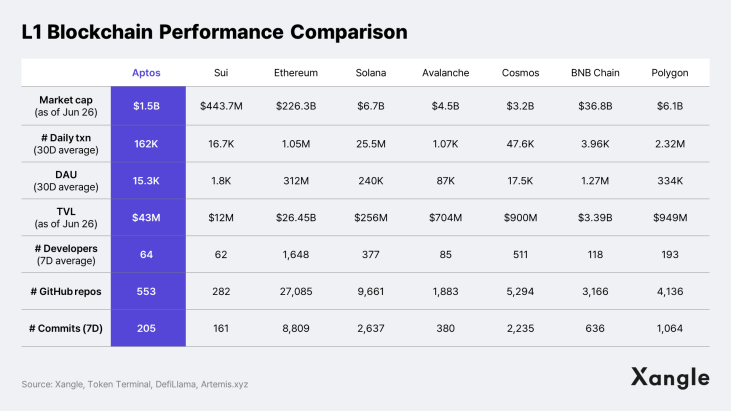
Aptos is a promising L1 with excellent technical capabilities as has been highlighted in the previous sections. With that said, its mainnet has only been out for about 9 months now, and almost all of its metrics are behind some other established L1s, including infrastructure, TVL, developer community, and number of users (see table below). A linchpin of Ethereum's continued dominance as the leading blockchain is not solely its superior infrastructure, but the continuous influx of capital and talent, including developers and researchers. On multiple fronts, Aptos has significant progress to make, especially when compared to Ethereum, which sports a 615x higher TVL, 26x more full-time developers, and 49x more github repos than Aptos. Hence, the burgeoning yet nascent state of Aptos requires investors and stakeholders to have patience and observe longer term—although, with the launch of the aforementioned game infrastructure and development tools in the latter part of this year, full-scale growth may start manifesting next year.
5. Appendix
Appendix 1: AptosBFT Consensus Process
While PBFT (Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance) relies on cross-validation among nodes after the leader propagates the block to each node, AptosBFT V4, AptosBFT V4 simplifies and unifies this validation process into one-way communication, improving the efficiency of node-to-node communication.
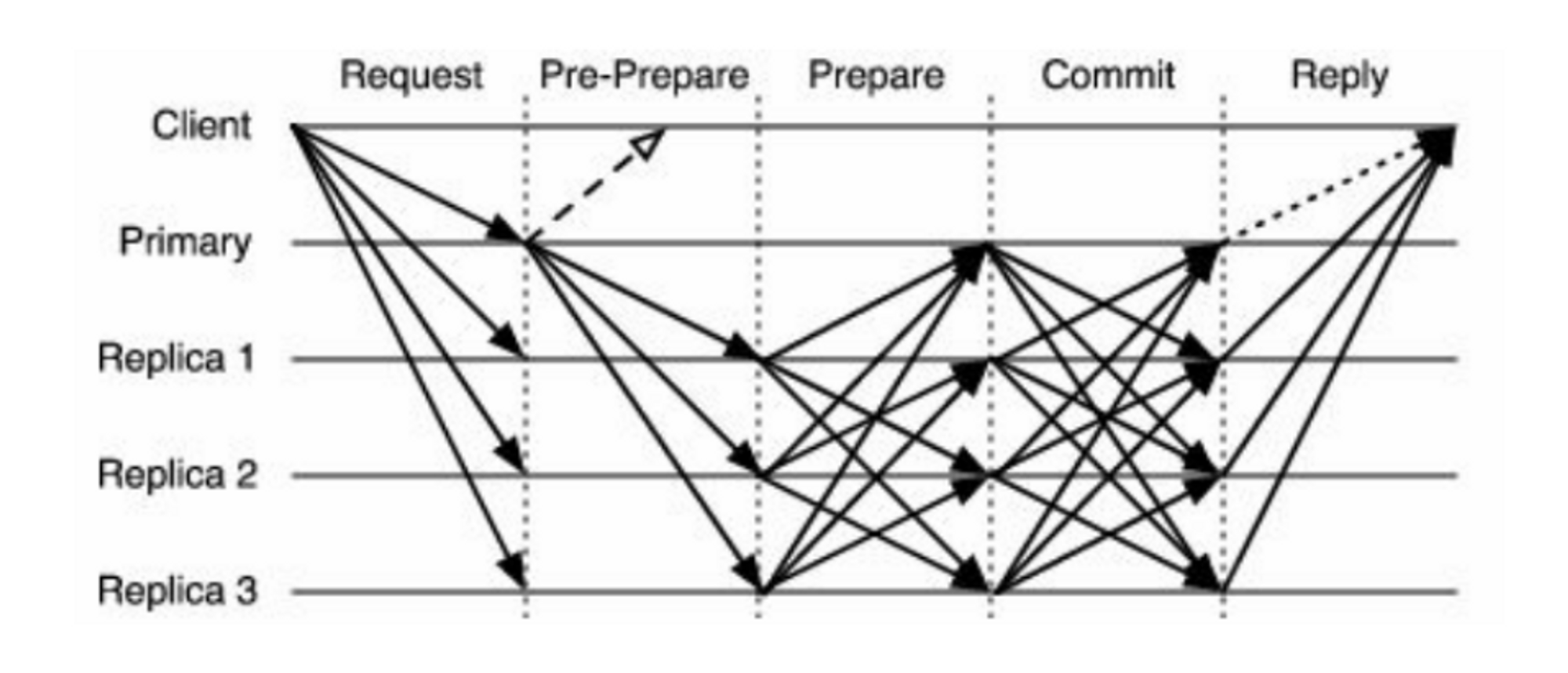 Existing PBFT Validation Process | Source: PARAMETA
Existing PBFT Validation Process | Source: PARAMETA
 DiemBFT Validation Process | Source: LibraBFT
DiemBFT Validation Process | Source: LibraBFT
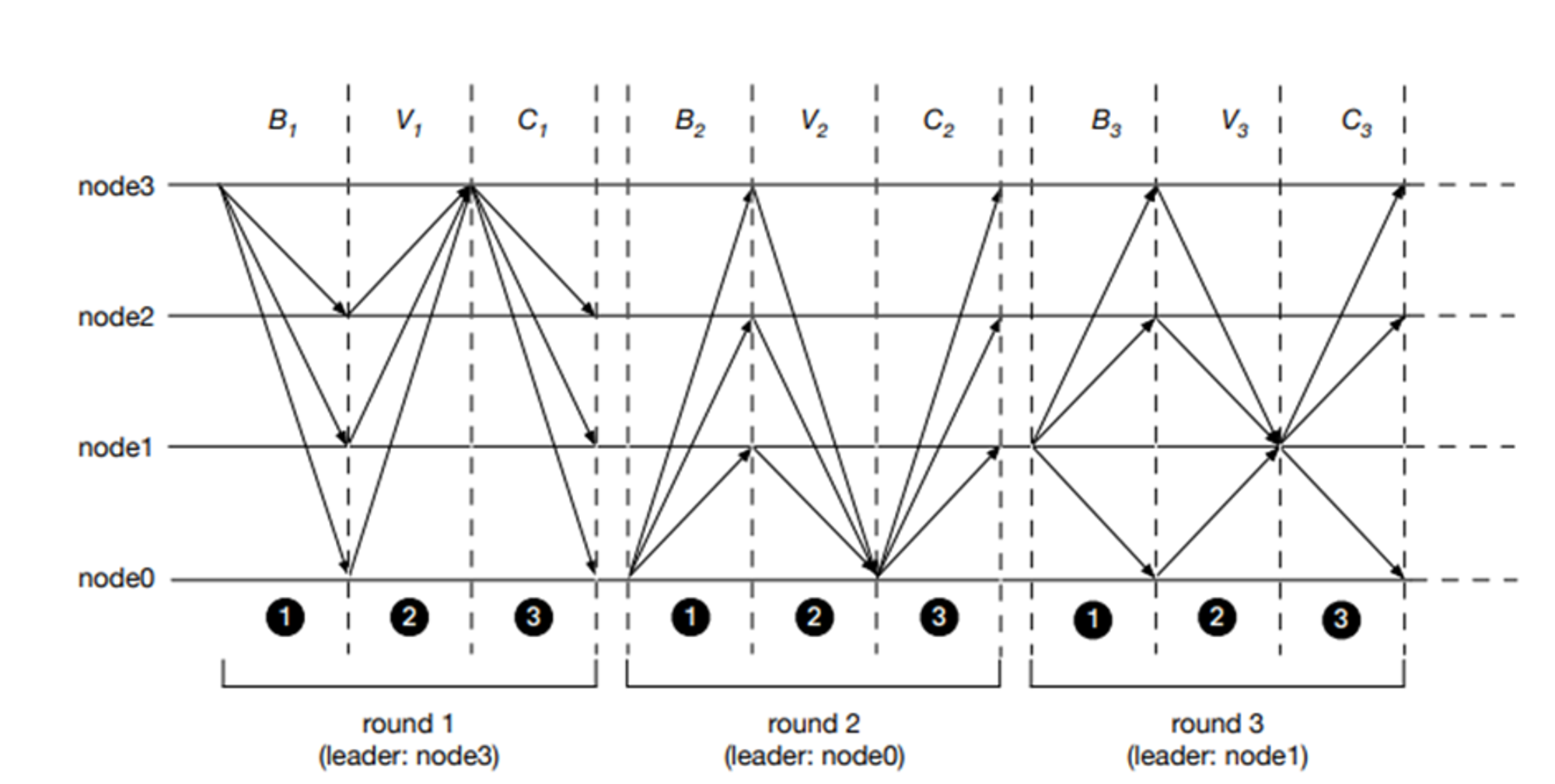
The above figure shows DiemBFT V1, which is similar to V4, except that in V4, validators forward their voting data to the leader of the next round instead of the current round to reduce network burden.
The process of a round with linear communication and chaining can be described as follows:
1. The leader sends the block generation proposal to the validators.
2. Validators submit their votes to the leader of the next round.
3. If more than 2/3 of the validators successfully deliver their votes, the leader issues a Quorum Certificate (QC).
4. The leader distributes the new proposal to the validators, along with the QC from the previous round. It's important to note that the leader issuing a QC and propagating it to validators in the next round (K+1) does not imply that the Kth block is committed. Instead, a chaining scheme is followed, where only QCs are received in round, K+1 and the actual block commit takes place in round K+2 (see figure below).
Chaining is a multi-round block validation process, which has the advantage of reducing the network load compared to the traditional PBFT method, which solves everything from proposal propagation to QC issuance and generation in one round.
Chaining Mechanism
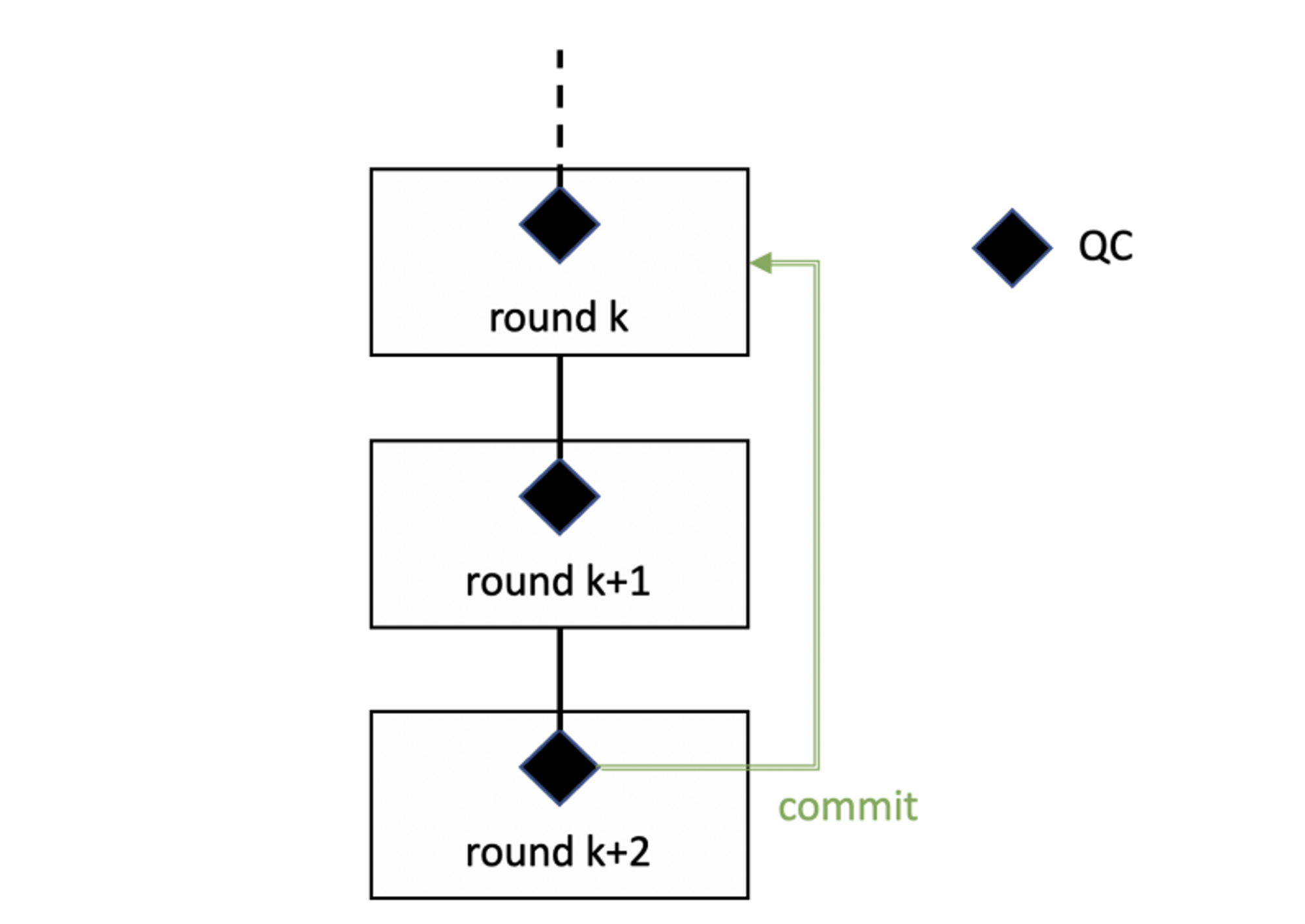 Source: DiemBFT V4 Whitepaper
Source: DiemBFT V4 Whitepaper
Appendix2: Core Features of BlockSTM
Largely, BlockSTM comprises three fundamental aspects:
- Optimistic concurrency control: It employs the optimistic concurrency control property of STM to enable multi-threading, assuming that users will not modify the same data at the same time and does not apply locks. It means that transactions are first processed in parallel, and if a conflict occurs during the validation process and the transaction cannot be committed, it is rolled back and executed again. In a way, it works similarly to optimistic rollup, where all transactions are executed first, assuming the transactions are valid. Since the majority of transactions are likely to be processed without issue, this approach can significantly increase speed.
- Dynamic dependency estimation: It is a mechanism that is designed to reduce inefficiencies by identifying transactions that fail validation as early as possible and determine the blockchain's commit rules. If a validator fails to validate a transaction, it is tagged as ESTIMATION. This allows the validator to skip to the next transaction without executing and validating all transactions that depend on the failed one until another validator successfully validates that transaction. This way, it prevents the potential waste of time and resources that can arise from executing and subsequently rolling back entire transactions that depend on a transaction failing validation.
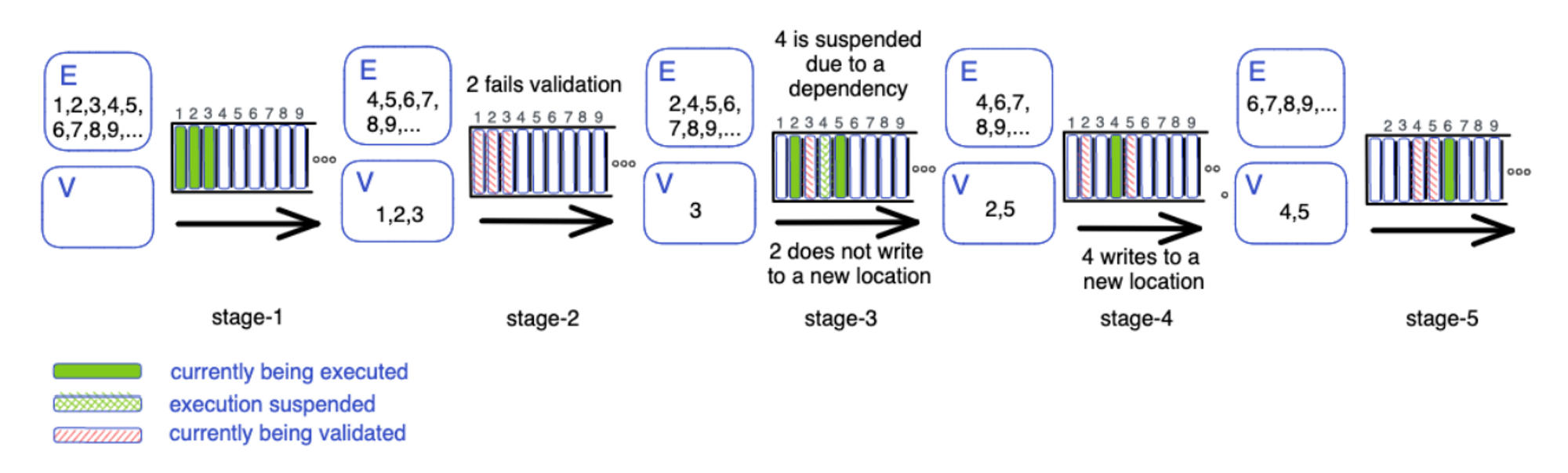
BlockSTM's transaction commit rules | Source: BlockSTM whitepaper
- Collaborative scheduler: It is a technology that assigns transaction validation and execution to threads, ensuring that transactions are processed in a pre-defined order. The scheduler prioritizes low transactions for execution. In BlockSTM, transaction execution and validation are separated, and successful execution of a transaction does not mean that the transaction is fully committed. If consensus is not reached during the validation process, not only the transaction itself but also all subsequent transactions need to be rolled back. This design avoids executing high transactions first, optimizing blockchain operation efficiency and minimizing wasted time.